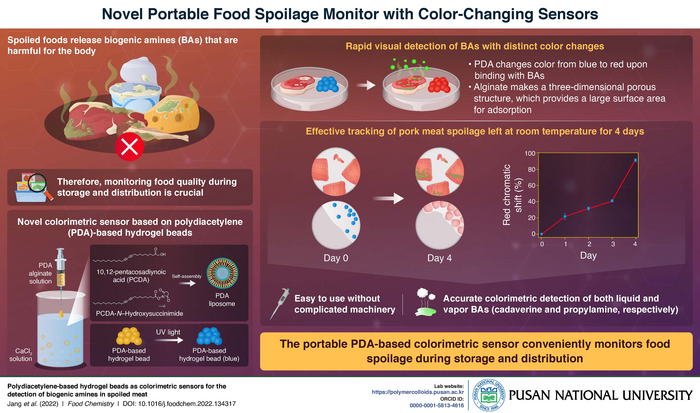
When foods like fish, meat, and cheese decompose, they release a variety of low molecular weight organic nitrogen compounds known as biogenic amines (BAs). While the body uses BAs in small amounts in processes like hormone synthesis, ingesting large amounts of BAs from spoiled food can cause serious health problems. Therefore, it is important to detect BAs during food storage and distribution. This motivated a team of researchers, including Prof. Sungbaek Seo, Associate Professor of Biomaterials Science at Pusan National University, to develop a portable molecular sensor that quickly detects the presence of BAs by changing colors. “The rapid and easy monitoring of deleterious BAs released from spoiled foods could alert us, prevent consumption of spoiled meat, maintain food quality, and establish further effective food storage and distribution conditions in the logistic chain”, notes Prof. Seo.
Credit: Sungbaek Seo from Pusan National University
When foods like fish, meat, and cheese decompose, they release a variety of low molecular weight organic nitrogen compounds known as biogenic amines (BAs). While the body uses BAs in small amounts in processes like hormone synthesis, ingesting large amounts of BAs from spoiled food can cause serious health problems. Therefore, it is important to detect BAs during food storage and distribution. This motivated a team of researchers, including Prof. Sungbaek Seo, Associate Professor of Biomaterials Science at Pusan National University, to develop a portable molecular sensor that quickly detects the presence of BAs by changing colors. “The rapid and easy monitoring of deleterious BAs released from spoiled foods could alert us, prevent consumption of spoiled meat, maintain food quality, and establish further effective food storage and distribution conditions in the logistic chain”, notes Prof. Seo.
The researchers have detailed this novel development in a recent article published in Food Chemistry. This paper was made available online on 20 September 2022 and was published in Volume 403, Issue 1 of the journal in March 2023. The team combined the distinct color-changing property of polydiacetylene (PDA)-based hydrogel beads upon binding with BAs with an alginate solution that rendered a three-dimensional porous structure with a large surface area to fabricate this novel sensor. The researchers demonstrated that the developed sensor beads easily detect biogenic amines like cadaverine and propylamine both in solution and vapor forms via distinct changes in color from blue to red. The team further put the sensor to test the spoilage of pork meat samples left at room temperature across 4 days. They showed that the sensor beads could efficiently track the gradual spoilage over time by showing a distinct shift in the shade of color.
The sensor is made of portable, light-weight beads and does not require complicated analytical equipment or skilled personnel. It offers rapid and seamless visual detection via colorimetric change in the beads from blue to red. As Prof. Seo observes, “The portable beads could be utilized on sites for monitoring whether the food quality is okay during storage and logistic chain. Further, the beads could be applied in evaluating whether ideal food storage and distribution conditions are well-preserved”.
Taken together, this portable PDA-based colorimetric sensor would facilitate the seamless monitoring of food spoilage during storage and distribution, and prevent health hazards arising from the ingestion of BAs.
***
Reference
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134317
Authors: Soojin Jang 1,2, Seong Uk Son 1,2, Junseok Kim 3, Hyungjun Kim 3, Jaewoo Lim 1,2, Seung Beom Seo 1,4, Byunghoon Kang 1, Taejoon Kang 1,5, Juyeon Jung 1,5, Sungbaek Seo 6, Eun-Kyung Lim 1,2,5
Affiliations:
1 Bionanotechnology Research Center, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Daejeon 34141, Republic of Korea
2 Department of Nanobiotechnology, KRIBB School of Biotechnology, UST, Daejeon 34113, Republic of Korea
3 Department of Chemistry and Research Institute of Basic Sciences, Incheon National University, Incheon 22012, Republic of Korea
4 Department of Cogno-Mechatronics Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Republic of Korea
5 School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon 16419, Republic of Korea 6 Department of Biomaterials Science (BK21 FOUR Program), College of Natural Resources and Life Science/Life and Industry Convergence Research Institute, Pusan National University, Miryang 50463, Republic of Korea
*Corresponding author’s email: [email protected] , [email protected]
About Pusan National University
Pusan National University, located in Busan, South Korea, was founded in 1946, and is now the no. 1 national university of South Korea in research and educational competency. The multi-campus university also has other smaller campuses in Yangsan, Miryang, and Ami. The university prides itself on the principles of truth, freedom, and service, and has approximately 30,000 students, 1200 professors, and 750 faculty members. The university is composed of 14 colleges (schools) and one independent division, with 103 departments in all.
Website: https://www.pusan.ac.kr/eng/Main.do
About the author
Prof. Sungbaek Seo is an Associate Professor of Biomaterials Science at Pusan National University. His group is developing surface adhesive and functional biomaterials (drug delivery systems, tissue adhesives, biosensors, and eco-friendly coatings/surfactants) using polymers and colloidal particles. He wants to realize functional materials by using unique functions that can be found from biological systems and natural ecosystems. Before coming to Pusan National University, he completed the Postdoctoral training at Craig Hawker’s lab at University of California, Santa Barbara. In 2014, Prof. Seo received a PhD in Macromolecular Science and Engineering from University of Michigan.
Lab website address: https://polymercolloids.pusan.ac.kr
ORCID ID: 0000-0001-5813-4616
Journal
Food Chemistry
DOI
10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134317
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Polydiacetylene-based hydrogel beads as colorimetric sensors for the detection of biogenic amines in spoiled meat
Article Publication Date
1-Mar-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.




