A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “1,5-anhydro-D-fructose induces anti-aging effects on aging-associated brain diseases by increasing 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α/brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway.”
Credit: 2023 Kikuchi et al.
A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “1,5-anhydro-D-fructose induces anti-aging effects on aging-associated brain diseases by increasing 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α/brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway.”
5’-Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a metabolic sensor that serves as a cellular housekeeper; it also controls energy homeostasis and stress resistance. Thus, correct regulation of this factor can enhance health and survival. AMPK signaling may have a critical role in aging-associated brain diseases. Some in vitro studies have shown that 1,5-anhydro-D-fructose (1,5-AF) induces AMPK activation.
In this new study, researchers Kiyoshi Kikuchi, Shotaro Otsuka, Seiya Takada, Kazuki Nakanishi, Kentaro Setoyama, Harutoshi Sakakima, Eiichiro Tanaka, and Ikuro Maruyama from Kagoshima University investigated the effects of 1,5-AF on the AMPK/PGC-1α/BDNF pathway in multiple animal models of human aging-associated brain diseases.
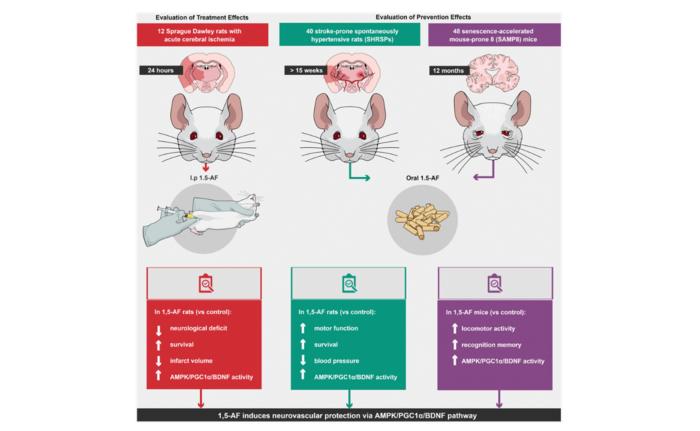
“In the present study, we experimentally evaluated the effects of 1,5-AF on aging-associated brain diseases in vivo using an animal model of acute ischemic stroke (AIS), stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRSPs), and the spontaneous senescence-accelerated mouse-prone 8 (SAMP8) model.”
In the AIS model, intraperitoneal injection of 1,5-AF reduced cerebral infarct volume, neurological deficits, and mortality. In SHRSPs, oral administration of 1,5-AF reduced blood pressure and prolonged survival. In the SAMP8 model, oral administration of 1,5-AF alleviated aging-related decline in motor cognitive function. Although aging reduced the expression levels of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α (PGC-1α) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), the researchers found that 1,5-AF activated AMPK, which led to upregulation of the PGC-1α/BDNF pathway.
“Our results suggest that 1,5-AF can induce endogenous neurovascular protection, potentially preventing aging-associated brain diseases. Clinical studies are needed to determine whether 1,5-AF can prevent aging-associated brain diseases.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205228
Corresponding Authors: Kiyoshi Kikuchi, Ikuro Maruyama
Corresponding Emails: [email protected], [email protected]
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinases, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, blood pressure, aging
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205228
About Aging:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- X, formerly known as Twitter
- YouTube
- LabTube
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.205228
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
1,5-anhydro-D-fructose induces anti-aging effects on aging-associated brain diseases by increasing 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activity via the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ co-activator-1α/brain-derived neurotrophic factor pathway
Article Publication Date
9-Nov-2023




