Enzymes work in the cells of all living organisms, allowing specific and complex reactions to be carried out quite easily. However, few natural enzymes are effective for industrial applications, which could benefit greatly from discoveries that make targeted enzyme creation a reality.
Credit: Nobutaka Fujieda, Osaka Metropolitan University
Enzymes work in the cells of all living organisms, allowing specific and complex reactions to be carried out quite easily. However, few natural enzymes are effective for industrial applications, which could benefit greatly from discoveries that make targeted enzyme creation a reality.
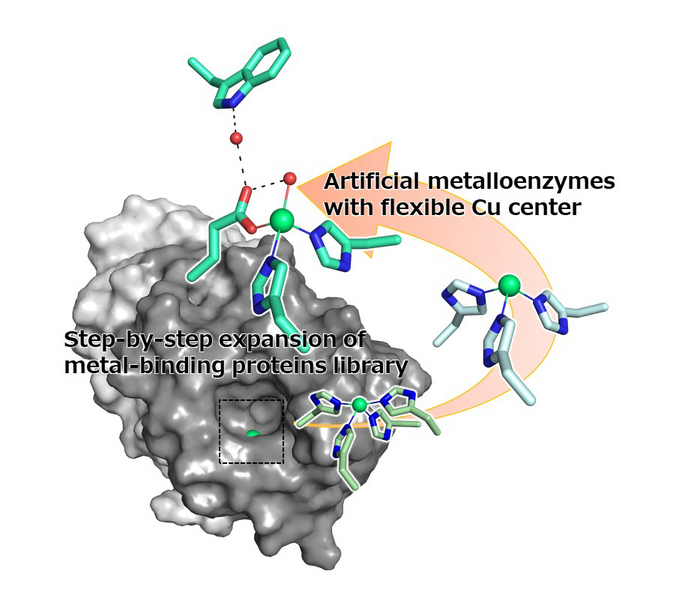
Artificial metalloenzymes can be created simply by binding metal ions or metallic compounds to proteins, so that they exhibit enzymatic activity. Currently, metalloenzymes are being studied to discover new functions or improve their reactivity when compared to natural enzymes. Nevertheless, the reaction mechanisms of metalloenzymes are still largely unknown, making it very difficult to design artificial enzymes for specific functions or improved efficiency.
A research group led by Professor Nobutaka Fujieda, Graduate School of Agriculture, Osaka Metropolitan University, has been creating artificial metalloenzymes using small heat-resistant metal-binding proteins. In their latest study, they describe an artificial metalloenzyme they created simply, making use of the 2-his-1-carboxylate metal-binding motif, which is commonly found naturally in non-heme metalloenzymes.
Their new artificial metalloenzyme has a metal-binding site composed of four amino acids, which originally were histidines. The research group mutated these amino acids to create a library of 12 slightly different proteins to compare. After screening the library, they found that the enzyme variant H52A/H58E, when bound with a copper ion, had the best stereoselectivity, so that it reacts selectively with the correct version of the target molecule.
The research group then performed X-ray crystallographic analysis of the metal-binding site, confirming two electron densities derived from the copper ions. Furthermore, docking simulations of two copper ions found that the copper, which protruded slightly, could bind to the substrate. Leading the group to believe that selectivity was maximized by the movement of the copper ion to where the substrate was most likely to bind.
“Such positional transitions of metal ions have also been observed in natural enzymes, so we believe that detailed analysis of our artificial metalloenzyme’s reaction mechanism will deepen what we know about natural enzymes. We hope that the advances of this research will lead to the creation of biocatalysts that can work under mild conditions,” Professor Fujieda concluded.
The research results were published in Chemical Science on March 13, 2023.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established in April 2022, formed by merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University. For more research news visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.
Journal
Chemical Science
DOI
10.1039/D2SC06809E
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
An artificial metallolyase with pliable 2-his-1-carboxylate facial triad for stereoselective Michael addition
Article Publication Date
13-Mar-2023




