For the first time, researchers including those at the University of Tokyo discovered a way to improve the durability of gold catalysts by creating a protective layer of metal oxide clusters. The enhanced gold catalysts can withstand a greater range of physical environments compared to unprotected equivalent materials. This could increase their range of possible applications, as well as reduce energy consumption and costs in some situations. These catalysts are widely used throughout industrial settings, including chemical synthesis and production of medicines, these industries could benefit from improved gold catalysts.
Credit: ©2024 Suzuki et al.
For the first time, researchers including those at the University of Tokyo discovered a way to improve the durability of gold catalysts by creating a protective layer of metal oxide clusters. The enhanced gold catalysts can withstand a greater range of physical environments compared to unprotected equivalent materials. This could increase their range of possible applications, as well as reduce energy consumption and costs in some situations. These catalysts are widely used throughout industrial settings, including chemical synthesis and production of medicines, these industries could benefit from improved gold catalysts.
Everybody loves gold: athletes, pirates, bankers — everybody. It’s historically been an attractive metal to craft things from, like medals, jewelry, coins and so on. The reason gold appears so shiny and alluring to us is because it’s chemically resilient to physical conditions that might otherwise tarnish other materials, for example, heat, pressure, oxidation and other detriments. Paradoxically, however, at nanoscopic scales, tiny particles of gold reverse this trend and become very reactive, so much so that for a long time now they have been essential to realize different kinds of catalysts, intermediary substances which accelerate or in some way enable a chemical reaction to take place. In other words, they’re useful or necessary to turn one substance into another, hence their widespread use in synthesis and manufacture.
“Gold is a wonderful metal and is rightly praised in society, and especially in science,” said Associate Professor Kosuke Suzuki from the Department of Applied Chemistry at the University of Tokyo. “It’s great for catalysts and can help us synthesize a range of things, including medicines. The reasons for this are that gold has a low affinity for absorbing molecules and is also highly selective about what it binds with, so it allows for very precise control of chemical synthesis processes. Gold catalysts often operate at lower temperatures and pressures compared to traditional catalysts, requiring less energy and reducing environmental impact.”
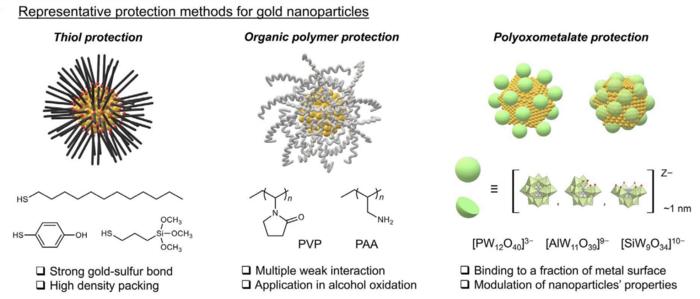
As good as gold is, though, it does have some drawbacks. It becomes more reactive the smaller particles are made of it, and there is a point at which a catalyst made with gold can begin to suffer negatively from heat, pressure, corrosion, oxidation and other conditions. Suzuki and his team thought they could improve upon this situation and devised a novel protective agent that could allow a gold catalyst to maintain its useful functions but across a greater range of physical conditions that usually hinder or destroy a typical gold catalyst.
“Current gold nanoparticles used in catalysts have some level of protection, thanks to agents such as dodecanethiols and organic polymers. But our new one is based on a cluster of metal oxides called polyoxometalates and it offers far superior results, especially in regard to oxidative stress,” said Suzuki. “We are currently investigating the novel structures and applications of polyoxometalates. This time we applied the polyoxometalates to gold nanoparticles and ascertained the polyoxometalates improve the nanoparticles’ durability. The real challenge was applying a wide range of analytical techniques to test and verify all this.”
The team used a variety of techniques collectively known as spectroscopy. It employed no less than six spectroscopic methods which vary in the kinds of information they reveal about a material and its behavior. But generally speaking, they work by casting some kind of light onto a substance and measuring how that light changes in some way with specialized sensors. Suzuki and his team spent months running various tests and different configurations of their experimental material until they found what they were seeking.
“We’re not just driven by trying to improve some methods of chemical synthesis. There are many applications of our enhanced gold nanoparticles that could be used to benefit society,” said Suzuki. “Catalysts to break down pollution (many gasoline cars already have a familiar catalytic converter), less impactful pesticides, green chemistry for renewable energy, medical interventions, sensors for foodborne pathogens, the list goes on. But we also want to go further. Our next steps will be to improve the range of physical conditions we can make gold nanoparticles more resilient to, and also see how we can add some durability to other useful catalytic metals like ruthenium, rhodium, rhenium and, of course, something people prize even more highly than gold: platinum.”
###
Journal article: Kang Xia, Takafumi Yatabe, Kentaro Yonesato, Soichi Kikkawa, Seiji Yamazoe, Ayako Nakata, Ryo Ishikawa, Naoya Shibata, Yuichi Ikuhara, Kazuya Yamaguchi & Kosuke Suzuki, “Ultra-stable and highly reactive colloidal gold nanoparticle catalysts protected using multi-dentate metal oxide nanoclusters”, Nature Communications,
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45066-9
Funding:
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from JST FOREST (JPMJFR213M for K.S., JPMJFR2033 for R.I.), JST PRESTO (JPMJPR18T7 for K.S., JPMJPR19T9 for S.Y., JPMJPR20T4 for A.N., JPMJPR227A for T.Y.), JSPS KAKENHI (22H04971 for K.Ya), and the JSPS Core-to-Core program. XAFS measurements were conducted at SPring-8 with the approval of the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (proposal numbers: 2023A1732, 2023A1554, 2022B1860, 2022B1684). A part of this work was supported by Advanced Research Infrastructure for Materials and Nanotechnology in Japan (ARIM) of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Grant Number JPMXP1222UT0184 and JPMXP1223UT0029.
Useful links:
Department of Applied Chemistry https://www.appchem.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Graduate School of Engineering https://www.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/soe
Research contact:
Associate Professor Kosuke Suzuki
Graduate School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-0033, Japan
[email protected]
Press contact:
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Public Relations Group, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
[email protected]
About The University of Tokyo:
The University of Tokyo is Japan’s leading university and one of the world’s top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world’s top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on X (formerly Twitter) at @UTokyo_News_en.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-024-45066-9
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Ultra-stable and highly reactive colloidal gold nanoparticle catalysts protected using multi-dentate metal oxide nanoclusters
Article Publication Date
6-Feb-2024




