Greenspace is an important component of urban nature, providing vital ecosystem services to society and protecting human health. The United Nations specified the need for ‘providing universal access to greenspace for urban residents’ in the 11th Sustainable Development Goal of making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. However, it remains unclear how far we are from achieving this goal in the global context because there are no reliable and accurate data on the exposure of population to green spaces in the world.
Credit: The University of Hong Kong
Greenspace is an important component of urban nature, providing vital ecosystem services to society and protecting human health. The United Nations specified the need for ‘providing universal access to greenspace for urban residents’ in the 11th Sustainable Development Goal of making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. However, it remains unclear how far we are from achieving this goal in the global context because there are no reliable and accurate data on the exposure of population to green spaces in the world.
Recent research conducted by researchers from The University of Hong Kong (HKU) in collaboration with colleagues from Yale University and Tsinghua University revealed a stark inequality in human exposure to greenspace between cities, highlighting the need for prioritizing greening policies and actions to mitigate environmental disparity and achieve sustainable development goals.
This is the first global study to reveal greenspace exposure and environmental inequalities among cities. The findings have been published in Nature Communications (link), supports the idea that urban greenspace is, in economic terms, a normal good, with supply increasing with income, and this analysis is the first to reveal the global pattern of its deficit among urbanized parts of the planet.
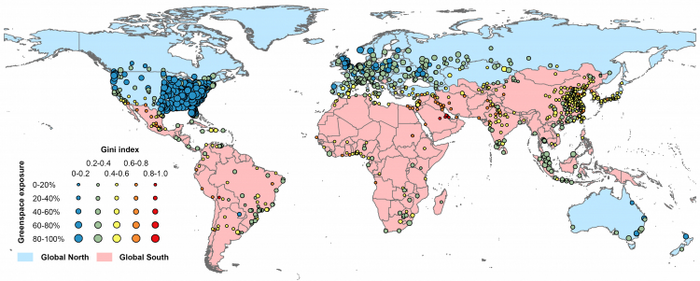
The research team developed a methodology incorporating fine-resolution population and greenspace mappings and used the results for 2020 to elucidate global differences in human exposure to greenspace, specifically at country, state, county, and city levels. The team examined 1,028 cities in the world and divided their sample into two groups: Global South cities and Global North cities. The former consists of cities in developing countries whereas the latter includes cities in developed countries.
The researchers found that Global South cities experience only one-third of the greenspace exposure level of Global North cities, even though the South cities are generally located in more rural countries. Greenspace exposure inequality in Global South cities is nearly twice that of Global North cities. Delving deeper into the data, they found that the severe disparity in greenspace exposure is deeply linked to the differences in greenspace provision and landscape design. Specifically, 22% of greenspace exposure inequality is associated with greenspace provision and 53% of the said inequality is caused jointly by greenspace provision and landscape configuration.
Dr. Bin Chen, lead researcher of this project, Assistant Professor of Division of Landscape Architecture at HKU, concluded two important contributions of this study. The research findings reveal that residents of Global South cities have lower levels of greenspace exposure and higher inequality in greenspace exposure. “This calls for greening policies that mitigates environmental disparity in order to achieve sustainable development goals,” says Dr. Chen. Another key finding in this study is the seasonal variation of greenspace exposure inequality, which as Dr. Chen concludes, “provides valuable insight for assessing urban green spaces and the associated health benefits by considering both spatial and temporal heterogeneities”.
The research team uses greenspace exposure as a metric index, and takes people’s actual access to greenspace into consideration. Compared with the previous indicators such as greenspace coverage or per capita greenspace to measure the basic status of a region’s greening, the new metric can provide a more objective measurement of the relationship between people and greenspace to help attain the goal of sustainable development of environmental equality.
According to the study, the level of greenspace exposure is generally lower than the greenspace coverage in more than 1,000 sample cities around the world. It means that greenspace coverage rate as an indicator of sustainable development, may not be effective in reflecting environmental justice to urban residents. For instance, Singapore and Hong Kong have a greenspace coverage rate of 84% and 70%, but their greenspace exposure levels are only 55% and 35% respectively; Paris and Beijing have an urban greenspace coverage rate of 52% and 34%, but their greenspace exposure levels are only 38% and 28%. Atlanta has the most ideal greenspace coverage and exposure, where its greenspace coverage and greenspace exposure levels are 76.92% and 77.12%, respectively.
“We find greenspace provision and spatial configuration are two main drivers for explaining urban greenspace exposure inequalities. This evidence calls for coordinated practices among policymakers, city planners, and landscape architects to balance greenspace supply and demand, and to optimize greenspace arrangement for facilitating sustainable and equitable greening management”, says Professor Chris Webster, Chair Professor of Urban Planning and Development Economics, Dean of Faculty of Architecture, HKU.
“As a nice contribution to the field of sustainable urban environments, this research provides a holistic understanding of human greenspace exposure in the global context,” says Professor Peng Gong, Chair Professor of Global Sustainability at Department of Geography and Department of Earth Sciences, also the Vice-President and Pro-Vice-Chancellor (Academic Development) of HKU. He reiterated that upgrading the low levels of health-facilitating greenspace in the Global South and the poor greenspace-provision areas of the Global North cities, will require decisive government and community actions.
“This analysis serves as a benchmark against which a wide range of future research, practices, and optimizations could be assessed, especially for the rapidly developing Greater Bay Area,” says Professor Peng Gong. He states that HKU is proactively contributing to scientific research and practice in support of achieving the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals, noticeably, launching a new research hub – Urban Systems Institute (USI).
The full paper can be accessed here: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-32258-4.
About the research team
This research was led by Dr. Bin Chen, Director of Future Urbanity & Sustainable Environment (FUSE) Lab, Division of Landscape Architecture, Faculty of Architecture, Urban Systems Institute, and Musketeers Foundation Institute of Data Science, HKU, Professor Peng Gong, Department of Geography, Department of Earth Sciences, and Urban Systems Institute, HKU, and Professor Bing Xu, Department of Earth System Science, Tsinghua University. The collaborative team also includes Dr. Shengbiao Wu, Post-doctoral fellow, Division of Landscape Architecture, Faculty of Architecture, HKU; Dr. Yimeng Song, Post-doctoral fellow, School of the Environment, Yale University; and Professor Chris Webster, HKUrbanLabs, Faculty of Architecture, Urban Systems Institute, and Musketeers Foundation Institute of Data Science, HKU.
About the FUSE Lab
FUSE Lab aims to leverage geospatial and remote sensing big data, data-model fusion, and advanced interdisciplinary approaches to investigate the interaction loops between urban environmental change, human activities, and public health, with the ultimate goal of contributing to sustainable and healthy cities. FUSE lab’s research focuses on four major directions: (1) Urban and Natural Environmental Changes; (2) Human-Environment Spatiotemporal Interaction; (3) Impact of Environment and Human activities on Public Health; and (4) Urban Environment Improvement Theory and Adaptation Pathways.
To promote knowledge exchange, more recent research activities can be viewed through https://fuselab.hku.hk/
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by The University of Hong Kong HKU-100 Scholars Fund, Seed Fund for Strategic Interdisciplinary Research Scheme Fund, the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong Early Career Scheme (No. HKU27600222), Major Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 42090015 and 72091514), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42071400).
For media enquiries, please contact:
HKU Communications and Public Affairs Office
Melanie Wan
Tel: 2859 2600 / Email: [email protected]
Jaymee Ng
Tel: 3910 3612 / Email: [email protected]
Kenneth Choi
Tel: 2859 2607/ Email: [email protected]
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-022-32258-4
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Contrasting inequality in human exposure to greenspace between cities of Global North and Global South
Article Publication Date
8-Aug-2022




