A collaborative study led by researchers from Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute has revealed the promising possibilities of using an agarose spot migration assay to examine the ability of extracellular vesicles to attract other cells in a controlled environment. The study has been recently published in the journal BMC Biology.
Credit: IGTP
A collaborative study led by researchers from Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute has revealed the promising possibilities of using an agarose spot migration assay to examine the ability of extracellular vesicles to attract other cells in a controlled environment. The study has been recently published in the journal BMC Biology.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoparticles released by cells which are present in various biological processes, including cellular communication. Recent research indicates that cancer-related EVs play an important role in forming a pre-metastatic niche (PMN) – a preparatory area that allows spreading tumour cells to establish and grow – by recruiting cells from the original tumour.
It is vital to understand and measure how these cancer-EVs can prompt cell migration and recruitment, both for developing cell-free therapeutic approaches and for improving our knowledge of cancer metastasis. In this context, classical in vitro (lab-based) migration assays do not fully capture the true ability of EVs to guide cells chemically to a new location.
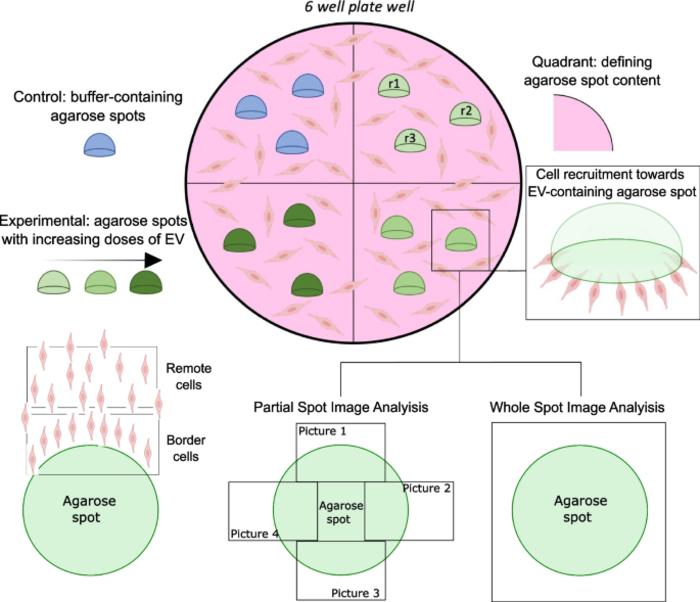
The study led by researchers from IGTP’s research groups Innovation in Vesicles and Cells for Application in Therapy (IVECAT), Badalona Applied Research Group in Oncology (B·ARGO) and Resistance, Chemotherapy and Predictive Biomarkers (RCPB) emphasises how EVs can influence cancer metastasis. The research team adapted a laboratory method known as the agarose spot migration assay to EV requirements, which measures how well these tiny particles can attract other cells in a controlled environment.
Their analysis, including still images and time-lapse videos among others, revealed that EVs differ in their ability to recruit endothelial cells. More importantly, they were able to identify a greater recruitment capability in EVs from highly metastatic PC3 cancer cells compared to those from less metastatic LNCaP cells.
The first author of the study, Marta Clos-Sansalvador, a predoctoral student from IGTP’s group IVECAT, explains that “the agarose spot migration assay may offer a diversity of measurements and migration settings not provided by classical migration assays, like scratch assays, and reveal its potential use in the EV and cancer metastasis fields”. Clos-Sansalvador also points out the assay’s practicality: “EV-adapted agarose spot migration assay is a simple, low-cost, and versatile technique that can be easily adapted to most laboratories”.
Journal
BMC Biology
DOI
10.1186/s12915-023-01729-5
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Agarose spot migration assay to measure the chemoattractant potential of extracellular vesicles: applications in regenerative medicine and cancer metastasis
Article Publication Date
26-Oct-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing interests.




