Legume plants have the unique ability to interact with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil, known as rhizobia. Legumes and rhizobia engage in symbiotic relations upon nitrogen starvation, allowing the plant to thrive without the need for externally supplied nitrogen. Symbiotic nodules are formed on the root of the plant, which are readily colonized by nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The cell-surface receptor SYMRK (symbiosis receptor-like kinase) is responsible for mediating the symbiotic signal from rhizobia perception to formation of the nodule. The activation mechanism of the receptor was until recently unknown.
Credit: Abel & Nørgaard et al. 2024
Legume plants have the unique ability to interact with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil, known as rhizobia. Legumes and rhizobia engage in symbiotic relations upon nitrogen starvation, allowing the plant to thrive without the need for externally supplied nitrogen. Symbiotic nodules are formed on the root of the plant, which are readily colonized by nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The cell-surface receptor SYMRK (symbiosis receptor-like kinase) is responsible for mediating the symbiotic signal from rhizobia perception to formation of the nodule. The activation mechanism of the receptor was until recently unknown.
In this study, the researchers have now identified four essential phosphorylation sites that act as the catalyst for the symbiotic relationship between legume plants and nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The initial steps of the symbiotic pathway at the cell-surface are well-characterized, however, understanding of how the signal is relayed downstream has eluded the research field for years. The discovery of these essential phosphorylation sites is an important step towards translating the ability to form symbiotic relations with nitrogen fixing bacteria into crop plants.
“We knew that the receptor and its activity is essential for the establishment of symbiosis, but we didn’t know how or why. Phosphorylation is a common mechanism for regulating kinase activity, so we theorized that SYMRK function was tied to specific phosphorylations,” Nikolaj Abel explains.
Through collaborations with the lab of Ole Nørregaard Jensen at the University of Southern Denmark, several phosphorylation sites were identified in distinct regions of the SYMRK kinase. The researchers were able to narrow down the essential sites by depleting or mimicking phosphorylations in vivo. Specifically, four sites in the N-terminal region of SYMRK gave strong phenotypes when mutated.
“We explore the impact of site-specific mutations by creating receptor variants and reintroducing them into plants lacking the functional SYMRK receptor. Observing either spontaneous nodulation without rhizobia or the absence of nodulation despite their presence indicates that we’ve targeted an element crucial to the symbiotic pathway,” Nikolaj Abel elaborates.
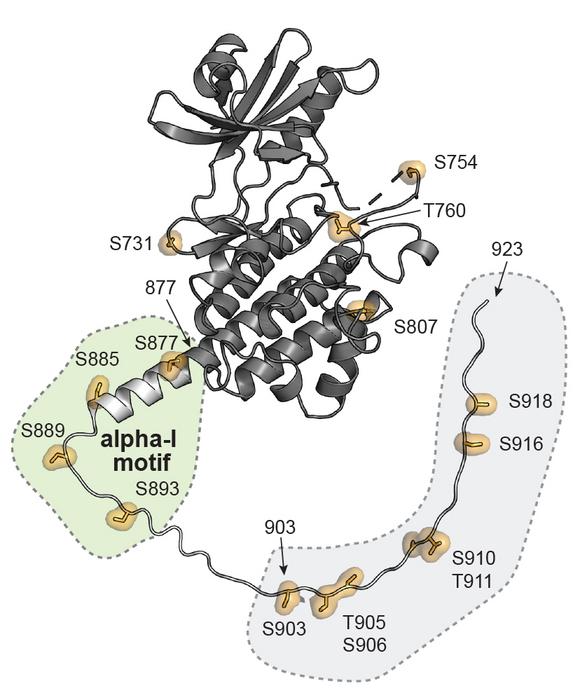
To understand where the identified phosphorylation sites were situated on the SYMRK kinase, the researchers determined the structure of the intracellular domain of SYMRK.
“We needed to be able to map the phosphorylation sites onto a structural model of the SYMRK kinase to truly understand how these phosphorylation sites enable downstream signaling. We identified a structurally conserved motif in the N-terminal alpha-helical region which we termed ‘the alpha-I motif’. This region contains the four conserved phosphorylation sites,” Malita Nørgaard explains.
Enabling root nodule symbiosis in important crops is the aim
The long-term goal is to enable root nodule symbiosis in important crops like barley, maize and rice. These crops require large amounts of nitrogen fertilizers to grow, resulting in enormous CO2 footprints and making small-holder farmers unable to produce stable yields.
With the successful identification of phosphorylation sites crucial to initiating the nodulation program in legume plants, the researchers believe this newfound knowledge holds promising implications for translating nitrogen-fixing traits into crops.
Link to the article: 10.1073/pnas.2311522121
10.1073/pnas.2311522121
For more information, please contact
Postdoc Dr. Nikolaj Birkebæk Abel – [email protected]
PhD-student Malita Malou Malekzadeh Nørgaard – [email protected]
Associate Professor Kasper Røjkjær Andersen – [email protected]
Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics
Aarhus University, Denmark
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI
10.1073/pnas.2311522121
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Phosphorylation of the alpha-I motif in SYMRK drives root nodule organogenesis
Article Publication Date
12-Feb-2024
COI Statement
Nikolaj B. Abel, Malita M. M. Nørgaard, Simon B. Hansen, Kira Gysel, Jens Stougaard & Kasper R. Andersen are inventors on a patent that captures these discoveries.




