Decline in the hypothalamic Menin may play a key role in aging, according to a new study publishing March 16th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Lige Leng of Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, and colleagues. The findings reveal a previously unknown driver of physiological aging, and suggest that supplementation with a simple amino acid may mitigate some age-related changes.
Credit: Lige Leng, Ziqi Yuan and Jie Zhang, 2023, PLOS Biology, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Decline in the hypothalamic Menin may play a key role in aging, according to a new study publishing March 16th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Lige Leng of Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, and colleagues. The findings reveal a previously unknown driver of physiological aging, and suggest that supplementation with a simple amino acid may mitigate some age-related changes.
The hypothalamus has been recognized as a key mediator of physiological aging, through an increase in the process of neuroinflammatory signaling over time. In turn, inflammation promotes multiple age-related processes, both in the brain and the periphery.
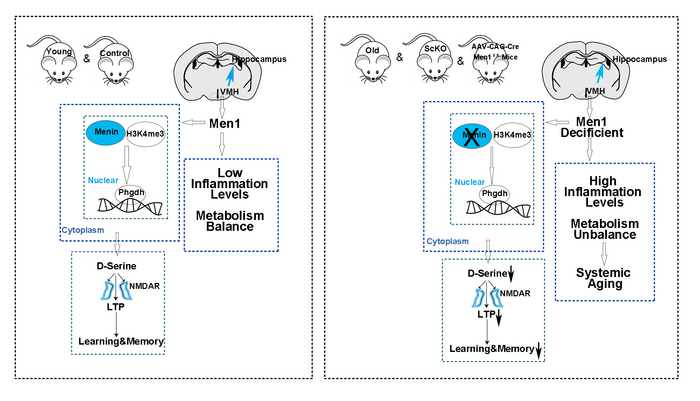
Recently, Leng and colleagues showed that Menin, a hypothalamic protein, is a key inhibitor of hypothalamic neuroinflammation, leading them to ask what role Menin may play in aging. Here, they observed that the level of Menin in the hypothalamus, but not astrocytes or microglia, declines with age. To explore this decline, they created conditional knockout mice, in which Menin activity could be inhibited. They found that reduction of Menin in younger mice led to an increase in hypothalamic neuroinflammation, aging-related phenotypes including reductions in bone mass and skin thickness, cognitive decline, and modestly reduced lifespan.
Another change induced by loss of Menin was a decline in levels of the amino acid D-serine, known to be a neurotransmitter and sometimes used as a dietary supplement found in soybeans, eggs, fish and nuts. The authors showed this decline was due to loss of activity of an enzyme involved in its synthesis (which was in turn regulated by Menin).
Could reversing age-related Menin loss reverse signs of physiological aging? To test that, the authors delivered the gene for Menin into the hypothalamus of elderly (20-month-old) mice. Thirty days later, they found improved skin thickness and bone mass, along with better learning, cognition, and balance, which correlated with an increase in D-serine within the hippocampus, a central brain region important for learning and memory. Remarkably, similar benefits on cognition, though not on the peripheral signs of aging, could be induced by three weeks of dietary supplementation with D-serine.
There is much left to be learned about Menin’s role in aging, including the upstream processes that lead to its decline, and there is much to learn about the potential for exploiting this pathway, including how much phenotypic aging can be slowed, and for how long, and whether supplementation with D-serine may trigger other changes, yet to be discovered.
Nonetheless, Leng said, “We speculate that the decline of Menin expression in the hypothalamus with age may be one of the driving factors of aging, and Menin may be the key protein connecting the genetic, inflammatory, and metabolic factors of aging. D-serine is a potentially promising therapeutic for cognitive decline.”
Leng adds, “Ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) Menin signaling diminished in aged mice, which contributes to systemic aging phenotypes and cognitive deficits. The effects of Menin on aging are mediated by neuroinflammatory changes and metabolic pathway signaling, accompanied by serine deficiency in VMH, while restoration of Menin in VMH reversed aging-related phenotypes.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002033
Citation: Leng L, Yuan Z, Su X, Chen Z, Yang S, Chen M, et al. (2023) Hypothalamic Menin regulates systemic aging and cognitive decline. PLoS Biol 21(3): e3002033. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002033
Author Countries: China, United States of America
Funding: see manuscript
Journal
PLoS Biology
DOI
10.1371/journal.pbio.3002033
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
COI Statement
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.




