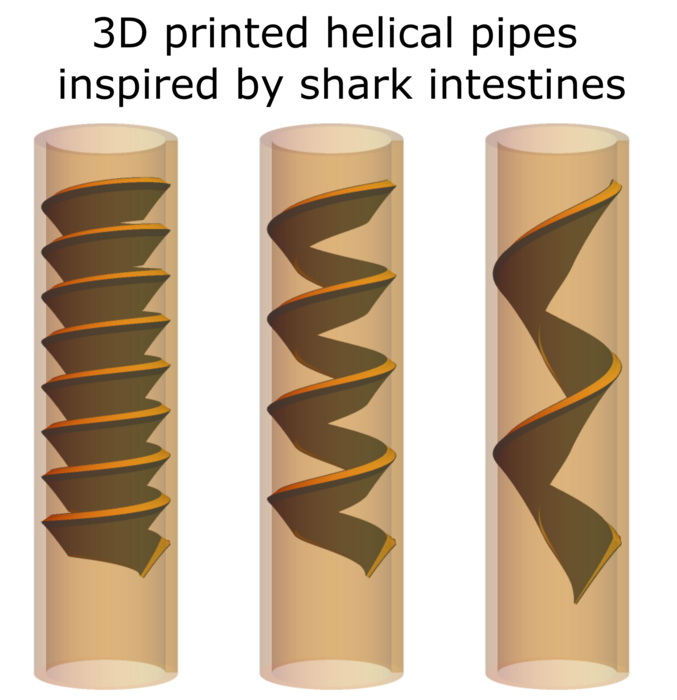
ROCKVILLE, MD – In 1920, inventor Nikola Tesla patented a type of pipe that he called a “valvular conduit,” which was built to draw fluid in one direction without any moving parts or added energy, and has applications ranging from soft robotics to medical implants. In 2021, scientists discovered that sharks’ spiral-shaped intestines work much the same way, favoring fluid flow in one direction—from head to pelvis. Ido Levin, a physicist in the lab of Sarah Keller at the University of Washington, became interested in the physics flow of fluid through these shark spirals. He will present how 3D printing models of shark intestines is helping them learn about how these spirals work on Monday, February 20 at the 67th Annual Biophysical Society Meeting in San Diego, California.
Credit: Image courtesy of Ido Levin.
ROCKVILLE, MD – In 1920, inventor Nikola Tesla patented a type of pipe that he called a “valvular conduit,” which was built to draw fluid in one direction without any moving parts or added energy, and has applications ranging from soft robotics to medical implants. In 2021, scientists discovered that sharks’ spiral-shaped intestines work much the same way, favoring fluid flow in one direction—from head to pelvis. Ido Levin, a physicist in the lab of Sarah Keller at the University of Washington, became interested in the physics flow of fluid through these shark spirals. He will present how 3D printing models of shark intestines is helping them learn about how these spirals work on Monday, February 20 at the 67th Annual Biophysical Society Meeting in San Diego, California.
Levin explained that “the researchers of the 2021 study connected a tube to the shark intestines, and put water with glycerin—a very viscous fluid—through these pipes. And they showed that if you connect these intestines in the same direction as a digestive tract, you get a faster flow of fluid than if you connect them the other way around. We thought this was very interesting from a physics perspective… One of the theorems in physics actually states that if you take a pipe, and you flow fluid very slowly through it, you have the same flow if you invert it. So we were very surprised to see experiments that contradict the theory. But then you remember that the intestines are not made out of steel—they’re made of something soft, so while fluid flows through the pipe, it deforms it.”
To study the fluid dynamics through spiral pipes, Levin and Keller collaborated with their colleagues in the Nelson Group at the University of Washington to create soft, 3D structures that mimic aspects of the shark intestines. “15 or 20 years ago, it was impossible to try and reconstruct these shapes in manmade materials,” Levin said. When they used a rigid material to 3D print the shapes, there was no difference in fluid flow in one direction or the other. However, printing the shapes using a softer elastomer led to faster fluid flow in one direction. Using these 3D printed structures, the team is studying how the radius, pitch, and thickness of the inner structure impacts the fluid flow. With the softer materials, they can also study the coupling between flow rate and how the pipe deforms. Understanding these parameters will help in engineering similar structures that can be used for things like soft robotics.
Up until recently, robots have been made with rigid materials and hinges. But using soft materials that can deform in different ways, like an octopus does, opens up a whole world of possibilities, Levin explains, “this is one step forward in trying to understand the basic mechanics of the interaction between membranes and flow.” One day, this seemingly simple system could control industrial or medical devices.
###
The Biophysical Society, founded in 1958, is a professional, scientific Society established to lead development and dissemination of knowledge in biophysics. The Society promotes growth in this expanding field through its annual meeting, publications, and committee and outreach activities. Its 7,500 members are located throughout the United States and the world, where they teach and conduct research in colleges, universities, laboratories, government agencies, and industry.




