UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A Penn State-led team of researchers has literally put pencil to paper to create an accessible, affordable, waterproof and wearable sensor to monitor multiple vital signals. The team published the details of the pencil-on-paper sensor in Chemical Engineering Journal.
Credit: Huanyu “Larry” Cheng
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A Penn State-led team of researchers has literally put pencil to paper to create an accessible, affordable, waterproof and wearable sensor to monitor multiple vital signals. The team published the details of the pencil-on-paper sensor in Chemical Engineering Journal.
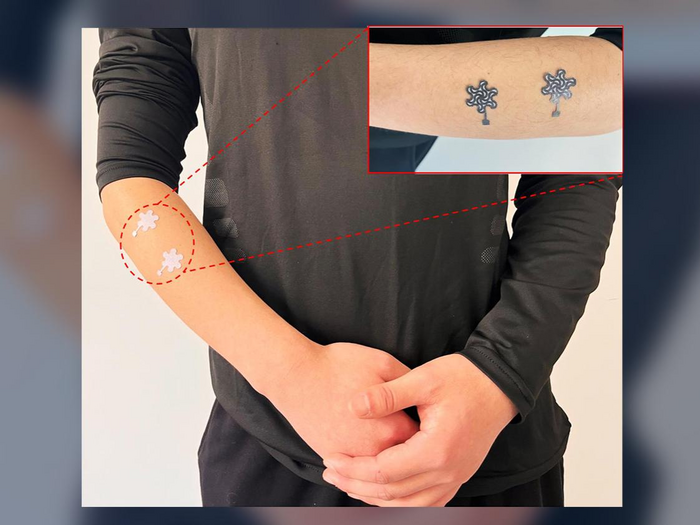
The team had previously designed a pencil-on-paper sensor that could be used in “smart diapers” to detect wetness. That sensor, however, was not hydrophobic, so while it was useful in detecting moisture, it could not be used to accurately monitor other health variables where moisture might interfere with the sensing and the results.
“In this case, we are looking to measure gas molecules, temperature and electrical physiological signals,” said co-corresponding author Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, James L. Henderson Jr. Memorial Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics at Penn State. “If we get interference from the moisture or rapid humidity, the signal and mechanical robustness will be compromised. That’s why we designed a superhydrophobic coating, making the sensor practically waterproof.”
The researchers used a silica hydrophobic coating, which had been used for other sensors, but never for the pencil-on-paper sensors. These sensors were also designed to be stretchable, making it possible to wear on the skin.
“With this sensor, you don’t need bulky equipment,” said co-corresponding author Li Yang, formerly a visiting scholar in the Penn State Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics and now of the School of Health Sciences and Biomedical Engineering at Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, China. “We use low-cost manufacturing approaches to make them accessible. The sensor is made of graphite material exfoliated from a pencil. So, the pencil material is really the sensing material because it’s a conducting material.”
In addition to capturing temperature and gas molecules, the sensors could capture electrical physiological action to monitor muscular motion, cardiovascular activity and brain signals. The researchers said that the device has the potential not just for sensing but also for stimulation — for example, the sensor could administer thermal therapy by sending a current to the skin.
Cheng said that the sensor’s affordability, accessibility and versatility — in terms of the scope of vital signs it could measure — may make it useful for public health applications, instead of solely individual health purposes.
“In general, we are interested in the population health,” Cheng said. “So, with this low-cost manufacturing process and sensor accessibility, we are hoping we can provide this to a really large population, and then collect information about the variation between individuals to be able to establish a baseline, according to the patient population in different geographic locations or in different populations.”
The other authors on the paper are Ankan Dutta, doctoral student in the Penn State Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics; and Ye Xue, Zihan Wang, Xue Chen, Peng Gao, Runze Li, Jiayi Yan, Guangyu Niu, Ya Wang, Shuajie Du and Li Yang, all of Hebei University of Technology in Yianjin, China.
Cheng is also affiliated with the Materials Research Institute; the Institutes of Energy and the Environment; the Institute for Computational and Data Sciences; the Engineering, Energy, and Environmental Institute; and the Sustainability Institute, all at Penn State.
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation and the Center for Human Evolution and Diversity at Penn State, as well as the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key Research and Development Project of Hebei Province and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation’s Project.
Journal
Chemical Engineering Journal
DOI
10.1016/j.cej.2023.142774
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Superhydrophobic, stretchable kirigami pencil-on-paper multifunctional device platform
Article Publication Date
12-Apr-2023




