Fungal pathogens have a major global impact upon human health – they are often difficult to diagnose and treat, and there is an urgent need for better diagnostics and more effective antifungal treatments. Using newly developed imaging technologies, Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute researchers have today (21/9) revealed how Candida albicans, a common fungus, evades immune responses. According to the researchers this involves an “alien-like” shape shifting that allows the fungus to break out of immune cells.
Credit: Monash University
Fungal pathogens have a major global impact upon human health – they are often difficult to diagnose and treat, and there is an urgent need for better diagnostics and more effective antifungal treatments. Using newly developed imaging technologies, Monash Biomedicine Discovery Institute researchers have today (21/9) revealed how Candida albicans, a common fungus, evades immune responses. According to the researchers this involves an “alien-like” shape shifting that allows the fungus to break out of immune cells.
The paper published in the journal Cell Reports, led by Professor Ana Traven and PhD student Françios Olivier, describes how Candida albicans uses a sword-like filament to engage toxin molecules and cell death pathways that damage immune cell membranes – allowing it to escape and spread.
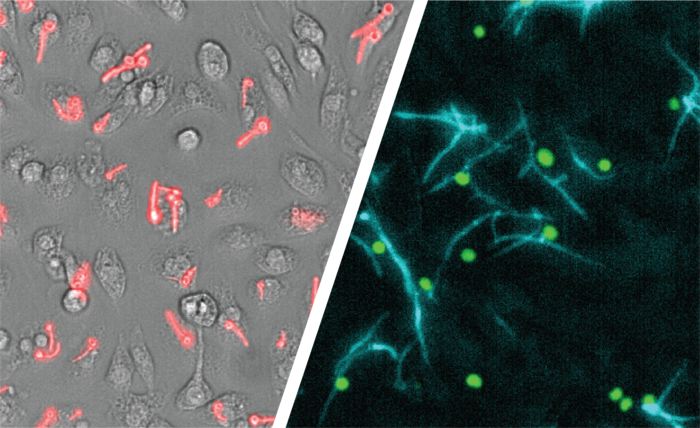
The imaging technology, developed by Olivier in collaboration with Monash Micro-Imaging, allows for escaping fungi to be pin-pointed in real time. According to Olivier, this study was made possible by the automation of imaging analysis and increased computer processing power: “We could harness a great deal of data which provided insight into this immune escape mechanism”.
Candida is a yeast that often lives in the human digestive tract and mouth, as well as urinary and reproductive organs. Usually, it doesn’t cause disease in its host, but under certain conditions, it can switch to a harmful form. Candida albicans remains a common cause of life-threatening disease in ICU, post- surgery and cancer patients. The immune system has a particular cell type, called the macrophage, which is responsible for gobbling up invaders (bacteria, fungi, cancer cells) and triggering immune responses. Candida albicans escape macrophages by morphing into long, filament-like cells. This escape leads to spreading of the fungus. In the process is triggers immune responses that can be harmful if not kept in check.
According to Professor Traven, targeting the fungus as it is escaping “presents a promising therapeutic avenue, preventing both the spread of the infection and having the potential to dampen inflammation”. Until now, the mechanisms behind this escape have remained unclear as researchers have not been able to study this escape manoeuvre in detail. Now they can. The research team developed a live-cell imaging platform that, in real time, maps Candida’s escape from macrophages, revealing several escape mechanisms.
Journal
Cell Reports
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
The escape of Candida albicans from macrophages is enabled by the fungal toxin candidalysin and two host cell death pathways