Using single photons as qubits has become a prominent strategy in quantum information technology. Accurately determining the number of photons is crucial in various quantum systems, including quantum computation, quantum communication, and quantum metrology. Photon-number-resolving detectors (PNRDs) play a vital role in achieving this accuracy and have two main performance indicators: resolving fidelity, which measures the probability of accurately recording the number of incident photons, and dynamic range, which describes the maximum resolvable photon number.
Credit: Kong (SIMIT).
Using single photons as qubits has become a prominent strategy in quantum information technology. Accurately determining the number of photons is crucial in various quantum systems, including quantum computation, quantum communication, and quantum metrology. Photon-number-resolving detectors (PNRDs) play a vital role in achieving this accuracy and have two main performance indicators: resolving fidelity, which measures the probability of accurately recording the number of incident photons, and dynamic range, which describes the maximum resolvable photon number.
Superconducting nanostrip single-photon detectors (SNSPDs) are considered the leading technology for single-photon detection. They offer near-perfect efficiency and high-speed performance. However, when it comes to photon-number resolution, SNSPD-based PNRDs have struggled to find a balance between fidelity and dynamic range. Existing array-style SNSPDs, which divide incident photons among a limited number of pixels, face fidelity constraints. These detectors are thus referred to as quasi-PNRDs.
SNSPDs operate by breaking the local superconductivity of a narrow, cooled, current-biased strip when a photon is absorbed. This creates a local resistive region called a hotspot, and the resulting current is diverted through a load resistor, generating a detectable voltage pulse. Therefore, an SNSPD with a sufficiently long superconducting strip can be seen as a cascade of thousands of elements, and n-photon simultaneously activating different elements should generate n non-overlapping hotspots. However, conventional SNSPDs combined with modified cryogenic readouts can only resolve 3-4 photon numbers, resulting in a low dynamic range.
As reported in Advanced Photonics, researchers from the Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology (SIMIT), Chinese Academy of Sciences, have made progress in enhancing the photon-number-resolving capability of SNSPDs. By increasing the strip width or total inductance, they were able to overcome bandwidth limitations and timing jitter in readout electronics. This resulted in stretched rising edges and improved signal-to-noise ratio in the response pulses, and thus enhanced readout fidelity.
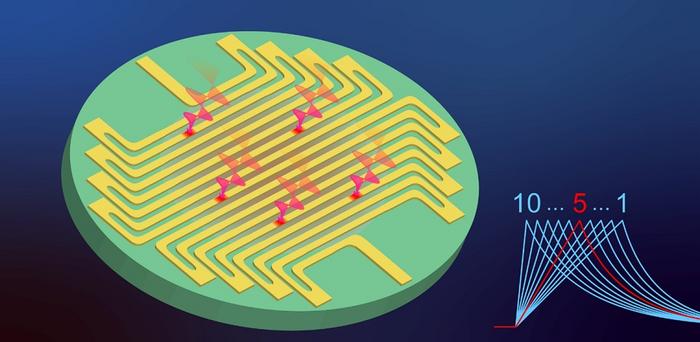
By widening the superconducting strip to micrometer scale, the researchers have presented the first observation of true-photon-number resolution up to 10 using the superconducting microstrip single-photon detector (SMSPD). Surprisingly, they achieved these results even without the use of cryogenic amplifiers. The readout fidelity reached an impressive 98 percent for 4-photon events and 90 percent for 6-photon events.
Furthermore, the researchers proposed a dual-channel timing setup to enable real-time photon-number readout. This approach significantly reduced data acquisition requirements by three orders of magnitude and simplified the readout setup. They also demonstrated the utility of their system in quantum information technology by creating a quantum random-number generator based on sampling the parity of a coherent state. This technology ensures unbiasedness, robustness against experimental imperfections and environmental noise, and resistance to eavesdropping.
This research represents a significant advancement in the field of PNRDs. With further improvement in the detection efficiency of SMSPDs, this technology could become readily accessible for various optical quantum information applications. These results highlight the potential of SNSPDs or SMSPDs for achieving high-fidelity and large-dynamic-range photon-number resolution.
For details, see the Gold Open Access article by Kong, Zhang et al., “Large-inductance superconducting microstrip photon detector enabling 10 photon-number resolution,” Adv. Photon. 6(1) 016004 (2024) doi 10.1117/1.AP.6.1.016004.
Journal
Advanced Photonics
DOI
10.1117/1.AP.6.1.016004
Article Title
Large-inductance superconducting microstrip photon detector enabling 10 photon-number resolution
Article Publication Date
2-Feb-2024




