We tend to eat, drink, and move less when we’re feeling under the weather. And we’re not alone—most animals reduce those same three behaviors when they’re fighting an infection.
Credit: Laboratory of Molecular Genetics at The Rockefeller University
We tend to eat, drink, and move less when we’re feeling under the weather. And we’re not alone—most animals reduce those same three behaviors when they’re fighting an infection.
Now, a new study pinpoints the cluster of neurons that control these responses, referred to as sickness behaviors. By provoking immune responses in mice, researchers demonstrated that a specific population of cells in the brainstem potently induce three telltale sickness behaviors. In addition, inhibiting these neurons blunts each of these behavioral elements of the sickness response. The findings, published in Nature, directly link inflammation to neural pathways regulating behavior, offering insight into how the immune system interacts with the brain.
“We are still in the early days of trying to understand the brain’s role in infection,” says Jeffrey M. Friedman, Marilyn M. Simpson Professor at The Rockefeller University. “But with these results, we now have a unique opportunity to ask: What does your brain look like when you’re sick?”
Sickness behaviors have been shown to play an important role in an animal’s recovery from an infection. Prior studies have bolstered that theory by demonstrating that animals forced to eat when they’re sick showed a significantly increased mortality. “These behavioral changes during infection are really important for survival,” says lead author Anoj Ilanges, a former graduate student in Friedman’s lab, now a group leader at the HHMI Janelia Research Campus
But it has never been clear how the brain coordinates that near-universal urge to refuse meals and curl up under the covers with the onset of infection. So Friedman and Ilanges set out to map the brain regions behind sickness behaviors in mice.
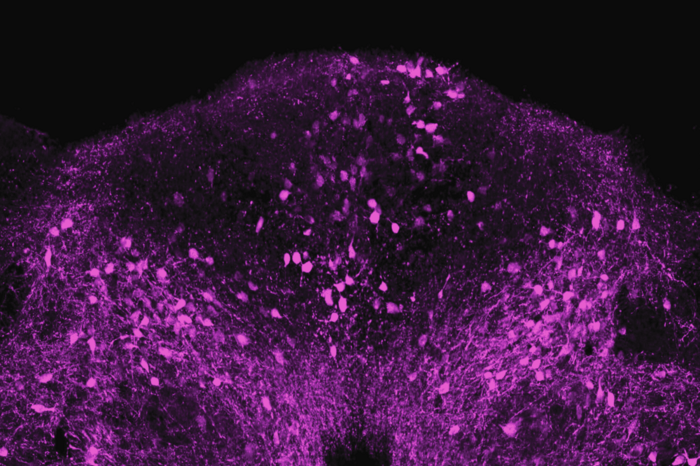
The team began by exposing mice to LPS, a piece of bacterial cell wall that activates the immune system and potently induces sickness behavior. Shortly after an injection of LPS, there was a spike in activity in a brainstem region known as the dorsal vagal complex, among a population of neurons expressing the neuropeptide ADCYAP1. To confirm that they had found the right brain cells, the researchers then activated those neurons in healthy mice and they found that the animals ate, drank, and moved around less. In contrast, when the ADCYAP1 neurons were deactivated , the effect of LPS on these behaviors was significantly reduced.
“We didn’t know if the same or different neurons regulated each of these behaviors,” Friedman says, “We found it surprising that a single neuronal population appears to regulate each of these components of the sickness response.”
The authors were not, however, altogether surprised that this brainstem region was involved in mediating sickness behaviors. The dorsal vagal complex is one of a precious few physiological crossroads of the central nervous system, where an absence of the blood brain barrier enables circulating factors in the blood to pass information directly to the brain. “This region has emerged as a kind of alert center for the brain, conveying information about aversive or noxious substances that, more often than not, reduce food intake,” Friedman says.
In the coming months, Friedman’s team at Rockefeller intends to incorporate these findings into their overall goal of understanding the physiological signals and neural circuitry that regulate feeding behavior. They are specifically interested in understanding why even mice engineered to eat voraciously will nonetheless stop eating when exposed to bacterial infections.
Meanwhile, Ilanges plans to investigate what role other brain regions play in response to infections, expanding our knowledge of the brain’s role during this critical process. “We looked at one region of the brain, but there are many others that become activated with the immune response,” he says. “This opens the door to asking what the brain is doing, holistically, during infection.”
Journal
Nature
DOI
10.1038/s41586-022-05161-7




