One of the grand challenges for materials science is the design and discovery of new materials that address global priorities such as Net Zero.
Credit: University of Liverpool
One of the grand challenges for materials science is the design and discovery of new materials that address global priorities such as Net Zero.
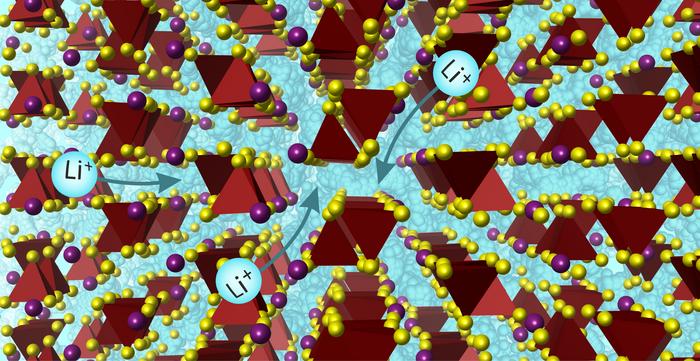
In a paper published in the journal Science, researchers at the University of Liverpool have discovered a solid material that rapidly conducts lithium ions. Such lithium electrolytes are essential components in the rechargeable batteries that power electric vehicles and many electronic devices.
Consisting of non-toxic earth-abundant elements, the new material has high enough Li ion conductivity to replace the liquid electrolytes in current Li ion battery technology, improving safety and energy capacity.
Using a transformative scientific approach to design the material, the interdisciplinary research team from the University synthesised the material in the laboratory, determined its structure (the arrangement of the atoms in space) and demonstrated it in a battery cell.
The new material is one of a very small number of solid materials that achieve Li ion conductivity high enough to replace liquid electrolytes, and operates in a new way because of its structure.
Its discovery was achieved through a collaborative computational and experimental workflow that used AI and physics-based calculations to support decisions made by chemistry experts at the University.
The new material provides a platform for the optimisation of chemistry to further enhance the properties of the material itself, and to identify other materials based on the new understanding provided by the study.
Professor Matt Rosseinsky, from the University of Liverpool’s Department of Chemistry, said: “This research demonstrates the design and discovery of a material that is both new and functional. The structure of this material changes previous understanding of what a high-performance solid-state electrolyte looks like.
“Specifically, solids with many different environments for the mobile ions can perform very well, not just the small number of solids where there is a very narrow range of ionic environments. This dramatically opens up the chemical space available for further discoveries.
Recent reports and media coverage herald the use of AI tools to find potentially new materials. In these cases, the AI tools are working independently and thus are likely to recreate what they were trained on in various ways, generating materials that may be very similar to known ones.
“This discovery research paper shows that AI and computers marshalled by experts can tackle the complex problem of real-world materials discovery, where we seek meaningful differences in composition and structure whose impact on properties is assessed based on understanding.”
“Our disruptive design approach offers a new route to discovery of these and other high-performance materials that rely on the fast motion of ions in solids.”
The study undertaken was a combined effort between researchers in University of Liverpool’s Department of Chemistry, Materials Innovation Factory, Leverhulme Research Centre for Functional Materials Design, Stephenson Institute for Renewable Energy, Albert Crewe Centre, and School of Engineering.
The work was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC), the Leverhulme Trust, and the Faraday Institution.
The paper `Superionic lithium transport via multiple coordination environments defined by two anion packing’ is published in Science.
Journal
Science
DOI
10.1126/science.adh5115
Article Title
Superionic lithium transport via multiple coordination environments defined by two anion packing
Article Publication Date
16-Feb-2024




