Telecommunications have reshaped many aspects of our lives over the past few decades by providing incredibly convenient ways to share and access information. One of the most important enablers for this transformation has been the adoption and improvement of broadband technologies, which cram enormous amounts of data over wide frequency bands to achieve unprecedented transfer speeds. Today, most large cities have fiber optics-based networks that distribute high-speed internet directly to every home.
Credit: Figure courtesy of Pierre Didier, LTCI, Telecom Paris, Institut Polytechnique de Paris.
Telecommunications have reshaped many aspects of our lives over the past few decades by providing incredibly convenient ways to share and access information. One of the most important enablers for this transformation has been the adoption and improvement of broadband technologies, which cram enormous amounts of data over wide frequency bands to achieve unprecedented transfer speeds. Today, most large cities have fiber optics-based networks that distribute high-speed internet directly to every home.
Unfortunately, it is not always feasible to deploy fiber optic links to remote locations and rural areas, due to the associated costs and civil engineering work required. Such places could benefit from a different approach to optical broadband communications: free-space optics. The main idea in free-space optical (FSO) communications is to set up aligned transmitter–receiver pairs where needed and use air as the medium to carry the signals. While there are still many challenges to address in FSO systems (such as low energy efficiency, impact of weather, and high background noise), scientists worldwide are continuously trying out new ways of solving these issues and achieving higher data rates.
Against this backdrop, a research team at Institut Polytechnique de Paris together with researchers from École Normale Supérieure in France, recently made substantial progress in FSO communications using unipolar quantum optoelectronic (UQO) devices. As reported in Advanced Photonics, the team successfully created long-range FSO links using an external modulator based on Stark effect associated with two types of UQO detectors in the receiver. They achieved unprecedented data rates with this type of technology, showcasing their untapped potential.
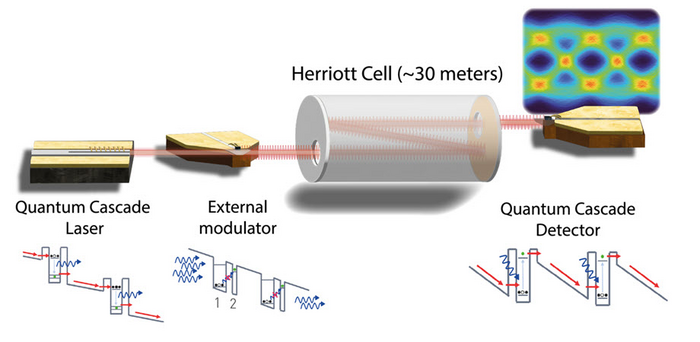
The transmitter and the two detectors the researchers used in their system operate in the midinfrared range — that is, using wavelengths between 8 and 12 µm. In this frequency range, the signal undergoes very low absorption, scattering, and distortion during its propagation in the atmosphere. The transmitter side used a commercial quantum cascade laser operating at room temperature combined with a novel external modulator. The detector side (which should properly sense and interpret small and noisy signals) used either a quantum cascade detector (QCD) or a quantum well infrared photodetector (QWIP). The latter is more complex and typically performs better but needs to be nitrogen-cooled, whereas the QCD can be left uncooled and used at room temperature. In other words, there is a trade-off between the performance, complexity, and cost of the two UQO detectors.
First, the team evaluated the maximum data rate of their FSO link in “back-to-back configuration,” which means directly sending the output of the transmitter into the input of the detector. Then, they introduced a commercial Herriott cell between the two. This hermetic device contains carefully designed mirrors to make an input optical signal bounce back and forth multiple times before it exits, thereby simulating a longer distance for the signal to travel. In this case, the effective length of the light path was 31 m.
To improve the performance of their communication system in terms of speed and error resistance, the researchers employed multiple independent techniques, namely pulse shaping the transmitted signal combined with some pre- and post-processing methods. “We achieved a record-setting bitrate of 30 Gbit/s for both 2-level (OOK) and 4-level (PAM-4) modulation schemes in a 31-meter propagation link,” remarks corresponding author Pierre Didier, a PhD student in Prof. Frédéric Grillot’s group at Télécom Paris, “Moreover, the observed bit error rates were compatible with established error-correction algorithms that can be implemented at the receiver’s end,” he adds.
It is worth noting that this is the first time an FSO transmission system has achieved high data rates in the 8-12 µm wavelength domain at such a long distance. Thus, this work marks a key step towards the realization of high-speed FSO telecommunication links that are resistant to weather conditions by adopting UQO devices. Further developments in the integration of UQO devices, as well as improvements in the supporting optics and electronics, can help to bring high-speed internet to challenging locations.
Read the Gold Open Access article by Didier, Dely, et al., “High-capacity free-space optical link in the midinfrared thermal atmospheric windows using unipolar quantum devices,” Adv. Photon. 4(5), 056004 (2022), doi 10.1117/1.AP.4.5.056004.
Journal
Advanced Photonics
DOI
10.1117/1.AP.4.5.056004
Article Title
High-capacity free-space optical link in the midinfrared thermal atmospheric windows using unipolar quantum devices
Article Publication Date
1-Nov-2022




