This study is led by Prof. Feng Fu (Research Institute of Comprehensive Energy Industry Technology, College of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, Yan’an University). The experiments were performed by the Ni3Se4 high-efficiency bifunctional electrocatalyst with Se vacancy was used for paired electrolysis of nitrate reduction and benzylamine oxidation in anion exchange membrane electrolyzer.
Credit: ©Science China Press
This study is led by Prof. Feng Fu (Research Institute of Comprehensive Energy Industry Technology, College of Chemistry & Chemical Engineering, Yan’an University). The experiments were performed by the Ni3Se4 high-efficiency bifunctional electrocatalyst with Se vacancy was used for paired electrolysis of nitrate reduction and benzylamine oxidation in anion exchange membrane electrolyzer.
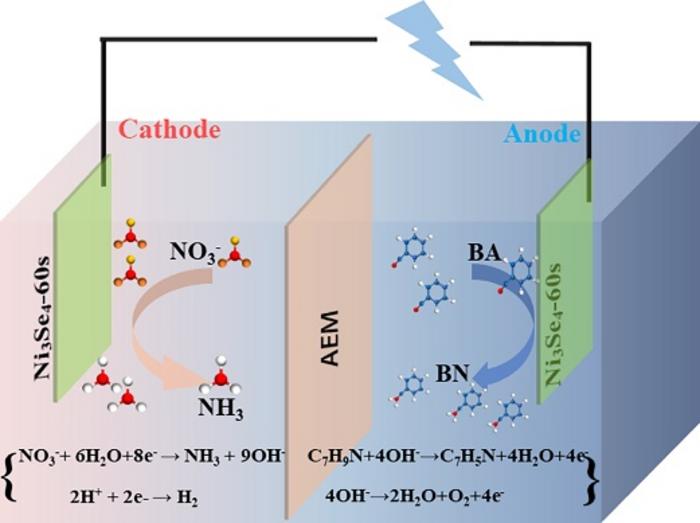
Anion exchange membrane (AEM) electrolyzers have the advantages of low cost and high electrolysis efficiency, which can be combined with renewable energy and have broad application prospects. Integrating benzylamine oxidation (BOR) into nitrate reduction (NO3RR) holds great potential for achieving significant benefits in economically paired electrolysis in AEM electrolyzers, enhancing overall electrolysis efficiency, and laying the foundation for the commercialization and large-scale industrial application of high-value organic chemicals.
The paper designs efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts, using Ni3Se4 with Se vacancies, for the paired electrolysis of NO3RR and BOR in AEM electrolyzers, yielding valuable nitrogen-containing compounds at both the cathode and anode. In the cathodic NO3RR process, the adsorption energies of reactants, products, and intermediates on the catalyst surface are regulated by vacancy engineering of the Ni3Se4 d-band center, promoting the reduction of nitrates to ammonia. At the anode, BOR is employed instead of traditional oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and the Se vacancies facilitate the adsorption of OH- ions and the formation of NiOOH, enabling efficient conversion of benzylamine to benzonitrile.
Techno-economic analysis demonstrates that paired electrolysis offers a 1.21 times lower cost and a 1.42 times higher profit compared to non-paired electrolysis, highlighting the feasibility and economic attractiveness of this approach. By applying the strategy of paired electrolysis in AEM electrolyzers, the groundwork is laid for the sustainable synthesis and industrial development of various high-value chemicals.
See the article:
Selenium vacancies regulate d-band centers in Ni3Se4 toward paired electrolysis in anion-exchange membrane electrolyzers for upgrading N-containing compounds https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-023-1636-7
Journal
Science China Chemistry
DOI
10.1007/s11426-023-1636-7




