Oxygen plays a crucial role for all living organisms on Earth. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have now found evidence that double ionised sulphur dioxide contribute to the formation of oxygen molecules. This could, in particular, explain the presence of oxygen in sulphur dioxide-rich atmospheres of several of Jupiter’s moons.
Credit: Måns Wallner
Oxygen plays a crucial role for all living organisms on Earth. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have now found evidence that double ionised sulphur dioxide contribute to the formation of oxygen molecules. This could, in particular, explain the presence of oxygen in sulphur dioxide-rich atmospheres of several of Jupiter’s moons.
How does oxygen form? On earth, the main explanation involves the biological process of photosynthesis, which was developed by cyanobacteria and kicked off the Great Oxidation Event about two billion years ago. Researchers have long realised that non-biological or abiotic processes also contribute to the formation of oxygen – especially out in space. On other celestial bodies where such bacteria are not present, the presence of oxygen can be explained by abiotic processes.
Researchers at the University of Gothenburg have now found a possible new abiotic pathway: the formation of oxygen from sulphur dioxide. The sulphur dioxide molecule is found in the atmosphere of many celestial bodies and large quantities can be ejected into the atmosphere during volcanic eruptions.
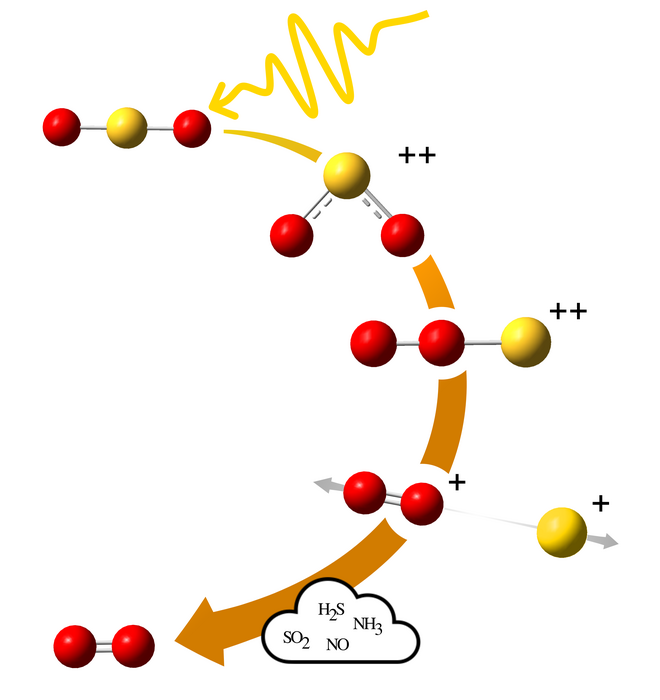
When the sulphur dioxide molecule is exposed to radiation of a sufficiently high energy, as provided by radiation from the Sun for example, this molecule can be ionised into a double positively charged system. It can then assume a linear form with the two oxygen atoms being adjacent and the sulphur atom at one of the terminal ends. Before ionisation, sulphur dioxide has a shape similar to the ‘Mickey Mouse’ shape of the water molecule.
The atoms switch places in the molecule
“Upon double ionisation, two of the bound electrons in the molecule get ejected and can lead to changes in the angle between the atoms in the molecule. Alternativetly, as crucial in the present case, roaming can occur, that is, the atoms switch places, and the molecule takes on a whole new shape,” says Måns Wallner, doctoral student in physics.
Once roaming has occurred, the sulphur atom may break up, leaving behind a simple positively charged oxygen molecule O2+, which can then be neutralised by receiving an electron from another molecule. This sequence of events can explain how oxygen formed in the atmospheres of several of Jupiter’s moons such as Io, Europa and Ganymede, despite the lack of biological life there.
“We also suggest in our article that this happens naturally on Earth,” says Raimund Feifel, co-author of the article reporting the findings, published in the August issue of Science Advances.
Research thanks to the coronavirus
Feifel says they have the COVID-19 pandemic to thank for these new findings.
“Well, we had a visiting professor who came here because daily life in his home country had become so restricted that he could barely do any research any longer during the pandemic. We dug up some old data from 2005 where we had irradiated sulphur dioxide with photons in our lab. We analysed the data and, with Chalmers’ gigantic computer cluster, we calculated what quantities of energy created which molecular structures,” says Raimund Feifel.
The next step will be to see if roaming occurs even when other molecules, such as carbon diselenide, are subjected to double ionisation.
“We want to see if it also happens then, or if it was just a happy coincidence with sulphur dioxide,” says Raimund Feifel.
Article: Abiotic molecular oxygen production—Ionic pathway from sulfur dioxide
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.abq5411
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Article Title
Abiotic molecular oxygen production – ionic pathway from sulfur dioxide
Article Publication Date
19-Aug-2022




