Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new chemical process which upcycles polyesters, including PET in plastic bottles, to morpholine amide, a versatile and valuable building block for synthesizing a vast range of compounds. The reaction is high yield, waste-free, does not require harmful chemicals, and is easily scalable. The team successfully break the often costly closed-loop recycling loop of plastic waste, allowing upcycling to more valuable products.
Credit: Tokyo Metropolitan University
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new chemical process which upcycles polyesters, including PET in plastic bottles, to morpholine amide, a versatile and valuable building block for synthesizing a vast range of compounds. The reaction is high yield, waste-free, does not require harmful chemicals, and is easily scalable. The team successfully break the often costly closed-loop recycling loop of plastic waste, allowing upcycling to more valuable products.
Recycling plays an indispensable part of our fight against plastic waste. But at what cost? The recycling of polyesters, for example, including polyethylene terephthalate (PET) in plastic bottles, often requires power to get the required chemical reactions hot enough, or strongly alkaline conditions which generate chemical waste. At the end of it all, we get intermediate compounds which are used to make the same products they came from. Not only can this be wasteful, it can also be economically unviable.
This is where “up”-cycling comes in. Scientists have been working to break this closed loop and create compounds from plastic waste which are more valuable and useful for society. An “open-loop” scheme like this is a vital part of practical strategies to help us transition to a greener society.
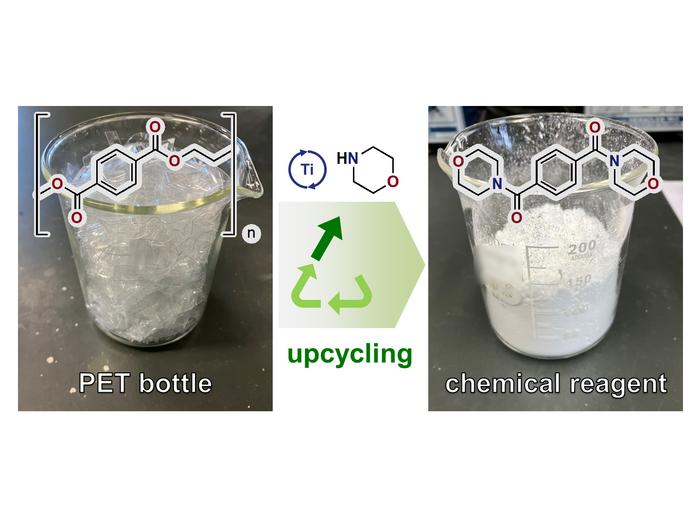
Now, a team led by Associate Professor Yohei Ogiwara and Professor Kotohiro Nomura from Tokyo Metropolitan University have come up with a virtually waste-free method of converting polyesters into a versatile building block that can be converted into a wide range of valuable chemical compounds. They used a cheap solvent called morpholine and a small amount of a titanium-based catalyst to turn polyesters into morpholine amides. Not only can they be converted into intermediate compounds for making more polyester (recycling), but they can also be easily reacted to make ketones, aldehydes, and amines, all vital families of chemicals that are used to make a vast array of other, more valuable compounds (upcycling).
The new process doesn’t require expensive reagents or harsh conditions and is virtually free of chemical waste. The yield is very high, and any unreacted solvent can be easily collected. They also found that only a small amount of catalyst was required to drive the reaction at a sensible speed, while all that is needed to separate the product is simple filtration. A key point which the team emphasize is that main reaction proceeds at normal pressure, meaning that no special reaction vessels or devices are required. This makes the reaction easily scalable, even in the lab. The team demonstrated this by taking 50g of PET material taken from an actual PET beverage bottle and reacting it with morpholine, getting more than 70 grams of morpholine amide, a yield of 90%.
As the global plastic waste problem becomes more and more acute, bold new strategies will be required to process and redeploy plastics into society. As a low-cost, waste-free, upcycling option, the team’s work may see application very soon to turn polyester waste into specialty chemicals.
This work was supported by a JST-CREST Grant, Grant Number JPMJCR21L5.
DOI
10.1021/acsorginorgau.3c00037
Article Title
Chemical Upcycling of PET into a Morpholine Amide as a Versatile Synthetic Building Block
Article Publication Date
28-Aug-2023




