Scientists from the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have made a major breakthrough in the study of ice by confirming the formation of pure-phase cubic ice at low-temperature interfaces.
Credit: Institute of Physics
Scientists from the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have made a major breakthrough in the study of ice by confirming the formation of pure-phase cubic ice at low-temperature interfaces.
The findings, published in Nature on Mar. 29, have significant implications for a wide range of fields, from materials science to climate science.
Ice is a common substance that exists in a variety of forms, depending on the conditions under which it forms. The most common form of ice, known as ice Ih, has a hexagonal lattice structure, but under certain conditions, ice can form other structures, with 20 different forms found so far.
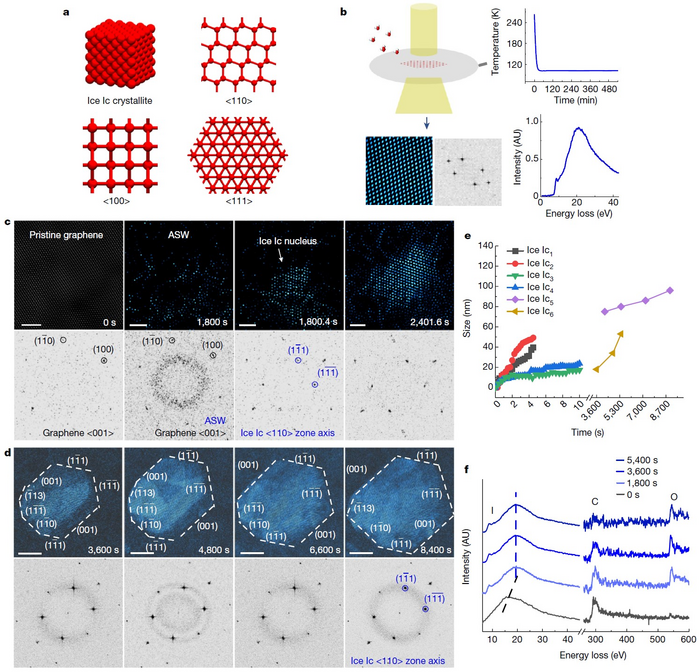
In the case of cubic ice, known as ice Ic, a hundred years ago it was thought to be responsible for a particular type of halo around the Sun or Moon. In fact, the question of whether cubic ice really exists has long been controversial, as it has been difficult to perfectly detect pure-phase ice Ic in a large number of experiments.
In this study, the researchers used in-situ cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging and water vapor deposition on graphene to follow the formation of ice crystallites in real time at molecular resolution.
They found that the resulting ice was pure-phase ice I, with a majority being single crystalline ice Ic and a small amount ice Ih. The preferential nucleation of ice Ic on low-temperature substrates was demonstrated. The polymorphic diversity of ice may well explain why pure-phase ice has not previously been found by diffraction methods.
The cubic ice controversy has thus been resolved on the basis of direct and real-space imaging by in-situ cryogenic TEM. This achievement will contribute greatly to the development of both microscopy and ice physics.
This fundamental advance has important implications for our understanding of ice formation behavior under different conditions, which has broad applications in fields such as materials science, geology, and climate science.
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation, the Ministry of Science and Technology of China, and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of CAS.
Journal
Nature
DOI
10.1038/s41586-023-05864-5
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Tracking cubic ice at molecular resolution
Article Publication Date
29-Mar-2023




