“A third of the global cancer deaths are attributed to primary liver cancer [1].”
Credit: Zaidi et al.
“A third of the global cancer deaths are attributed to primary liver cancer [1].”
BUFFALO, NY- August 22, 2022 – A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on June 6, 2022, entitled, “Using quantitative immunohistochemistry in patients at high risk for hepatocellular cancer.”
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the primary form of liver cancer and a major cause of cancer death worldwide. Early detection is key to effective treatment. Yet, early diagnosis is challenging, especially in patients with cirrhosis, who are at high risk of developing HCC.
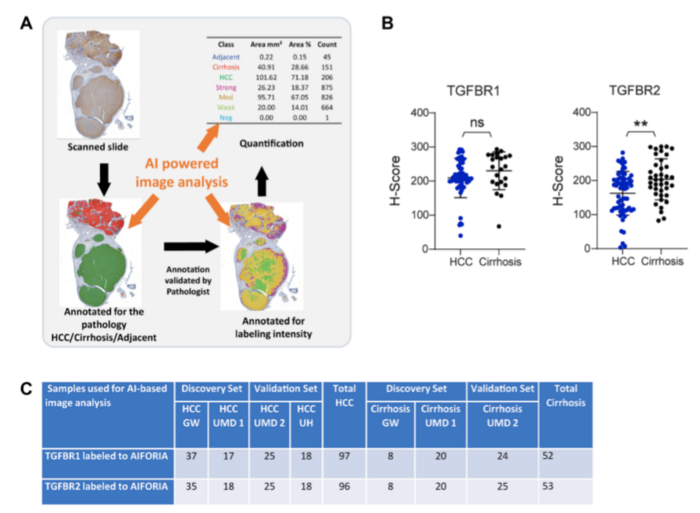
Researchers Sobia Zaidi, Richard Amdur, Xiyan Xiang, Herbert Yu, Linda L. Wong, Shuyun Rao, Aiwu R. He, Karan Amin, Daewa Zaheer, Raj K. Narayan, Sanjaya K. Satapathy, Patricia S. Latham, Kirti Shetty, Chandan Guha, Nancy R. Gough, and Lopa Mishra from Northwell Health, The George Washington University, Georgetown University Medical Center, University of Hawaii, University of Hawaii Cancer Center, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra, North Shore University Hospital, University of Maryland, and Albert Einstein College of Medicine investigated changes in the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) pathway for potential biomarkers that may differentiate HCC from cirrhosis.
“Here, using quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of samples from a multi-institutional repository, we evaluated if differences in TGF-β receptor abundance were present in tissue from patients with only cirrhosis compared with those with HCC in the context of cirrhosis.”
The researchers determined that TGFBR2, not TGFBR1, was significantly reduced in HCC tissue compared with cirrhotic tissue. They developed an artificial intelligence (AI)-based process that correctly identified cirrhotic and HCC tissue and confirmed the significant reduction in TGFBR2 in HCC tissue compared with cirrhotic tissue.
In conclusion, the researchers proposed that a reduction in TGFBR2 abundance represents a useful biomarker for detecting HCC in the context of cirrhosis and that incorporating this biomarker into an AI-based automated imaging pipeline could reduce variability in diagnosing HCC from biopsy tissue.
“Our findings support further analyses to determine if this reduction is an early occurrence that can be used diagnostically in combination with other morphological characteristics or biomarkers to detect HCC at early stages in high-risk patients.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/genesandcancer.220
Correspondence to: Lopa Mishra and Nancy R. Gough – Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Keywords: liver cancer; immunohistochemistry; diagnostic model; cirrhosis; transforming growth factor beta
About Genes & Cancer: Genes & Cancer covers all aspects of the structure and function of oncogenes, growth suppressor and apoptotic genes, their role in signal transduction and the mechanisms by which their expression and function are altered during tumor development. In addition to publishing manuscripts that directly relate to these areas of research, Genes & Cancer also aims to attract papers in the areas of genomics, drug development and systems biology.
To learn more about Genes & Cancer, visit www.genesandcancer.com and connect with us on social media:
- YouTube
For media inquiries, please contact: [email protected].
Genes & Cancer Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1C
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-212-659-5400
###
Journal
Genes & Cancer
DOI
10.18632/genesandcancer.220
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Human tissue samples
Article Title
Using quantitative immunohistochemistry in patients at high risk for hepatocellular cancer
Article Publication Date
6-Jun-2022




