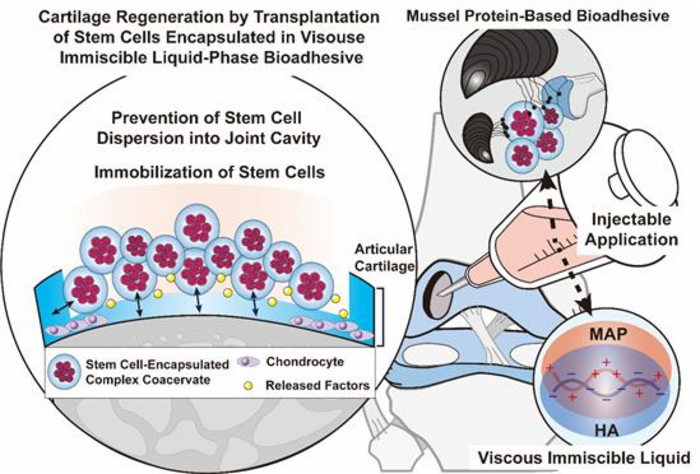
Cartilage is a tissue that protects bones by providing shock absorption and facilitates smooth joint movement. Unfortunately, due to its limited intrinsic healing capacity, stem cell transplantation is a promising therapeutic approach to address cartilage inflammation and damage, as well as to promote cartilage regeneration. However, a major limitation of this technique is the rapid disappearance of transplanted stem cells from the smooth cartilage surface and fluidic environment around cartilage, resulting in less effective treatment outcomes. Recently, a joint team of researchers from POSTECH, Dongguk University Medical Center, and Nature Gluetech in Korea has developed a novel treatment strategy for damaged cartilage, involving the use of a viscous immiscible liquid that is capable of facilitating the transplantation of stem cells into affected tissue by means of adhesive protein derived from mussels and hyaluronic acid.
Credit: POSTECH
Cartilage is a tissue that protects bones by providing shock absorption and facilitates smooth joint movement. Unfortunately, due to its limited intrinsic healing capacity, stem cell transplantation is a promising therapeutic approach to address cartilage inflammation and damage, as well as to promote cartilage regeneration. However, a major limitation of this technique is the rapid disappearance of transplanted stem cells from the smooth cartilage surface and fluidic environment around cartilage, resulting in less effective treatment outcomes. Recently, a joint team of researchers from POSTECH, Dongguk University Medical Center, and Nature Gluetech in Korea has developed a novel treatment strategy for damaged cartilage, involving the use of a viscous immiscible liquid that is capable of facilitating the transplantation of stem cells into affected tissue by means of adhesive protein derived from mussels and hyaluronic acid.
The joint team was led by Professor Hyung Joon Cha (Department of Chemical Engineering and School of Convergence Science & Technology), Ph.D. candidate Seong-Woo Maeng, Dr. Tae Yoon Park, and Professor Kye Il Joo (currently, at Ewha Womans University) from the Department of Chemical Engineering at POSTECH, Professor Gun-Il Im and Dr. Ji-Yun Ko from Dongguk University Medical Center, and Dr. Seongmin Ha from Nature Gluetech Co., Ltd. The research, supported by the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through Korea Health Industry Development under the Ministry of Health and Welfare, has been published in the Chemical Engineering Journal, a highly esteemed journal in the field of chemical engineering.
The researchers developed a novel bioadhesive material in the form of a viscous immiscible liquid phase to overcome the limitations of the conventional treatment strategy. This was achieved by combining adhesion protein derived from mussels with high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, which exhibits opposing charges and thus facilitates electrostatic interactions between them. By engineering a highly viscous liquid bioadhesive that does not disintegrate or swell in water, the team formulated an adhesive material that can securely encapsulate stem cells and facilitate their firm attachment to the transplantation site.
In addition, the team demonstrated that stem cells encapsulated within the liquid bioadhesive were retained in situ when transplanted into defective cartilage in a rabbit model evaluation. The prolonged retention of transplanted stem cells within damaged cartilage facilitated cartilage regeneration and enhanced the therapeutic effects of stem cell transplantation. An additional benefit of the adhesive liquid developed by the team includes a natural adhesive that does not require any additional physical or chemical processes.
Professor Hyung Joon Cha who led the research stated, “The therapeutic effects of stem cells can be significantly enhanced by using mussel adhesion protein, an original biomaterial developed in Korea.” He also noted that “Because the liquid bioadhesive can be formulated for injection, it has the potential to be an effective treatment for damaged cartilage when used in stem cell transplantation via an arthroscope, similar to an endoscope.”
The material technology for mussel adhesion protein has been transferred to Nature Gluetech Co., Ltd. and a clinical study of the stem cell adhesive named CartiFix, which was developed for arthritis treatment in this research, is expected to begin soon.
Journal
Chemical Engineering Journal
DOI
10.1016/j.cej.2023.142379
Article Title
Adipose stem cell transplantation using adhesive protein-based viscous immiscible liquid for cartilage reconstruction
Article Publication Date
15-Mar-2023




