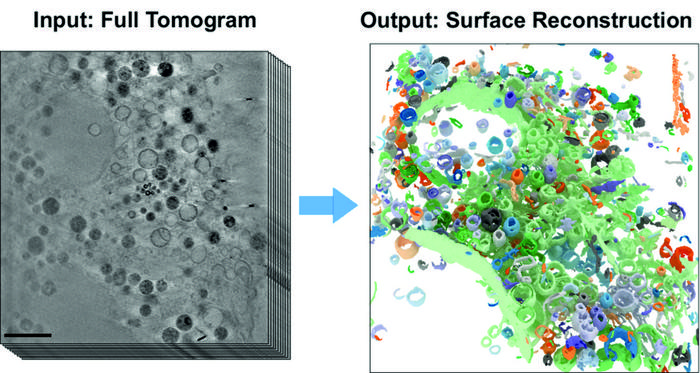
BESSY II’s high-brilliance X-rays can be used to produce microscopic images with spatial resolution down to a few tens of nanometres. Whole cell volumes can be examined without the need for complex sample preparation as in electron microscopy. Under the X-ray microscope, the tiny cell organelles with their fine structures and boundary membranes appear clear and detailed, even in three dimensions. This makes cryo x-ray tomography ideal for studying changes in cell structures caused, for example, by external triggers. Until now, however, the evaluation of 3D tomograms has required largely manual and labour-intensive data analysis. To overcome this problem, teams led by computer scientist Prof. Dr. Frank Noé and cell biologist Prof. Dr. Helge Ewers (both from Freie Universität Berlin) have now collaborated with the X-ray microscopy department at HZB. The computer science team has developed a novel, self-learning algorithm. This AI-based analysis method is based on the automated detection of subcellular structures and accelerates the quantitative analysis of 3D X-ray data sets. The 3D images of the interior of biological samples were acquired at the U41 beamline at BESSY II.
Credit: HZB
BESSY II’s high-brilliance X-rays can be used to produce microscopic images with spatial resolution down to a few tens of nanometres. Whole cell volumes can be examined without the need for complex sample preparation as in electron microscopy. Under the X-ray microscope, the tiny cell organelles with their fine structures and boundary membranes appear clear and detailed, even in three dimensions. This makes cryo x-ray tomography ideal for studying changes in cell structures caused, for example, by external triggers. Until now, however, the evaluation of 3D tomograms has required largely manual and labour-intensive data analysis. To overcome this problem, teams led by computer scientist Prof. Dr. Frank Noé and cell biologist Prof. Dr. Helge Ewers (both from Freie Universität Berlin) have now collaborated with the X-ray microscopy department at HZB. The computer science team has developed a novel, self-learning algorithm. This AI-based analysis method is based on the automated detection of subcellular structures and accelerates the quantitative analysis of 3D X-ray data sets. The 3D images of the interior of biological samples were acquired at the U41 beamline at BESSY II.
“In this study, we have now shown how well the AI-based analysis of cell volumes works, using mammalian cells from cell cultures that have so-called filopodia,” says Dr Stephan Werner, an expert in X-ray microscopy at HZB. Mammalian cells have a complex structure with many different cell organelles, each of which has to fulfil different cellular functions. Filopodia are protrusions of the cell membrane and serve in particular for cell migration. “For cryo X-ray microscopy, the cell samples are first shock-frozen, so quickly that no ice crystals form inside the cell. This leaves the cells in an almost natural state and allows us to study the structural influence of external factors inside the cell,” Werner explains.
“Our work has already aroused considerable interest among experts,” says first author Michael Dyhr from Freie Universität Berlin. The neural network correctly recognises about 70% of the existing cell features within a very short time, thus enabling a very fast evaluation of the data set. “In the future, we could use this new analysis method to investigate how cells react to environmental influences such as nanoparticles, viruses or carcinogens much faster and more reliably than before,” says Dyhr.
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI
10.1073/pnas.2209938120
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animal tissue samples
Article Title
3D surface reconstruction of cellular cryo-soft X-ray microscopy tomograms using semisupervised deep learning
Article Publication Date
5-Jun-2023
COI Statement
none




