Understanding the molecular mechanism that triggers disease is essential for identifying new treatments. Cholera, a disease caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, is no exception.
Credit: A. Canals, IRB Barcelona
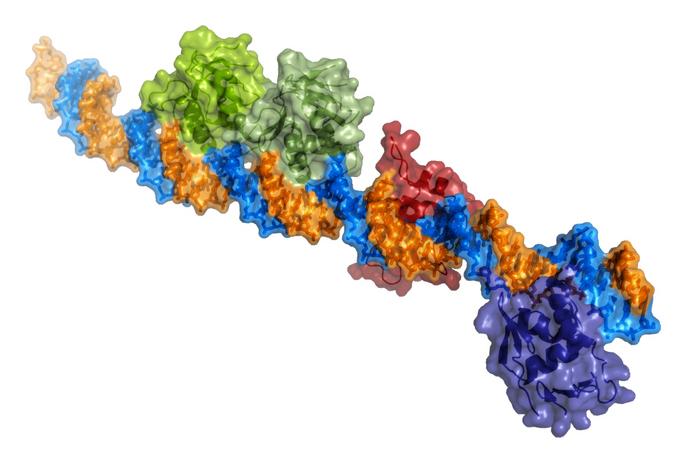
- Scientists from IRB Barcelona, CSIC, and the University of Detroit Mercy discover the atomic structure of the ToxR protein bound to DNA.
- This transcription factor regulates the virulence of the Vibrio cholerae bacterium, which causes cholera, by activating various genes.
- The study has been published in the journal PNAS.
Understanding the molecular mechanism that triggers disease is essential for identifying new treatments. Cholera, a disease caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, is no exception.
A team led by Dr. Miquel Coll at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and the Institute of Molecular Biology of Barcelona (IBMB-CSIC), in collaboration with researchers led by Dr. Eric Krukonis at the University of Detroit Mercy in the USA, has revealed the atomic structure of the ToxR protein bound to the DNA of two promoters of the genes that cause the virulence of this bacterium.
To carry out the study, the scientists used X-ray diffraction techniques, employing synchrotron radiation, as well as artificial intelligence.
“ToxR is a protein that belongs to the transcription factor family. It activates the toxT and ompU genes, causing, among other effects, the production of the cholera toxin. This toxin causes severe diarrhea and consequent dehydration, which can be fatal in a few days if left untreated,” says Dr. Coll.
This study has revealed that ToxR binds to multiple regulatory sequences in bacterial DNA, in tandem or inverted, in turn recruiting RNA polymerase, the molecular machine that transcribes genes.
“What we know is that this transmembrane transcription factor, called ToxR, receives a signal when the bacterium reaches the human intestine, as it detects bile salts. The signal is transduced, that is, it is transmitted, until it reaches the DNA inside the bacterium, thereby triggering the toxicity cascade,” explains Dr. Albert Canals, first author of the research.
“The key V. cholerae virulence gene activator ToxR has been studied for years by various laboratories, but how exactly it engages DNA has been a bit of a mystery. This study demonstrates ToxR recognizes DNA structure more than specific DNA sequences, providing some explanation for its apparent promiscuous binding to DNA and revealing insights into its role in removing repressor proteins from virulence genes that prevent expression of factors like cholera toxin until the bacterium enters the host,” observes Dr. Eric Krukonis.
The forgotten pandemic
Cholera is a diarrheal disease caused by the ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacillus Vibrio cholerae. Although eradicated in a large number of developed countries, cholera continues to be a threat to public health in countries with poor sanitary conditions and an indicator of inequality and lack of social development.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), during the 19th century, cholera spread throughout much of the world from the Ganges delta in India. This bacterium has given rise to up to six seven pandemics to date, causing the death of millions of people across all continents. We are currently experiencing the seventh pandemic of an infectious disease that is endemic in many developing countries, affecting children in particular.
In 2022, 29 countries reported cholera cases, among these Haiti, Malawi, Yemen, and Syria, which reported large epidemic outbreaks. The increase in cases worldwide has grown in recent years, becoming more numerous, more widespread, and more serious due, in large part, to climate change, which causes floods, droughts and massive migration. Armed conflicts and natural catastrophes also limit drinking water and facilitate the spread of disease. In 2023, the global resurgence of cholera has sounded the alarm in the international organizations UNICEF and WHO.
Related article:
ToxR activates the Vibrio cholerae virulence genes by tethering DNA to the membrane through versatile binding to multiple sites
Albert Canals, Simone Pieretti, Mireia Muriel-Masanes, Nour El Yaman, Sarah C. Plecha, Joshua J. Thomson, Montserrat Fàbrega-Ferrer, Rosa Pérez-Luque, Eric S. Krukonis, and Miquel Coll
PNAS (2022) DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2304378120
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI
10.1073/pnas.2304378120
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
ToxR activates the Vibrio cholerae virulence genes by tethering DNA to the membrane through versatile binding to multiple sites
Article Publication Date
10-Jul-2023




