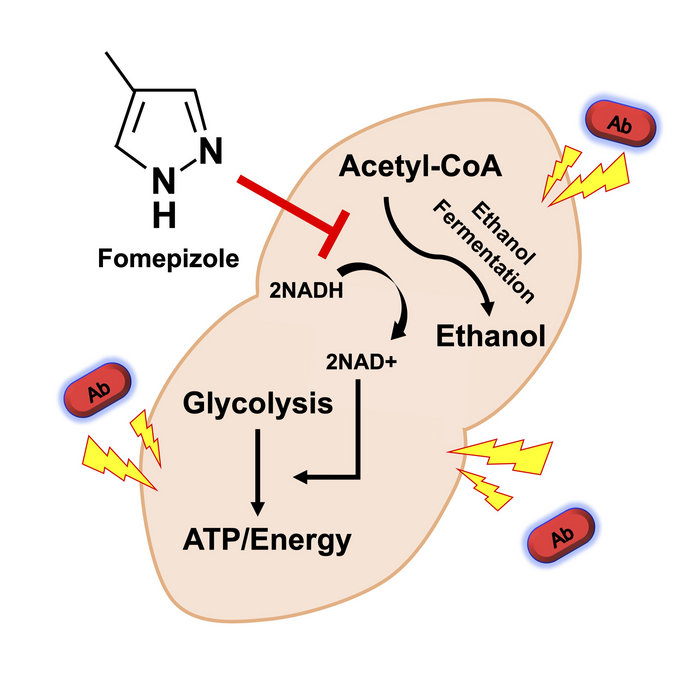
Pneumococcal disease leads to over three million hospitalizations and hundreds of thousands of deaths annually. A study publishing March 16th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Carlos J. Orihuela at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Alabama, United States, and colleagues suggests that the FDA-approved drug Fomepizole may reduce disease severity in the lungs of mice with some forms of bacterial pneumonia and enhance the efficacy of the antibiotic erythromycin as well.
Credit: Carlos J. Orihuela (CC-BY 4.0, https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
Pneumococcal disease leads to over three million hospitalizations and hundreds of thousands of deaths annually. A study publishing March 16th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Carlos J. Orihuela at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Alabama, United States, and colleagues suggests that the FDA-approved drug Fomepizole may reduce disease severity in the lungs of mice with some forms of bacterial pneumonia and enhance the efficacy of the antibiotic erythromycin as well.
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the leading cause of community-acquired pneumonia. While vaccines to protect against the bacteria are available, these vaccines are not effective against all strains, with some versions being especially problematic as they are multidrug-resistant. Currently, there are very limited treatment options for combating multidrug-resistant S. pneumoniae infections.
In order to test the effects of novel treatments for antibiotic-resistant S. pneumoniae, the researchers conducted a series of experiments with mice. Fomepizole is an FDA-approved drug normally used as an antidote for the ingestion of toxic alcohols (such as methanol or ethylene glycol), and works by inhibiting the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase. Researchers inoculated mice with a multidrug-resistant S. pneumoniae and tested the effect of fomepizole in a combinatorial treatment with antibiotics. They quantified the bacterial burden in the organs of infected mice, comparing the experimental group with the control group.
The researchers found that using Fomepizole blocked normal energy production by S. pneumoniae and enhanced the bacteria’s susceptibility to antibiotics and reduced bacterial burden in the lungs of mice with pneumonia. The combination treatment was effective in preventing the development of invasive disease. Future research is needed however, as this novel drug treatment has not been replicated in clinical studies on humans, who may present with complicating factors such as comorbidities, advanced age, or environmental variables that may play a role in disease outcomes.
Orihuela adds, “Pharmacological targeting of fermentation pathways is a new way to enhance the susceptibility of some bacteria to antimicrobials. Combination treatment of erythromycin and fomepizole, an alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor, prevented the in vivo dissemination of antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002020
Citation: Im H, Pearson ML, Martinez E, Cichos KH, Song X, Kruckow KL, et al. (2023) Targeting NAD+ regeneration enhances antibiotic susceptibility of Streptococcus pneumoniae during invasive disease. PLoS Biol 21(3): e3002020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002020
Author Countries: United States of America
Funding: This work was supported by National Institute of Health (AI114800, AI148368, AI156898, and AI172796 to C.J.O; and HL129948 to H.I.). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Journal
PLoS Biology
DOI
10.1371/journal.pbio.3002020
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Animals
COI Statement
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.




