Dibaryons are the subatomic particles made of two baryons. Their formations through baryon-baryon interactions play a fundamental role in big-bang nucleosynthesis, in nuclear reactions including those within stellar environments, and provide a connection between nuclear physics, cosmology and astrophysics. Interestingly, the strong force, which is the key to the existence of nuclei and provides most of their masses, allows formations of numerous other dibaryons with various combinations of quarks. However, we do not observe them abound — deuteron is the only known stable dibaryon.
Credit: Nilmani Mathur
Dibaryons are the subatomic particles made of two baryons. Their formations through baryon-baryon interactions play a fundamental role in big-bang nucleosynthesis, in nuclear reactions including those within stellar environments, and provide a connection between nuclear physics, cosmology and astrophysics. Interestingly, the strong force, which is the key to the existence of nuclei and provides most of their masses, allows formations of numerous other dibaryons with various combinations of quarks. However, we do not observe them abound — deuteron is the only known stable dibaryon.
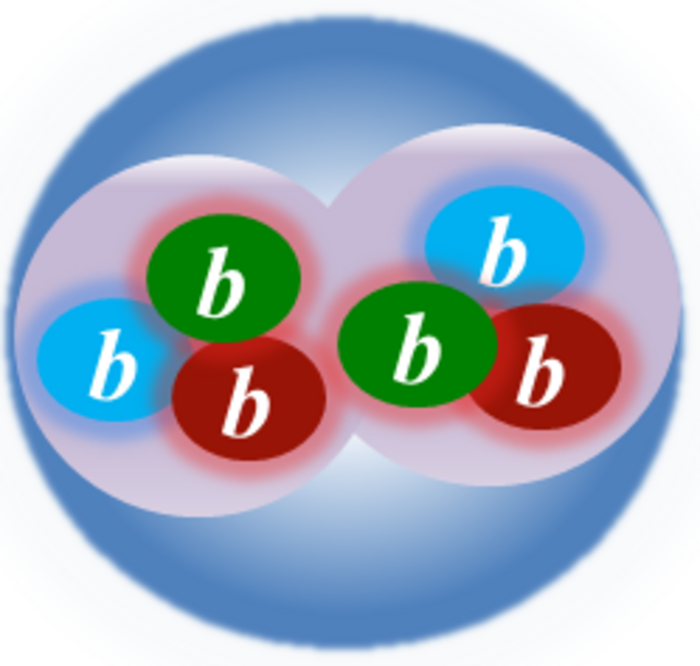
To resolve this apparent dichotomy, it is essential to investigate dibaryons and baryon-baryon interactions at the fundamental level of strong interactions. In a recent publication in Physical Review Letters, physicists from the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) and The Institute of Mathematical Science (IMSc) have provided strong evidence for the existence of a deeply bound dibaryon, entirely built from bottom (beauty) quarks. Using the computational facility of the Indian Lattice Gauge Theory Initiative (ILGTI), Prof. Nilmani Mathur and graduate student Debsubhra Chakraborty from the Department of Theoretical Physics, TIFR, and Dr. M. Padmanath from IMSc have predicted the existence of this subatomic particle. The predicted dibaryon (D6b) is made of two triply bottom Omega (Ωbbb) baryons, having the maximal beauty flavor. Its binding energy is predicted to be as large as 40-times stronger than that of the deuteron, and hence perhaps entitled it to be the most strongly bound beautiful dibaryon in our visible universe. This finding elucidates the intriguing features of strong forces in baryon-baryon interactions and leads the path for further systematic study of quark mass dependence of baryon-baryon interactions which possibly can explain the emergence of bindings in nuclei. It also brings motivation to search for such heavier exotic subatomic particles in next-generation experiments.
Since the strong-force is highly non-perturbative in the low energy domain, there is no first-principles analytical solution as yet for studying the structures and interactions of composite subatomic particles like protons, neutrons and the nuclei they form. Formulation of quantum chromodynamics (QCD) on space-time lattices, based on an intricate amalgamation between a fundamental theory and high-performance computing, provides an opportunity for such study. Not only does it require a sophisticated understanding of the quantum field-theoretic issues, but the availability of large-scale computational resources is also crucial. In fact, some of the largest scientific computational resources in the world are being utilized by lattice gauge theorists who are trying to solve the mystery of strong interactions of our Universe through their investigations inside the femto-world (within a scale of about one million-billionth of a meter). Lattice QCD calculations can also play a crucial role in understanding the nuclei formation at the Big Bang, their reaction mechanisms, in aiding the search for the physics beyond the standard model as well as for investigating the matter under the extreme conditions of high temperature and density similar to those at the early stages of the Universe after the Big Bang.
Journal
Physical Review Letters
DOI
10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.111901




