“Determining the mechanism underlying RNA sequestration in [stress granules] […] could represent a key goal in the discovery and development of suitable [Alzheimer’s disease] biomarkers and therapies.”
Credit: 2023 Sato et al.
“Determining the mechanism underlying RNA sequestration in [stress granules] […] could represent a key goal in the discovery and development of suitable [Alzheimer’s disease] biomarkers and therapies.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 1, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 10, entitled, “Stress granules sequester Alzheimer’s disease-associated gene transcripts and regulate disease-related neuronal proteostasis.”
Environmental and physiological stresses can accelerate Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathogenesis. Under stress, a cytoplasmic membraneless structure termed a stress granule (SG) is formed and is associated with various neurodegenerative disorders, including AD. SGs contain translationally arrested mRNAs, suggesting that impaired RNA metabolism in neurons causes AD progression; however, the underlying mechanism remains unclear.
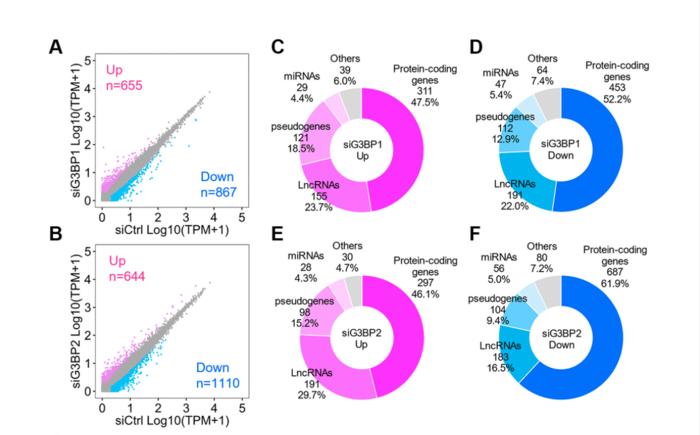
In this new study, researchers Kaoru Sato, Ken-ichi Takayama and Satoshi Inoue from Tokyo Metropolitan Institute for Geriatrics and Gerontology identified numerous mRNAs and long non-coding RNAs that are directly targeted by the SG core proteins G3BP1 and G3BP2.
“In this study, we conducted a genome-wide investigation of the G3BP1- and G3BP2-bound RNAs using enhanced cross-linking and immunoprecipitation-sequencing (eCLIP-seq) in the human neuroblastoma (NB) cell line SH-SY5Y.”
G3BP1 and G3BP2 redundantly target RNAs before and after stress conditions. The researchers further identified RNAs within SGs, wherein AD-associated gene transcripts accumulated, suggesting that SGs can directly regulate AD development. Furthermore, gene-network analysis revealed a possible link between the sequestration of RNAs by SGs and the impairment of protein neurohomeostasis in AD brains.
“Together, our study provides a comprehensive RNA regulatory mechanism involving SGs, which could be targeted therapeutically to slow AD progression mediated by SGs.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204737
Corresponding Author: Satoshi Inoue – [email protected]
Keywords: stress granule, RNP granule, eCLIP-seq, G3BP, Alzheimer’s disease
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204737
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
- SoundCloud
- YouTube
- LabTube
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
Journal
Aging-US
DOI
10.18632/aging.204737
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Stress granules sequester Alzheimer’s disease-associated gene transcripts and regulate disease-related neuronal proteostasis
Article Publication Date
22-May-2023




