Vortices are ubiquitous in nature: Whirling up water can create swirls. When the atmosphere is stirred up, huge tornadoes can form. This is also the case in the quantum world, except that there many identical vortices are being formed simultaneously – the vortex is quantized. In many quantum gases, such quantized vortices have already been demonstrated. “This is interesting because such vortices are a clear indication of the frictionless flow of a quantum gas – the so-called superfluidity,” says Francesca Ferlaino from the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the Austrian Academy of Sciences.
Credit: Ella Maru Studio scientific-illustrations.com
Vortices are ubiquitous in nature: Whirling up water can create swirls. When the atmosphere is stirred up, huge tornadoes can form. This is also the case in the quantum world, except that there many identical vortices are being formed simultaneously – the vortex is quantized. In many quantum gases, such quantized vortices have already been demonstrated. “This is interesting because such vortices are a clear indication of the frictionless flow of a quantum gas – the so-called superfluidity,” says Francesca Ferlaino from the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck and the Institute of Quantum Optics and Quantum Information at the Austrian Academy of Sciences.
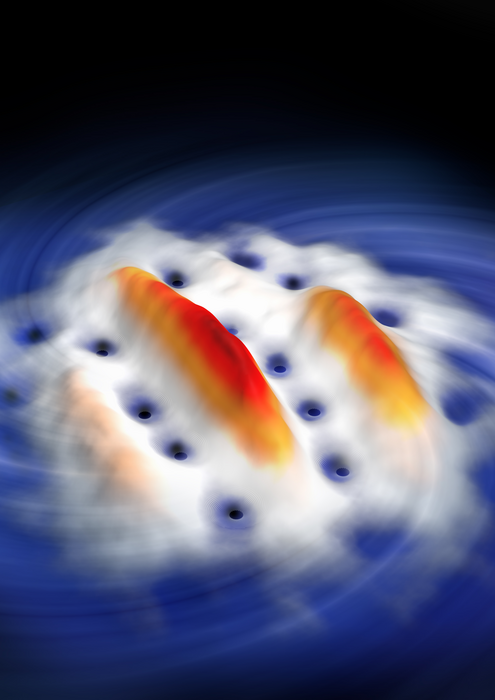
Ferlaino and her team are researching quantum gases made of strongly magnetic elements. For such dipolar quantum gases, in which atoms are highly connected to each other, quantum vortices could not be demonstrated so far. Scientists have developed a new method: “We use the directionality of our quantum gas of dysprosium, whose atoms behave like many small magnets, to stir the gas,” explains Manfred Mark from Francesca Ferlaino’s team. To do this, the scientists apply a magnetic field to their quantum gas in such a way that this initially round, pancake-shaped gas becomes elliptically deformed due to magnetostriction. This idea, as simple as it is powerful, originated from a theoretical proposal a few years ago by the Newcastle University theoretical team, led by Nick Parker and of which Thomas Bland, the paper’s second author, was a member. “By rotating the magnetic field, we can rotate the quantum gas,” explains Lauritz Klaus, first author of the current paper. “If it spins fast enough, then small vortices form in the quantum gas. This is how the gas tries to balance the angular momentum.” At sufficiently high rotational speeds, peculiar stripes of vortices form along the magnetic field. These are a special characteristic of dipolar quantum gases and have now been observed for the first time at the University of Innsbruck, Austria.
The new method, now presented in Nature Physics, will be used to study superfluidity in supersolid states in which quantum matter is simultaneously solid and liquid. “It is indeed still a major open question the degree of superfluid character in the newly discovered supersolid states, and this question remains still very little studied today.”
The work was done in cooperation with Giacomo Lamporesi from the University of Trento, Italy, and the theorist Russell Bisset from the University of Innsbruck, and was financially supported by the European Research Council ERC, the Austrian Science Fund FWF and the Austrian Academy of Sciences ÖAW, among others.
Journal
Nature Physics
DOI
10.1038/s41567-022-01793-8
Method of Research
Experimental study
Article Title
Observation of vortices and vortex stripes in a dipolar condensate
Article Publication Date
31-Oct-2022




