“Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major cellular change observed in the hippocampus during aging.”
Credit: Jung et al.
“Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major cellular change observed in the hippocampus during aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 22, entitled, “Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes by facilitating neuronal plasticity and reducing age-related genes in the hippocampus.”
In this new study, researchers Hyo Young Jung, Hyun Jung Kwon, Kyu Ri Hahn, Woosuk Kim, Dae Young Yoo, Yeo Sung Yoon, Dae Won Kim, and In Koo Hwang from Seoul National University, Chungnam National University, Gangneung-Wonju National University, Hallym University, and Konkuk University investigated the effects of heat shock protein 10 (HSP10) protein on memory function, hippocampal neurogenesis, and other related genes/proteins in adult and aged mice.
“In the present study, we investigated the effects of HSP10 on hippocampal function in both adult and aged mice.”
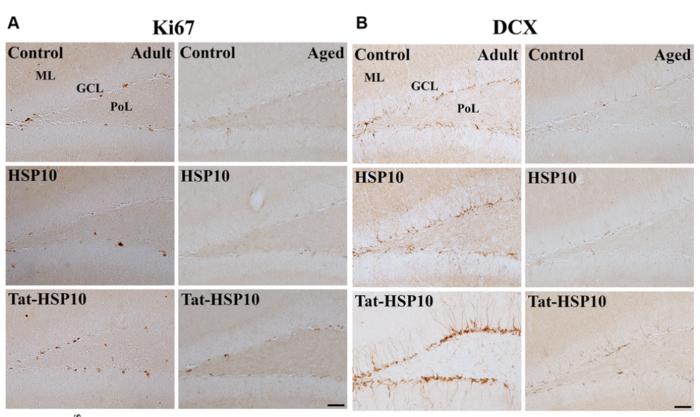
To translocate the HSP10 protein into the hippocampus, the Tat-HSP10 fusion protein was synthesized, and Tat-HSP10, not HSP10, was successfully delivered into the hippocampus based on immunohistochemistry and western blotting. Tat-HSP10 (0.5 or 2.0 mg/kg) or HSP10 (control protein, 2.0 mg/kg) was administered daily to 3- and 21-month-old mice for 3 months, and observed the senescence maker P16 was significantly increased in aged mice and the treatment with Tat-HSP10 significantly decreased P16 expression in the hippocampus of aged mice.
In novel object recognition and Morris water maze tests, aged mice demonstrated decreases in exploratory preferences, exploration time, distance moved, number of object contacts, and escape latency compared to adult mice. Treatment with Tat-HSP10 significantly improved exploratory preferences, the number of object contacts, and the time spent swimming in the target quadrant in aged mice but not adults. Administration of Tat-HSP10 increased the number of proliferating cells and differentiated neuroblasts in the dentate gyrus of adult and aged mice compared to controls, as determined by immunohistochemical staining for Ki67 and doublecortin, respectively.
Additionally, Tat-HSP10 treatment significantly mitigated the reduction in sirtuin 1 mRNA level, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 1, and postsynaptic density 95 protein levels in the hippocampus of aged mice. In contrast, Tat-HSP10 treatment significantly increased sirtuin 3 protein levels in both adult and aged mouse hippocampus. These suggest that Tat-HSP10 can potentially reduce hippocampus-related aging phenotypes.
“Our results suggest that Tat-HSP10 treatment facilitates mitochondrial function, and Tat-HSP10 supplementation ameliorates the aging phenotypes in the mouse hippocampus.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205182
Corresponding Authors: Dae Won Kim, In Koo Hwang
Corresponding Emails: [email protected], [email protected]
Keywords: heat shock protein 10, aging, hippocampus, memory, neurogenesis, synaptic plasticity
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205182
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- X, formerly known as Twitter
- YouTube
- LabTube
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.205182
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Tat-heat shock protein 10 ameliorates age-related phenotypes by facilitating neuronal plasticity and reducing age-related genes in the hippocampus
Article Publication Date
25-Nov-2023




