Microresonators based frequency combs, microcombs, have attracted huge interest in the last decades for their revolutionary performance of compact size, flexible comb spacing, and broad bandwidth. Wide applications of microcombs including optical frequency synthesizer, atomic clock, lidar, spectroscopy and optical communications have been reported. Among these applications, it is highly desired that the microcombs simultaneously have a broad spectral coverage while maintaining a small mode spacing (typically < 50 GHz). However, limited by waveguide loss or dispersion control, it is still very challenging for microcomb generation techniques.
Credit: by Zeyu Xiao, Tieying Li, Minglu Cai, Hongyi Zhang, Yi Huang, Chao Li, Baicheng Yao, Kan Wu and Jianping Chen
Microresonators based frequency combs, microcombs, have attracted huge interest in the last decades for their revolutionary performance of compact size, flexible comb spacing, and broad bandwidth. Wide applications of microcombs including optical frequency synthesizer, atomic clock, lidar, spectroscopy and optical communications have been reported. Among these applications, it is highly desired that the microcombs simultaneously have a broad spectral coverage while maintaining a small mode spacing (typically < 50 GHz). However, limited by waveguide loss or dispersion control, it is still very challenging for microcomb generation techniques.
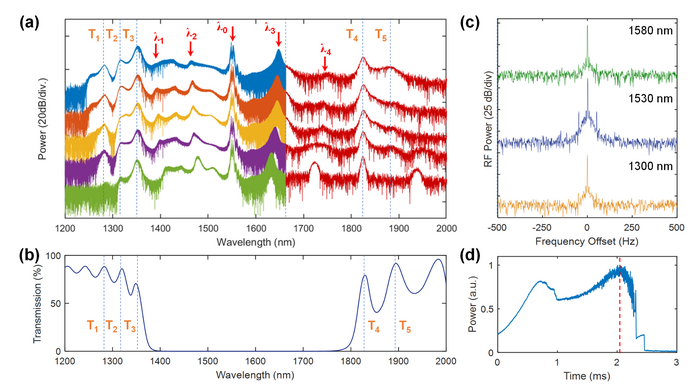
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Kan Wu from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Professor Baicheng Yao from University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, explores the dynamics of Kerr comb generation in the near-zero anomalous-dispersion regime. Thanks to the ultra-small anomalous group-velocity dispersion, they have experimentally obtained a 2/3-octave-spaning microcomb in the broadband modulational instability (MI) state with a spectrum from 1240 nm to 1950 nm and a mode spacing of 10 GHz. The corresponding number of comb lines is more than 8400. Moreover, they have observed a novel soliton structure in near-zero anomalous-dispersion regime, and term these solitons as “anomalous-dispersion based near-zero-dispersion soliton”. This near-zero-dispersion soliton (NZDS) has tightly packed multi-soliton structures with local repetition frequency up to 8.6 THz and individual pulse width less than 100 fs. The corresponding spectral span is >32 THz and the comb line number is >3200. The reported technique provides a new sight into the nonlinear dynamics of the Kerr microcombs near the zero-dispersion regime and presents a feasible solution for generating broadband microcomb with dense comb lines.
This work is performed in a high-Q Fabry-Perot microresonator based on highly nonlinear fiber. The fiber F-P microresonator is a flexible platform to study the Kerr soliton dynamics near zero-dispersion region. This platform guarantees that the observed phenomena are representative of the pure χ(3) nonlinearity and high-order dispersion, with no need to consider the avoided mode-crossing effects in integrated multimode microresonators, or the periodic perturbations due to dispersive waves in a long fiber cavity. These scientists summarize the technical characteristics of their work.
“We adopt a pulsed pumping scheme to drive this near-zero dispersion F-P microresonator. Pulsed pumping scheme can effectively reduce the demand for average pumping power and alleviate the intracavity thermal effect.”
“The microcombs in broadband MI state and near-zero-dispersion soliton state possess their own potential application scenarios. The MI microcomb state has advantages of high conversion efficiency and widely accessible range, which is suitable for the high power microcomb application. In contrast, near-zero-dispersion soliton state has relatively low phase-noise feature and self-organized structures, which provides unique capabilities in the applications of optical computing, light sensing, communication and spectroscopy, etc. This work presents a flexible strategy to choose the operating state of the microcombs depending on the requirement of the application.” the scientists forecast.
Journal
Light Science & Applications
DOI
10.1038/s41377-023-01076-8




