Osaka, Japan – Did you know that not only does organism’s body have a biological clock that can tell the time of the day, it can also tell the time of the year? Now, researchers from Japan have found that one capable little molecule may be behind the mechanism by which the biological clock keeps track of the seasons.
Credit: 2022, Masaharu Hasebe and Sakiko Shiga, Clock-gene-dependent glutamate dynamics in the bean bug brain regulate photoperiodic reproduction, PLOS Biology
Osaka, Japan – Did you know that not only does organism’s body have a biological clock that can tell the time of the day, it can also tell the time of the year? Now, researchers from Japan have found that one capable little molecule may be behind the mechanism by which the biological clock keeps track of the seasons.
In a study that was recently published in PLOS Biology, researchers from Osaka University reveal that glutamate signaling is responsible for the seasonal regulation of reproduction in bean bugs by genes involved in maintaining circadian rhythm.
The circadian rhythm is driven by a biological clock that controls body processes based on time of day. A related process is photoperiod sensitivity, or seasonal regulation, in which body processes are regulated on a seasonal basis based on the length of the daytime and nighttime periods.
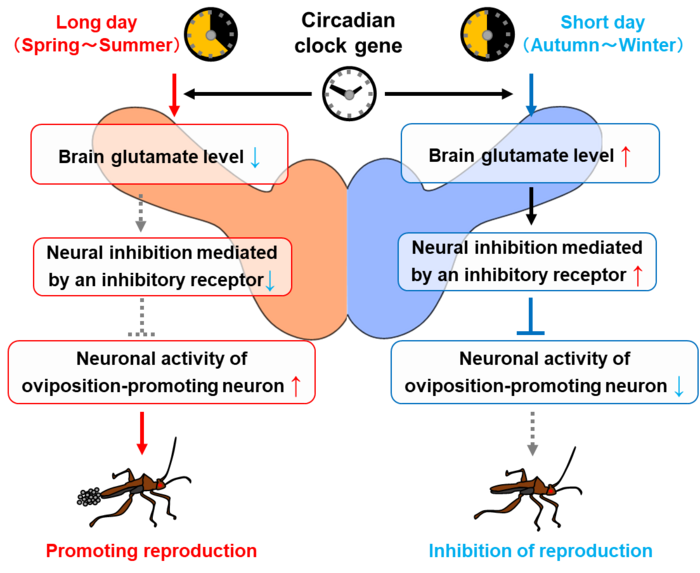
“Previous studies have shown that circadian clock genes are involved not only in regulating daily processes, but also in regulating seasonal events, such as reproduction in insects,” states Masaharu Hasebe, first author on the study. “However, the mechanism governing this interaction was unclear.”
To address this, the researchers focused on glutamate, a neurotransmitter that is involved in transmitting a wide variety of signals in the brains of many animals, from invertebrates to mammals. Using bean bugs, a convenient model of circadian clock-related seasonal rhythms, a brain glutamate level was assessed in different photoperiodic conditions related to the seasonal reproductive cycle and in response to interference with circadian clock genes.
“The results were very clear,” explains Sakiko Shiga, senior author of the study. “Extracellular glutamate levels in the whole brain were significantly higher under short-day conditions than under long-day conditions, and knocking down the clock gene period abolished this difference.”
Directly reducing or increasing glutamate levels in bean bug brains also decreased season-specific changes in reproductive status. In addition, reducing or increasing glutamate levels disrupted the photoperiodic responses of pars intercerebralis neurons, which typically change their neural activity seasonally and promote egg laying.
“Our results show that extracellular glutamate dynamics are regulated by clock genes and play an essential role in the photoperiodic control of reproduction,” says Hasebe.
Given that glutamate is widely used for neurotransmission in animals, from insects to mammals, the findings from this study have implications beyond bean bug biology. It is possible that further studies investigating this newly discovered mechanistic link between the circadian clock and photoperiod regulation will advance our understanding of seasonal adaptation in a wide range of animals.
###
The article, “Clock-gene-dependent glutamate dynamics in the bean bug brain regulate photoperiodic reproduction” was published in PLOS Biology at DOI: https://doi.org/ 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001734
Journal
PLoS Biology
DOI
10.1371/journal.pbio.3001734
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Clock-gene-dependent glutamate dynamics in the bean bug brain regulate photoperiodic reproduction
Article Publication Date
6-Sep-2022




