Credit: Image: KIT
Researchers of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have made major progress in the production of two-dimensional polymer-based materials. To produce cloths from monomolecular threads, the scientists used SURMOFs, i.e. surface-mounted metal-organic frameworks, developed by KIT. They inserted four-armed monomers, i.e. smaller molecular building blocks, into some SURMOF layers. Cross-linking of the monomers then resulted in textiles consisting of interwoven polymer threads. This work is now presented in Nature Communications. (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14442)
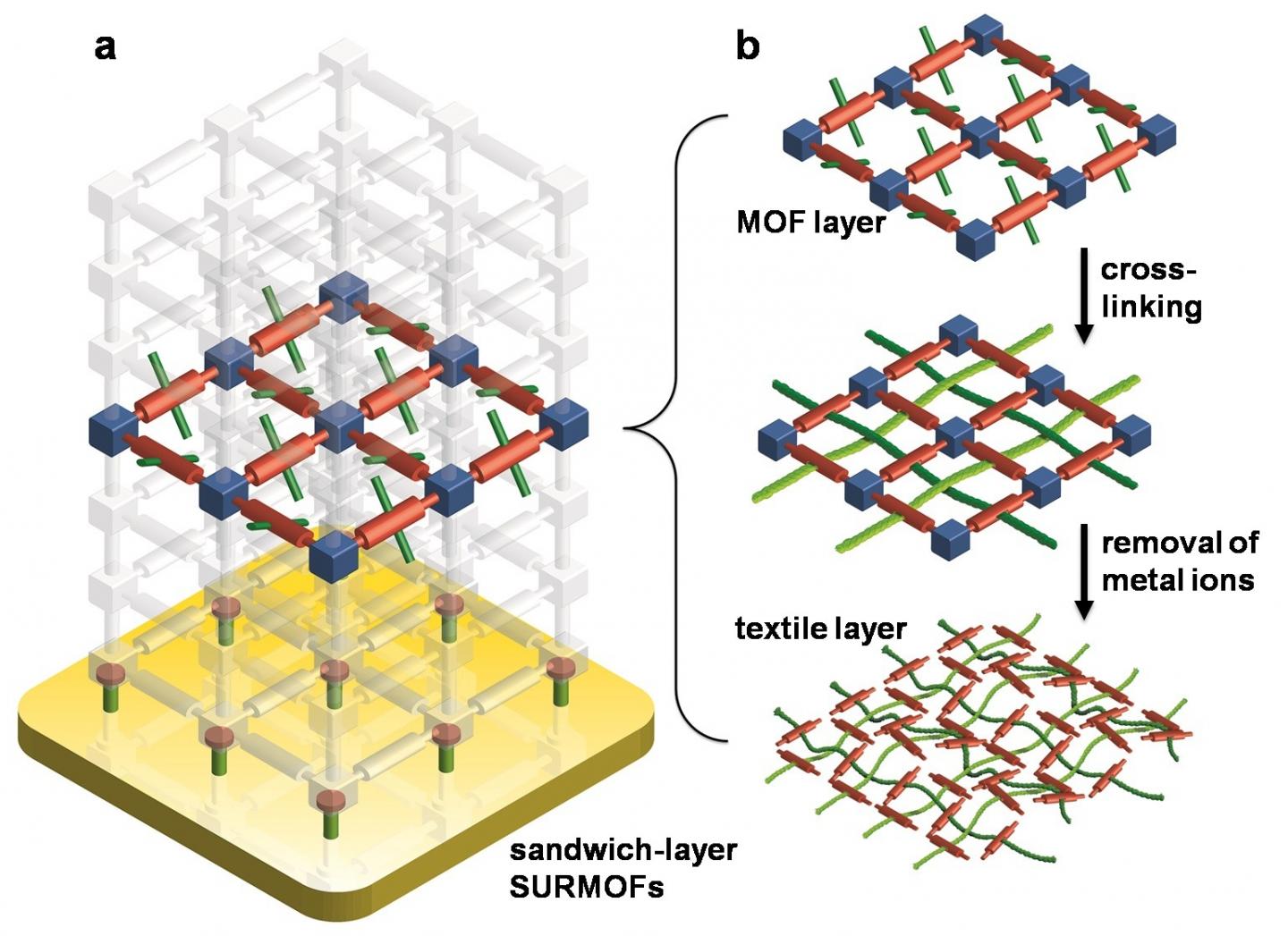
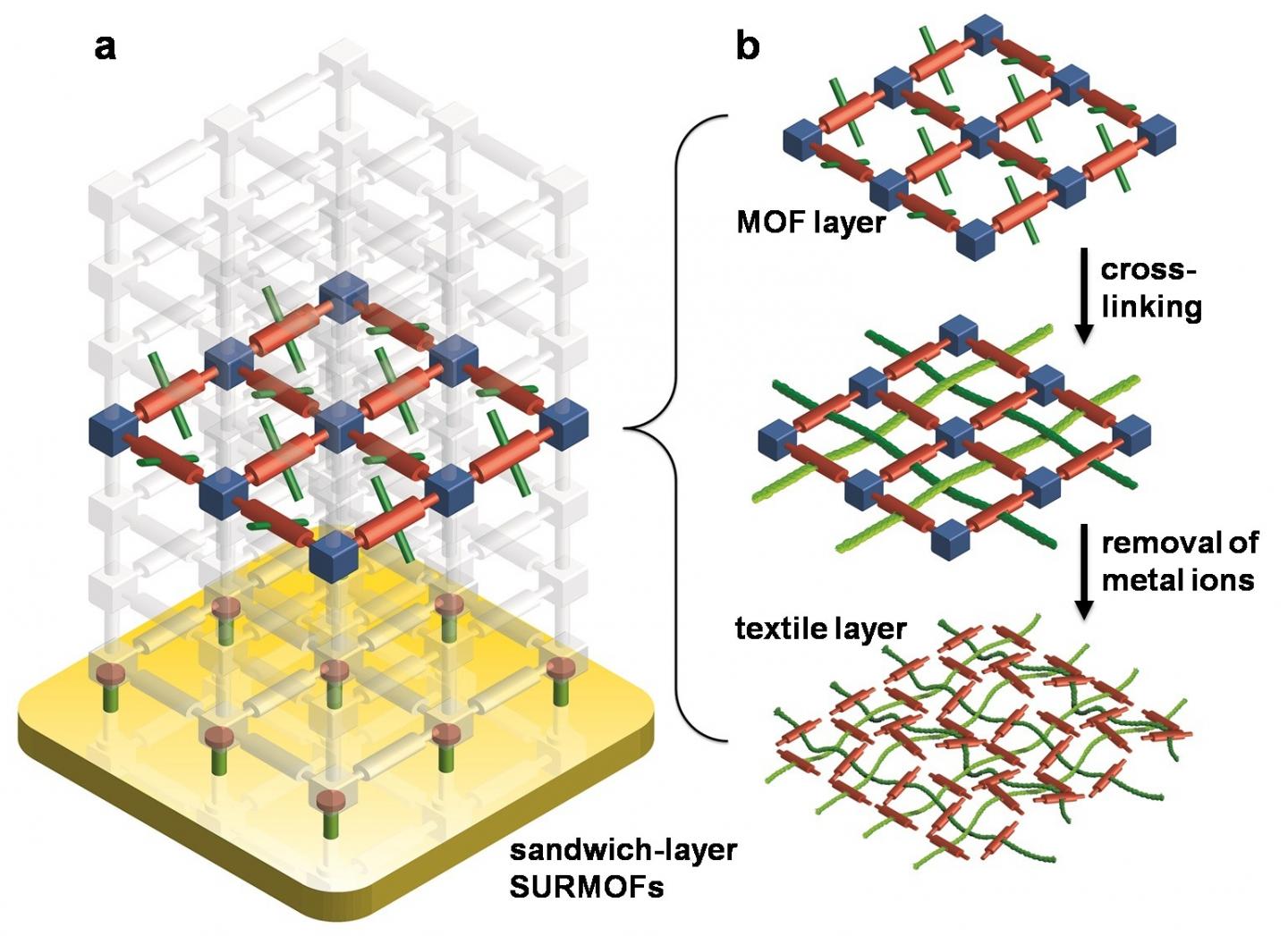
Self-organized cross-linking of polymer threads, i.e. of extremely long molecules, to two-dimensional tissues is a big challenge in polymer chemistry. With the help of a bottom-up process to cross-link smaller molecules, so-called monomers, scientists of the Institute of Functional Interfaces (IFG) and Institute of Nanotechnology (INT) of KIT now made an important step towards reaching this objective. They produced a tissue from monomolecular polymer threads by using SURMOFs, i.e. surface-mounted metal-organic frameworks, as looms. This approach is now presented in Nature Communications.
The SURMOFs developed by IFG are frameworks consisting of metallic node points and organic linkers that are assembled on a substrate layer by layer. They have a crystalline structure and can be customized to a large range of the applications by combining various materials and varying the pore sizes. For weaving two-dimensional textiles, the KIT scientists specifically inserted special connection elements, i.e. four-armed monomers, into the SURMOF layers for later cross-linking. Then, these active SURMOF layers were embedded between so-called sacrificial layers. "In this way, we produced a sandwich-type setup to ensure that the textiles produced really are two-dimensional, which means that they have a thickness of one molecule layer only," Professor Christof Wöll says. He heads the IFG and is the corresponding author of the publication together with Professor Marcel Mayor of INT.
The scientists then applied a catalyst in these active SURMOF layers to start a reaction for linking the monomers to polymers. Afterwards, the metallic node points were removed. Flat tissues of monomolecular polymer threads remained. "The polymer threads are kept together by the mechanical forces resulting from the weave pattern," Marcel Mayor explains. "Hence, the molecular tissues are as flexible as textiles produced in a conventional way."
###
Zhengbang Wang, Alfred Błaszczyk, Olaf Fuhr, Stefan Heissler, Christof Wöll, Marcel Mayor. Molecular weaving via surface-templated epitaxy of crystalline coordination networks. Nature Communications, 2017. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14442
For further information, please contact: Margarete Lehné, Media Relations Officer, Phone: 49-721-608-4 8121, Fax: +49 721 608-4 3658, Email: [email protected]
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) pools its three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation in a mission. With about 9,300 employees and 25,000 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
KIT – The Research University in the Helmholtz Association
Since 2010, the KIT has been certified as a family-friendly university.
This press release is available on the internet at http://www.kit.edu.
Media Contact
Monika Landgraf
[email protected]
49-721-608-47414
@KITKarlsruhe
http://www.kit.edu/index.php
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag