Fertility is finite for mammalian females. From birth, females possess a limited number of primordial follicles, collectively called the ovarian reserve. Within each follicle is an oocyte that eventually becomes an egg. But with age, the follicles in the ovarian reserve decrease.
Credit: Satoshi Namekawa, UC Davis
Fertility is finite for mammalian females. From birth, females possess a limited number of primordial follicles, collectively called the ovarian reserve. Within each follicle is an oocyte that eventually becomes an egg. But with age, the follicles in the ovarian reserve decrease.
“Despite its fundamental importance, our understanding how the ovarian reserve is established and maintained remains poor,” said Professor Satoshi Namekawa, Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics at the University of California, Davis.
Researchers define the epigenetic machinery that governs the establishment and function of the mammalian ovarian reserve, providing molecular insights into female reproductive health and lifespan, in a new study published Aug. 10 in Nature Communications. Epigenetics refers to changes that influence how genes work without altering DNA itself. Lead scientists on the paper include Namekawa, project scientist Mengwen Hu and UC Davis Professors Richard Schultz and Neil Hunter.
“In human females over the age of 35, you see a decline in fertility,” said Namekawa. “Our study may give us the foundation to understand how female fertility is established and maintained at the molecular level and why it declines with age.”
Pausing primordial production
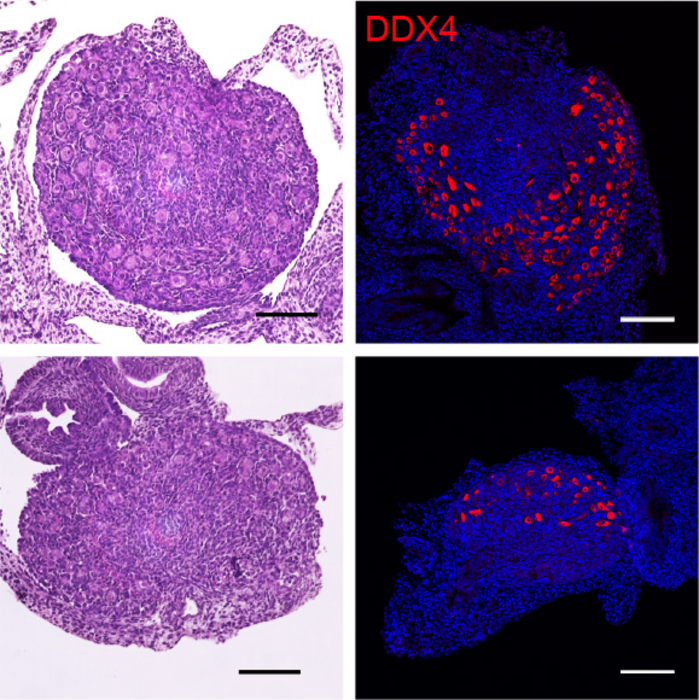
When the ovarian reserve is established, all the oocytes in primordial follicles pause their development and can remain in such an arrested state for decades.
“Fertility is supported by these arrested oocytes,” said Namekawa, noting that some hitherto unknown molecular machinery pauses development. “The main question is how can these cells be maintained for decades? It’s a big question. They cannot divide, they cannot proliferate, they just stay quiescent in the ovaries for decades. How is this possible?”
Using mouse mutants, the team found that the pausing of this oocyte transition phase was mediated by a group of proteins called the Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 (PRC1).
A molecular understanding of fertility
PRC1 suppresses the development process, called meiosis, that occurs prior to establishing the ovarian reserve, thereby ensuring a proper gene expression program in the ovarian reserve. When the team created mouse mutants with depleted PRC1 machinery, they found that the ovarian reserve could not be established and the cells underwent cell death.
“We show that a conditional PRC1 deletion results in rapid depletion of follicles and sterility,” said Namekawa. “These results strongly implicate PRC1 in the critical process of maintaining the epigenome of primordial follicles throughout the protracted arrest that can last up to 50 years in humans.”
According to Namekawa and his colleagues, deficiencies in PRC1 functionality may help explain cases of premature ovarian failure and infertility in humans.
“Now that we found that this epigenetic process is key for establishment, the next question is can we uncover a more detailed mechanism of this process?” Namekawa said. “How can the ovarian reserve be maintained for decades?”
Additional authors on the paper are: at UC Davis, Yu-Han Yeh, Yasuhisa Manukata and Hironori Abe; Akihiko Sakashita and So Maezawa, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center; Miguel Vidal, Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas Margarita Salas, Madrid, Spain; and Haruhiko Koseki, RIKEN Center for Allergy and Immunology, Yokohama, Japan. The work was supported by grants from the NIH.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-022-31759-6
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
PRC1-mediated epigenetic programming is required to generate the ovarian reserve
Article Publication Date
10-Aug-2022
COI Statement
None declared.




