Researchers from Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine have identified the role of iron in ocular toxoplasmosis (OT), a form of toxoplasmosis that causes blindness. They found reduced iron concentration in the clear gel part of the eye of human patients and iron accumulation in the retina of mice. Treatment of mice with a compound that decreases iron was successful in reducing their symptoms. Their findings show the important role of iron in the disease and that controlling it may lead to a successful treatment. Their study was published in Redox Biology.
Credit: Hiroki Kaneko, Department of Ophthalmology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine
Researchers from Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine have identified the role of iron in ocular toxoplasmosis (OT), a form of toxoplasmosis that causes blindness. They found reduced iron concentration in the clear gel part of the eye of human patients and iron accumulation in the retina of mice. Treatment of mice with a compound that decreases iron was successful in reducing their symptoms. Their findings show the important role of iron in the disease and that controlling it may lead to a successful treatment. Their study was published in Redox Biology.
Toxoplasma is a parasite that affects approximately one third of the world’s population. OT is one of its major symptoms. A quarter of patients with OT experience a loss of vision in at least one eye, often to the extent of legal blindness. Part of this is because the PCR diagnostic test used to diagnose the disease is unreliable, with an accuracy of only 30%.
“This limitation reveals the urgent need for the development and implementation of more accessible diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, especially in developing countries where medical resources are scarce,” said lead researcher Dr. Kasuhisa Yamada. “Since there are still differences in medical resources between developing and developed countries, which affect the control of infectious diseases, our group wanted to develop a diagnostic test that has a higher diagnostic rate and does not require specialized equipment.”
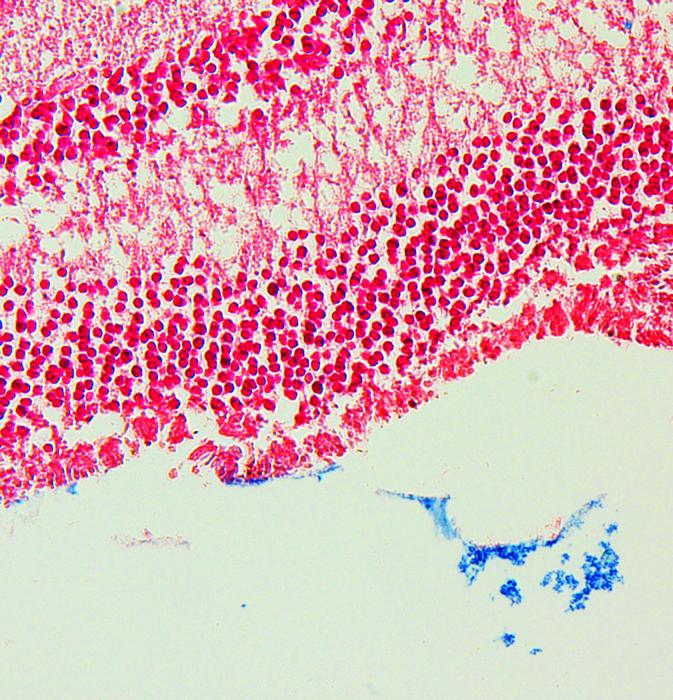
The answer to this problem may lie in controlling iron levels. The researchers found that patients with OT had a decreased iron concentration in the vitreous humor compared to patients with other eye diseases. Furthermore, when they examined sections taken from the eyes of mice with toxoplasmosis, they found increased iron uptake into the retinas.
Further investigation identified ferroptosis, a form of iron-associated cell death, in the affected areas of the retina. As the retina is a key part of the eye that converts light into electrical signals from a person’s optic nerve to their brain, cell death may explain why some patients are blinded by OT.
If iron caused the disease, the researchers wondered, could eliminating it inhibit its development? To better understand, they administered deferiprone, a drug that binds to iron, to mice. The results were unexpected. The treatment not only reduced iron uptake but also improved retinal inflammation, significantly helping with OT-related retinochoroiditis.
The group’s findings show promise for preventive and therapeutic treatments. “In this investigation, deferiprone was administered concurrently with Toxoplasma infection in mice, demonstrating its effectiveness as a prophylactic,” Yamada said. “Nevertheless, our findings suggest promising potential for deferiprone as a therapeutic agent, as we used both oral and intravitreal injections, that both exhibited notable improvements in retinochoroiditis.”
“Our analysis of the study data yielded a sensitivity and specificity exceeding 80%,” Yamada said. “These findings suggest a strong potential for iron measurement as a diagnostic tool, particularly when the disease has progressed to a stage with noticeable symptoms.”
Journal
Redox Biology
DOI
10.1016/j.redox.2023.102890
Article Publication Date
17-Sep-2023




