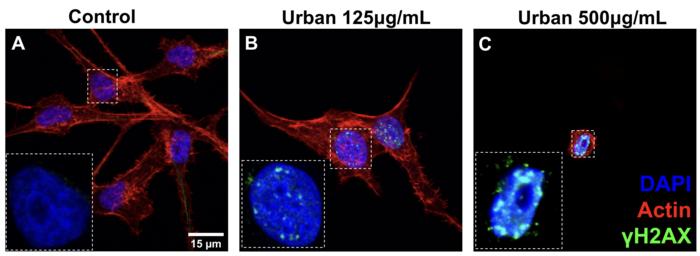
Particulate matter causes health problems for those who inhale the fine droplets and particles, but the chemical composition of the mixture matters—and can vary widely across space and time. Lydia Contreras and colleagues characterize the consequences of varying levels of exposure to three chemically distinct particulate matter mixes, sourced from the National Institutes of Standards and Technology (NIST), in a human bronchial epithelial cell model. Following exposures, the authors measured changes in gene expression and cell morphology. NIST’s “Urban” and “Fine” particulate matter mixes, which were collected in St. Louis, Missouri and Prague, Czech Republic, respectively, induced significant changes in gene expression. Particulate matter collected from a diesel engine produced fewer changes. Higher exposures caused more significant changes. Different particulate matter mixes also induced different morphological changes, with exposure to the “Urban” and “Fine” mixtures causing cells to become smaller and more rounded than exposure to the “Diesel” mix. These small rounded cells had signs of significant DNA damage. Next, the authors worked to identify which chemicals were responsible for these changes. Cadmium levels varied between the three mixes tested. Further, when the “Diesel” mix was supplemented with cadmium, it induced changes similar to that of the “Urban” and “Fine” mixes. This indicated that cadmium is at least partially responsible for differences in DNA damage and toxicity between the mixtures, according to the authors.
Credit: Engels et al.
Particulate matter causes health problems for those who inhale the fine droplets and particles, but the chemical composition of the mixture matters—and can vary widely across space and time. Lydia Contreras and colleagues characterize the consequences of varying levels of exposure to three chemically distinct particulate matter mixes, sourced from the National Institutes of Standards and Technology (NIST), in a human bronchial epithelial cell model. Following exposures, the authors measured changes in gene expression and cell morphology. NIST’s “Urban” and “Fine” particulate matter mixes, which were collected in St. Louis, Missouri and Prague, Czech Republic, respectively, induced significant changes in gene expression. Particulate matter collected from a diesel engine produced fewer changes. Higher exposures caused more significant changes. Different particulate matter mixes also induced different morphological changes, with exposure to the “Urban” and “Fine” mixtures causing cells to become smaller and more rounded than exposure to the “Diesel” mix. These small rounded cells had signs of significant DNA damage. Next, the authors worked to identify which chemicals were responsible for these changes. Cadmium levels varied between the three mixes tested. Further, when the “Diesel” mix was supplemented with cadmium, it induced changes similar to that of the “Urban” and “Fine” mixes. This indicated that cadmium is at least partially responsible for differences in DNA damage and toxicity between the mixtures, according to the authors.
Journal
PNAS Nexus
Article Title
Particulate matter composition drives differential molecular and morphological responses in lung epithelial cells
Article Publication Date
28-Dec-2023




