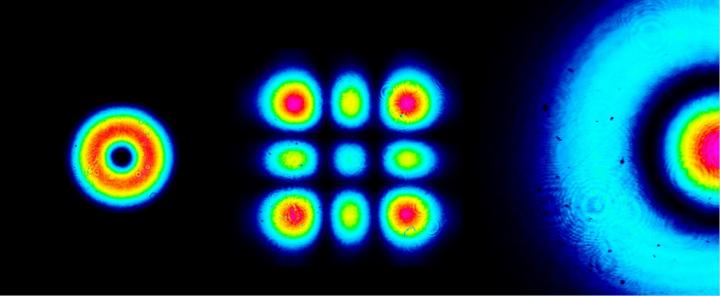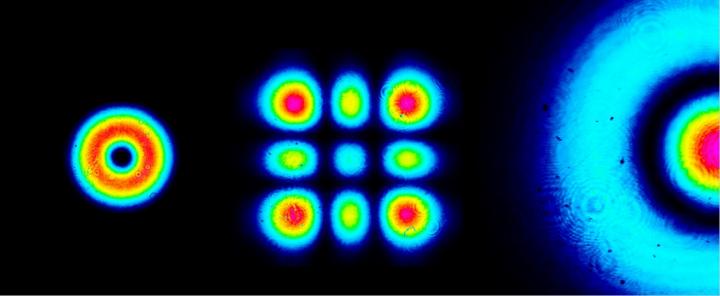
Credit: Egor Kovlakov
Members of the Faculty of Physics, the Lomonosov Moscow State University have elaborated a new technique for creation of entangled photon states, exhibiting photon pairs, which get correlated (interrelated) with each other. Scientists have described their research in an article, published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Physicists from the Lomonosov Moscow State University have studied an entangled photon state, in which the state is determined only for the whole system and not for each separate particle.
Stanislav Straupe, Doctor of Sciences in Physics and Mathematics, a member of the Quantum Electronics Department and Quantum Optical Technologies Laboratory at the Faculty of Physics, the Lomonosov Moscow State University, and one of the article co-authors says the following. He explains: "Entangled states are typical and general. The only problem is in the point that for the majority of particles interaction with the environment destroys the entanglement. And photons hardly ever interact with other particles, thus they are a very convenient object for experiments in this sphere. The largest part of light sources we face in our life is a classical one — for instance, the Sun, stars, incandescent lamps and so on. Coherent laser radiation also belongs to the classical part. To create nonclassical light isn't an easy thing. You could, for instance, isolate a single atom or an artificial structure like a quantum dot and detect its radiation – this is the way for single photons obtaining."
An effect of spontaneous parametric down-conversion in nonlinear crystal is most commonly used for obtaining of entangled photon states. In this process a laser pumping photon splits into two. As this takes place photon states get correlated, entangled due to the conservation laws. Egor Kovlakov, a doctoral student from the Quantum Electronics Department at the Radio Physics Division of the Faculty of Physics, the Lomonosov Moscow State University and an article co-author shares: "In our project we've offered and tested a new technique of the spatial entanglement creation. Photon pairs, generated in our experiment, propagate by beams, which get correlated in "spatial profile". Efficiency is the key peculiarity of our technique in comparison with the previously known ones."
Studies of entangled photon states started in 1970-s years and nowadays they are most actively used in quantum cryptography, an area relating to quantum information transfer and quantum communication.
Stanislav Straupe notices: "Quantum cryptography is not the only one of the possible applications, but at the moment it is the most developed one. Unlike classical communication, where it's not important which alphabet is used for message coding and it's enough to use a binary one (0 or 1), everything is more complicated in quantum communication. It turns out that enhancement of alphabet dimension not only increases amount of information coded in one photon, but also strengthens communication security. That's why it'd be interesting to develop quantum communication systems, based also on information coding in spatial profile of photons." The scientists suppose that in the future their solution will be applied for creation of an optical channel with a satellite, where you can't install optical fiber (an optical fiber guide) — a basis for fiber-optic communication.
###
Media Contact
Vladimir Koryagin
[email protected]
http://www.msu.ru
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag