Plant roots play a critical role in taking up, selecting, enriching and retaining a range of different mineral elements thereby supplying distant plant tissues with nutrients while sequestering excessive amounts of metals. To execute such element-specific functions, a range of ion transporters present at roots mediate the uptake, efflux and intracellular compartmentalization of different mineral elements. Most ion transporters show characteristic tissue and cell type-specific localization patterns, which can be altered in response to internal signalling or external cues. To fully understand the role of the multitude ion transporters and transport pathways acting in roots, it is necessary to determine their contribution to element distribution in cells and tissues.
Credit: IPK Leibniz Institute
Plant roots play a critical role in taking up, selecting, enriching and retaining a range of different mineral elements thereby supplying distant plant tissues with nutrients while sequestering excessive amounts of metals. To execute such element-specific functions, a range of ion transporters present at roots mediate the uptake, efflux and intracellular compartmentalization of different mineral elements. Most ion transporters show characteristic tissue and cell type-specific localization patterns, which can be altered in response to internal signalling or external cues. To fully understand the role of the multitude ion transporters and transport pathways acting in roots, it is necessary to determine their contribution to element distribution in cells and tissues.
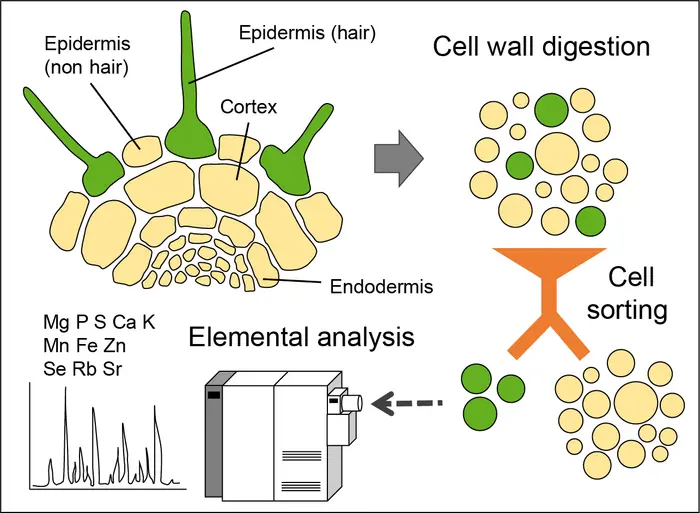
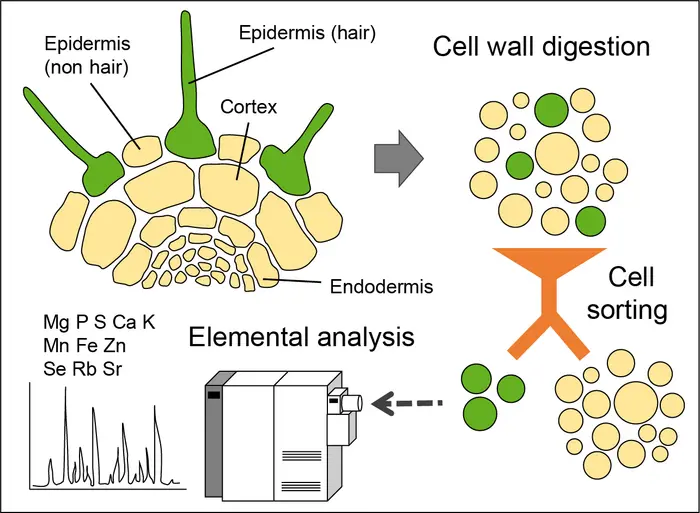
The best method for simultaneous quantification of multiple elements is inductively couple plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). However, ICP-MS is still largely restricted to the analysis of whole-tissues instead of single tissues or specific cell types. Overcoming this limitation would allow to simultaneously map the distribution of several mineral elements along different root cell layers, a critical step to fully understand how roots protect highly sensitive stem cells from toxic elements but share essential and beneficial elements with aboveground parts.
“With this in mind, we developed a method in which distinct cell types isolated from roots of various reporter lines are separated via fluorescence-activated cell sorting prior to elemental analysis with ICP-MS”, says Dr. Ricardo Giehl, first author of the study. “Our new method enabled us to determine the concentration of up to 11 mineral elements in different cell types, and to explore the consequences of perturbed xylem loading or altered nutrient availabilities at high spatial resolution.”
The researchers used the new FACS-ICP-MS method to reveal significant cell type-specific element distribution and the existence of a steep concentration gradient between outer and inner cell layers in roots. “Furthermore, the cellular concentration ranges for most macro- and micronutrients estimated with our method can serve as reference for future studies”, emphasises Prof. Dr. Nicolaus von Wirén, head of IPK’s research department “Physiology and Cell Biology”.
The method also helped the researchers to identify a cell type-specific enrichment of manganese in roots of plants exposed to iron-limiting conditions. By installing a manganese sequestration mechanism in specific cell types, the researchers uncovered that root hairs play a critical role in retaining the excess manganese taken up by iron-deficient plants, thereby preventing that toxic concentrations of manganese build up in shoots.
“Our results highlight the importance of the particular “topographical” placement of ion transporters for directing radial movement of ions destined to shoots or for efficient metal sequestration in roots”, says Dr. Ricardo Giehl. “The possibility to combine our method with transcriptomics and to develop it further toward single cell ICP-MS offers the possibility to investigate transcriptome-ionome networks at very high spatial resolution. This knowledge is critical to understand and manipulate transport pathways in order to increase nutrient use efficiency while simultaneously preventing accumulation of toxic elements in aboveground tissues.”
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-023-38880-0
Article Title
Cell type-specific mapping of ion distribution in Arabidopsis thaliana roots
Article Publication Date
13-Jun-2023