As the main character widens his or her eyes before a securely shut door, the iris recognition system swiftly responds, swinging the door open. This scenario isn’t confined to the realm of cinema; today, numerous airports worldwide employ iris recognition sensors. This is possible thanks to the photodiode, a device that transforms light into electrical signals. However, the electron acceptor, which enhances these signals, is highly susceptible to environmental factors, impeding its commercialization.
Credit: POSTECH
As the main character widens his or her eyes before a securely shut door, the iris recognition system swiftly responds, swinging the door open. This scenario isn’t confined to the realm of cinema; today, numerous airports worldwide employ iris recognition sensors. This is possible thanks to the photodiode, a device that transforms light into electrical signals. However, the electron acceptor, which enhances these signals, is highly susceptible to environmental factors, impeding its commercialization.
Recently, a collaborative research team led by Professor Dae Sung Chung and Dr. Juhee Kim from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), Professor BongSoo Kim from the Department of Chemistry at UNIST, Professor Do Hwan Kim and Hyukmin Kweon from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Hanyang University, and Myeongjae Lee from Korea University developed a photomultiplication-type organic photodiode (PM-OPD) that operates without the need for an electron receptor. Their findings were published on July 8 (local time) in Advanced Materials, a renowned journal in the field of materials science.
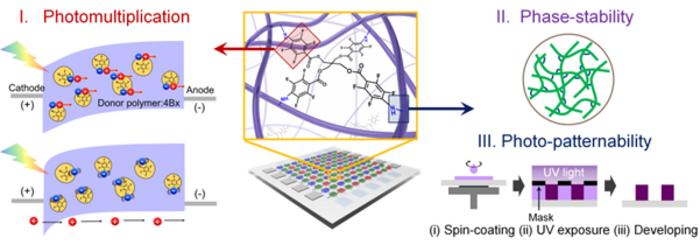
Organic photodiodes possess the capability to recognize various colors without the use of color filters, making them valuable in diverse applications such as biometric recognition technology, cameras, and optical communications. Among these, the PM-OPD stands out as an optical device that efficiently covers and amplifies visible light into electrical signals, excelling even in low-light conditions. This process hinges on the absorption of photons, resulting in the creation of electrons and holes at the interface between the electron donor and acceptor, ultimately leading to the trapping of electrons.
In this research, the research team employed a perfluoroarene-based photo-crosslinker to bolster the electrochemical stability of the device, replacing the electron acceptor. Capitalizing on the “Interfacial band bending” effect occurring between the perfluoroarene and the electron donor, the PM-OPD swiftly disassembled the exciton into discrete electrons and holes. Furthermore, these segregated electrons catalyzed the generation of additional holes within the device through the phenomenon of electron trapping, consequently enhancing the flow of current. This study is the first case that demonstrates the induction of an optical amplification phenomenon in organic photodiodes without the electron acceptor, a crucial component in conventional designs.
Subsequently, the research team achieved a milestone by fabricating an organic image sensor characterized by exceptional sensitivity, stability, and full-color capability. They accomplished this by patterning the PM-OPD in accordance with the three primary colors of light (red, green, and blue) on the sensor’s surface.
Professor Dae Sung Chung who led the research remarked, “Through this research, we have realized an organic photodiode with stability and color selectivity.” He further noted, “We anticipate that this breakthrough will greatly contribute to the future commercialization of organic image sensors.”
The research was sponsored by Samsung Future Technology Incubation Program.
Journal
Advanced Materials
DOI
10.1002/adma.202302786




