Credit: Photo: KIT
The Middle Ages certainly were far from being science-friendly: Whoever looked for new findings off the beaten track faced the threat of being burned at the stake. Hence, the contribution of this era to technical progress is deemed to be rather small. Scientists of Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), however, were inspired by medieval mail armor when producing a new metamaterial with novel properties. They succeeded in reversing the Hall coefficient of a material.
The Hall effect is the occurrence of a transverse electric voltage across an electric conductor passed by current flow, if this conductor is located in a magnetic field. This effect is a basic phenomenon of physics and allows to measure the strength of magnetic fields. It is the basis of magnetic speed sensors in cars or compasses in smartphones. Apart from measuring magnetic fields, the Hall effect can also be used to characterize metals and semiconductors and in particular to determine charge carrier density of the material. The sign of the measured Hall voltage allows conclusions to be drawn as to whether charge carriers in the semiconductor element carry positive or negative charge.
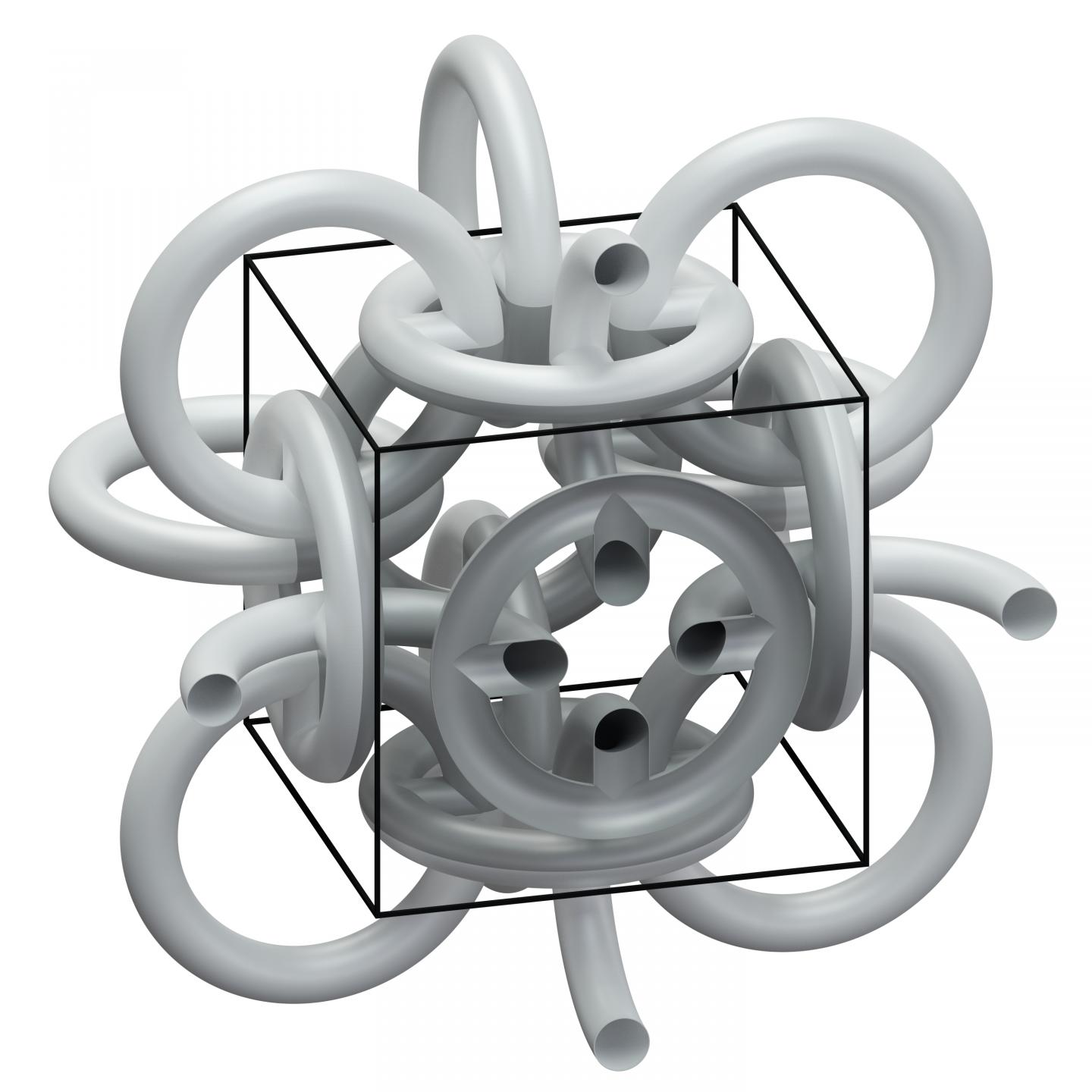
Mathematicians already predicted theoretically that it is possible to reverse the Hall coefficient of a material (such as gold or silicon), i.e. to reverse its sign. This was expected to be achieved by a three-dimensional ring structure resembling medieval mail armor. How-ever, this was considered difficult, as the ring mesh of millionths of a meter in size would have to be composed of three different components.
Christian Kern, Muamer Kadic, and Martin Wegener of KIT's Institute of Applied Physics now found that a single basic material is sufficient, provided that the ring structure chosen follows a certain geometric arrangement. First, they produced polymer scaffolds with a highest-resolution 3D printer. Then, they coated these scaffolds with semiconducting zinc oxide.
The result of the experiment: The scientists can produce meta-materials with a positive coefficient, even though their components have negative coefficients. This sounds a bit like the philosopher's stone, the formula, by means of which medieval alchemists tried to convert one substance into another. But here, no conversion takes place. "The charge carriers in the metamaterial remain negatively charged electrons," Christian Kern explains. "Hall measurements only make them appear positively charged, as the structure forces them to take detours."
Kern admits that this discovery so far is of no practical use. There are sufficient solids with both negative and positive Hall coefficients. But Kern wants to continue research. The next step will be the production of anisotropic structures with a Hall voltage in the direction of the magnetic field. Normally, Hall voltage is directed vertically to current and magnetic fields. Such unconventional materials might be applied in novel sensors for the direct measurement of magnetic field eddies.
###
For further information, please contact: Dr. Felix Mescoli, Press Officer, Phone: +49 721 608 48120, Fax: +49 721 608 43658, Email: [email protected]
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) pools its three core tasks of research, higher education, and innovation in a mission. With about 9,300 employees and 25,000 students, KIT is one of the big institutions of research and higher education in natural sciences and engineering in Europe.
KIT – The Research University in the Helmholtz Association
Since 2010, the KIT has been certified as a family-friendly university.
This press release is available on the internet at http://www.kit.edu.
Media Contact
Monika Landgraf
[email protected]
49-721-608-47414
@KITKarlsruhe
http://www.kit.edu/index.php
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag