Important signaling molecules called phospholipids are active throughout cells in small compartments called condensates, rather than functioning primarily in cell membranes as previously thought, according to a study from researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The finding helps open a new avenue of investigation in cell biology and may also be relevant to the study of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease.
Credit: Dr. Jason Dumelie
Important signaling molecules called phospholipids are active throughout cells in small compartments called condensates, rather than functioning primarily in cell membranes as previously thought, according to a study from researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The finding helps open a new avenue of investigation in cell biology and may also be relevant to the study of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer’s disease.
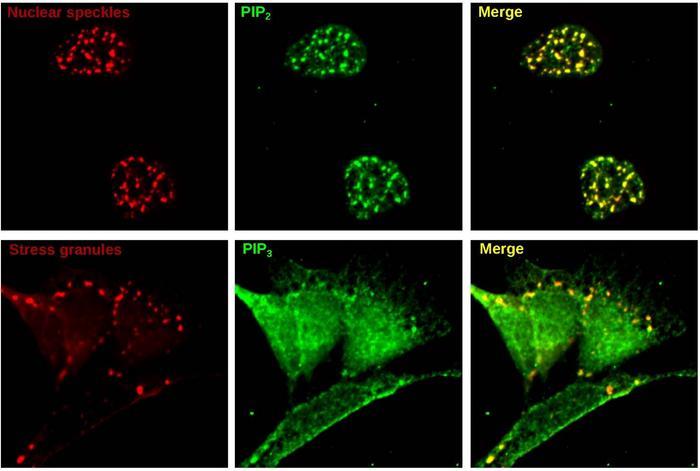
Condensates in cells, also called biomolecular condensates, behave like oil drops within water. They are made of proteins, and often RNA molecules, that have weakly conglomerated to form distinct globules in the cell. These globules form compartments with chemical properties that differ from those of the surrounding, watery interior of the cell. There are many different kinds of condensates, and their apparent functions include concentrating proteins that work together to support cellular processes, and sequestering RNAs when cells are under stress. Condensates are now also seen as potential sites for the formation of abnormal protein aggregates found in neurodegenerative disorders including ALS, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and Huntington’s disease.
In the study, published Nov. 16 in Nature Chemical Biology, the researchers found evidence that condensates frequently contain phospholipids along with their well known protein and RNA constituents. These condensates often contain enzymes that act on phospholipids, suggesting a previously overlooked role for condensates as phospholipid signaling centers. The scientists also found that they could manipulate the numbers and properties of condensates by altering phospholipid levels.
“This is a basic science discovery that shows major sites of lipid signaling in cells,” said study senior author Dr. Samie Jaffrey, the Greenberg-Starr Professor in the Department of Pharmacology at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The study’s first author is Dr. Jason Dumelie, an instructor in pharmacology and a member of the Jaffrey lab at Weill Cornell Medicine. The study also included a collaboration with the laboratory of analytical chemistry expert Dr. Steven Gross, a professor of pharmacology at Weill Cornell Medicine.
Although scientists increasingly see condensates as important in health and disease, they know relatively little about condensates’ molecular constituents apart from proteins and RNAs.
In the study, Drs. Jaffrey and Dumelie and their colleagues focused on small organic molecules in cells that are often involved in biochemical processes, and are known as metabolites. The researchers made lab-dish versions of common condensates and surrounded them with an ordinary cellular mix of hundreds of metabolites. With the help of Gross lab member Dr. Qiuying Chen, an associate professor of research in pharmacology, they used a technique called mass spectrometry to catalogue metabolites that became more concentrated inside the condensates.
To their surprise, they found that condensates formed from different protein conglomerations nevertheless tended to attract similar sets of metabolites. Prominent among these metabolites were fat-related molecules called lipids, particularly phospholipids.
Phospholipids are key constituents of cell membranes that work as signaling molecules in a variety of cell processes, including immune, stress-response and cognitive functions.
“Normally if you ask scientists where phospholipids reside in cells, they’ll say in cell membranes,” Dr. Dumelie said. “But as our study shows, they are also in these condensates.”
The finding helps explain prior research, which had found that enzymes known to mediate phospholipid signaling are mysteriously present in condensates. But the implications could go well beyond basic cell biology, given the links between condensates and protein aggregation in neurodegenerative disorders.
“We found in our study that by adding phospholipids we could substantially change the properties of one of the condensates we looked at,” Dr. Dumelie said. “That suggests the possibility—which we’re investigating now—of using such lipids to alter condensates to prevent the formation of toxic protein aggregates in neurodegenerative disorders.”
Journal
Nature Chemical Biology
Article Title
Biomolecular condensates create phospholipid-enriched microenvironments
Article Publication Date
16-Nov-2023




