Lithium-ion batteries powered the device on which these words appear. From phones and laptops to electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are critical to the technology of the modern world — but they can also explode. Comprising negatively and positively charged electrodes and an electrolyte to transport ions across the divide, lithium-ion batteries are only as good as the limitations of their components. Liquid electrolytes are potentially volatile at high temperatures, and their efficiency can be limited by nonuniformity and instabilities in the other components.
Credit: Energy Materials and Devices, Tsinghua University Press
Lithium-ion batteries powered the device on which these words appear. From phones and laptops to electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are critical to the technology of the modern world — but they can also explode. Comprising negatively and positively charged electrodes and an electrolyte to transport ions across the divide, lithium-ion batteries are only as good as the limitations of their components. Liquid electrolytes are potentially volatile at high temperatures, and their efficiency can be limited by nonuniformity and instabilities in the other components.
Researchers are working toward developing safer, more efficient batteries with solid electrolytes, a significant change over the liquid version that currently transports ions in most commercially available batteries now. The challenge is that each solid-state material has as many drawbacks as advantages, according to a team based at the Shenzhen All-Solid-State Lithium Battery Electrolyte Engineering Research Center in Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School’s Institute of Materials Research.
To solve this conundrum, the researchers combined two of the prime solid-state candidates — ceramic and polymer — into a new composite electrolyte.
They published their results on Sept. 21 in Energy Materials and Devices.
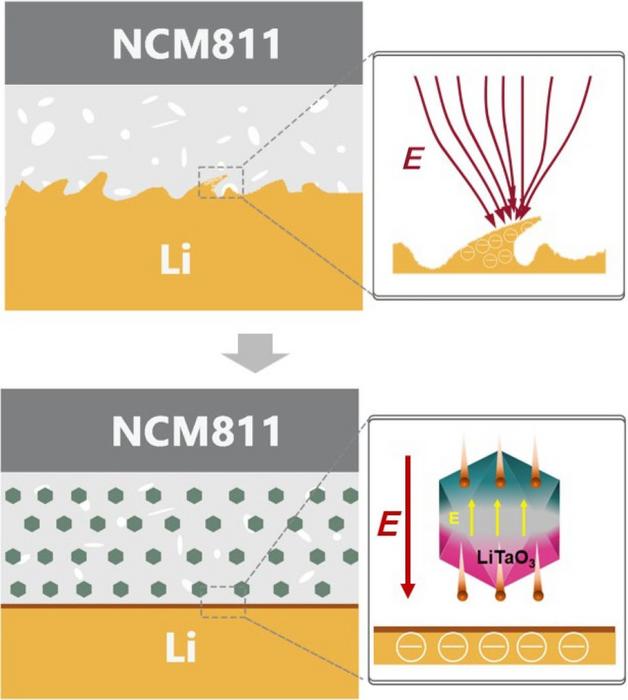
“Composite solid-state electrolytes have received significant attention due to their combined advantages as inorganic and polymer electrolytes,” said co-first author Yu Yuan, who is also affiliated with Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School. “However, conventional inorganic ceramic fillers offer limited ion conductivity enhancement for composite solid-state electrolytes due to the space-charge layer between the polymer matrix and ceramic phase.”
Inorganic ceramic electrolytes offer high conductivity, but they develop resistance when faced with another solid and are complicated to synthesize. Polymer electrolytes are easier to produce, more flexible and work better with electrodes, but their conductivity at room temperature is too low for commercial application. According to Yuan, combining the two should produce a highly conductive, flexible electrolyte that is easier to synthesize. In reality, however, when mixed, the composite solid-state electrolytes have a separation — called a space-charge layer — between their constituent parts that limits their conductivity.
To correct this, the researchers used lithium tantalate, which has a crystalline structure that lends itself to unique optical and electrical properties, as a functional filler to mitigate the space-charge layer. The ceramic ion conductor material is ferroelectric, mean it can reverse electric charge when a current is applied.
“Not only does the filler alleviate the space-charge layer, but it also provides an extra lithium-ion transport pathway,” said co-first author Likun Chen, who is also affiliated with Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School.
The researchers experimentally demonstrated that the lithium tantalate filler eases the bottleneck for lithium-ion transport across the polymer-ceramic interface, resulting in lithium ions moving in both increased numbers and speed through the electrolyte.
The result, the researchers said, is an electrolyte with high conductivity and a long-cycling life — referring to how often the ions can be transported across the battery in charging and discharging cycles — even at low temperatures.
“This work proposes a novel strategy for designing integrated ceramic fillers with ferroelectric and ion-conductive properties to achieve high-throughput lithium-ion transport of composite-solid electrolytes for advances solid-state lithium metal batteries,” Yuan said. “Our approach sheds light on the design of functional ceramic fillers for composite solid-state electrolytes to effectively enhance ion conductivity and battery performance.”
Other co-authors include Yuhang Li, Xufei An, Jianshuai Lv, Shaoke Guo, Xing Cheng, Yang Zhao, Ming Liu, Yan-Bing He and Feiyu Kang. Li, An, Lv, Guo, Cheng, Zhao and Kang are also affiliated with Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School.
The National Natural Science Foundation of China, Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen Outstanding Talents Training Fund, All-Solid-State Lithium Battery Electrolyte Engineering Research Center and Shenzheng Technical Plan Project supported this research.
##
About Energy Materials and Devices
Energy Materials and Devices is launched by Tsinghua University, published quarterly by Tsinghua University Press, aiming at being an international, single-blind peer-reviewed, open-access and interdisciplinary journal in the cutting-edge field of energy materials and devices. It focuses on the innovation research of the whole chain of basic research, technological innovation, achievement transformation and industrialization in the field of energy materials and devices, and publishes original, leading and forward-looking research results, including but not limited to the materials design, synthesis, integration, assembly and characterization of devices for energy storage and conversion etc.
About SciOpen
SciOpen is a professional open access resource for discovery of scientific and technical content published by the Tsinghua University Press and its publishing partners, providing the scholarly publishing community with innovative technology and market-leading capabilities. SciOpen provides end-to-end services across manuscript submission, peer review, content hosting, analytics, and identity management and expert advice to ensure each journal’s development by offering a range of options across all functions as Journal Layout, Production Services, Editorial Services, Marketing and Promotions, Online Functionality, etc. By digitalizing the publishing process, SciOpen widens the reach, deepens the impact, and accelerates the exchange of ideas.
Journal
Energy Materials and Devices
DOI
10.26599/EMD.2023.9370004
Article Title
Functional LiTaO3 filler with tandem conductivity and ferroelectricity for PVDF-based composite solid-state electrolyte
Article Publication Date
21-Sep-2023




