WASHINGTON, Jan. 9, 2024 – Badminton traces its roots back more than a millennium, but the modern version of the racket game originated in the late 19th century in England. Today, it is the second most popular sport in the world behind soccer, with an estimated 220 million people who enjoy playing. For the last three decades, badminton has been a competitive Olympic sport, and with “bird” speeds topping 300 mph in “smash” shots, it certainly makes for exciting spectator sport.
Credit: Sanjay Mittal
WASHINGTON, Jan. 9, 2024 – Badminton traces its roots back more than a millennium, but the modern version of the racket game originated in the late 19th century in England. Today, it is the second most popular sport in the world behind soccer, with an estimated 220 million people who enjoy playing. For the last three decades, badminton has been a competitive Olympic sport, and with “bird” speeds topping 300 mph in “smash” shots, it certainly makes for exciting spectator sport.
Shuttlecocks, also known as birdies or birds, are traditionally made from duck feathers, but nylon shuttlecocks have become more widely used because of their superior durability. Their flight behavior, however, is far different from that of traditional feather birdies.
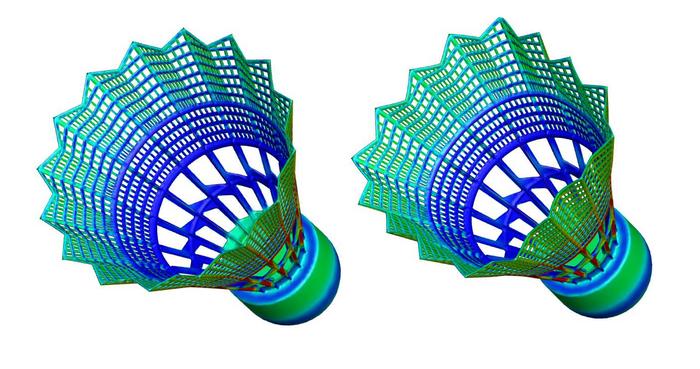
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, a trio of scientists in India explored the aerodynamic performance of nylon shuttlecocks at various flight speeds. Through computational analyses based on two-way fluid-structure interactions, the team coupled equations governing air flow with equations determining skirt deformation of a shuttlecock in flight.
“We studied the flow by examining aerodynamic forces on the shuttlecock as well as its deformations at each flight speed,” said author Sanjay Mittal. “The pressure on the skirt causes it to deform inwards and this deformation increases with speed.”
The team identified four distinct regimes of deformation. At speeds less than 40 meters per second (89 mph), the skirt maintains circularity despite cross-sectional deformation; at higher speeds, it buckles and deforms into a square before it then vibrates radially. Eventually, it undergoes a low frequency wavelike circumferential deformation.
“The cross-sectional area of the shuttlecock decreases with speed, which lowers the air flow rate through the shuttlecock,” said Mittal. “The vortex structures that form inside the shuttlecock weaken when it deforms. As a result of these effects, the deformed shuttlecock offers a much lower air resistance compared to its rigid counterpart.”
The study’s computational results confirm experimental measurements, explaining the phenomenology of why a duck feather shuttlecock does not deform as much as a nylon shuttlecock – and why the flight of each at high speed is quite different. From the perspective of a player on the receiving end of a smash shot, the nylon shuttlecock, which travels faster, is harder to return.
Ultimately, the research may represent a new arc in the history of the beloved sport.
“Our study opens up the possibility for improved designs that make the nylon shuttlecock structurally stiffer so that it more closely mimics the aerodynamic performance of feather shuttlecocks,” said Mittal. “This could be a game-changer, literally.”
###
The article “Computational analysis of the fluid-structure interactions of a synthetic badminton shuttlecock” is authored by Darshankumar Zala, Harish Dechiraju, and Sanjay Mittal. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on Jan. 9, 2024 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0182411). After that date, it can be accessed at http://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/5.0182411.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
Journal
Physics of Fluids
DOI
10.1063/5.0182411
Article Title
Computational analysis of the fluid-structure interactions of a synthetic badminton shuttlecock
Article Publication Date
9-Jan-2024




