WHAT:
Although COVID-19 booster vaccinations in adults elicit high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, antibody levels decrease substantially within 3 months, according to new clinical trial data. The findings, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, are from a study sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. The trial was led by NIAID’s Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium.
Credit: NIAID
WHAT:
Although COVID-19 booster vaccinations in adults elicit high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, antibody levels decrease substantially within 3 months, according to new clinical trial data. The findings, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, are from a study sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. The trial was led by NIAID’s Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium.
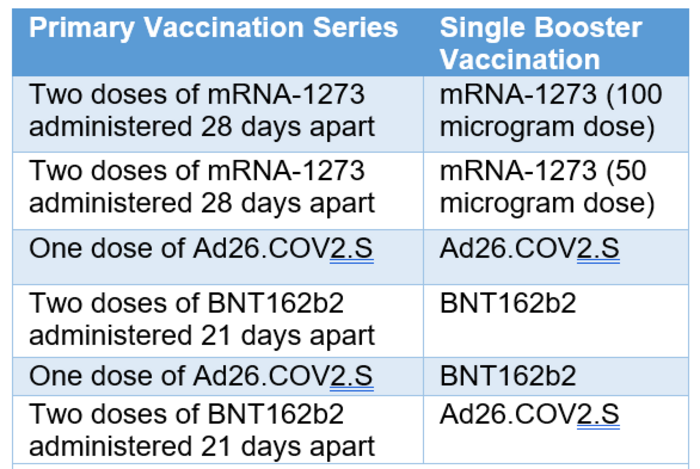
As part of a “mix and match” clinical trial, investigators administered COVID-19 booster vaccines to adults in the United States who had previously received a primary COVID-19 vaccination series under Emergency Use Authorization. Some participants received the same vaccine as their primary series, and others received a different vaccine. Investigators then evaluated immune responses over time. Results previously reported in The New England Journal of Medicine showed all combinations of primary and booster vaccines resulted in increased neutralizing antibody levels in the recipients.
In the new analysis, investigators report that nearly all vaccine combinations evaluated (see table) elicited high levels of neutralizing antibodies to the Omicron BA.1 sub-lineage. However, antibody levels against Omicron were low in the group that received Ad26.COV2.S as both a primary vaccine and boost. Moreover, immune responses to Omicron in all groups waned substantially, with neutralizing antibody levels decreasing 2.4- to 5.3-fold by three months post-boost. Omicron sub-lineages BA.2.12.1 and BA.4/BA.5 were 1.5 and 2.5 times less susceptible to neutralization, respectively, compared to the BA.1 sub-lineage, and 7.5 and 12.4 times less susceptible relative to the ancestral D614G strain. BA.5 currently is the dominant variant in the U.S.
The authors note that the findings are consistent with real-world reports showing waning protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection during the Omicron wave in people who received a primary vaccine series plus a booster shot. Additionally, the immune response to Omicron sub-lineages show reduced susceptibility to these rapidly emerging subvariants. The data could be used to inform decisions regarding future vaccine schedule recommendations, including the need for variant vaccine boosting.
NIAID grants supporting this research were UM1AI48372, UM1AI148373, UM1AI148450, UM1AI148452, UM1AI148573, UM1AI148574, UM1AI148575, UM1AI148576, UM1AI148684 and UM1AI148689. Contract 75N93019C00050 from the NIAID Collaborative Influenza Vaccine Innovation Centers (CIVICs) also provided support.
ARTICLES:
KE Lyke et al. Rapid Decline in Vaccine-Boosted Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS CoV-2 Omicron Variant. Cell Reports Medicine DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100679 (2022).
RL Atmar et al. Homologous and heterologous COVID-19 booster vaccinations. The New England Journal of Medicine DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116414 (2022).
WHO:
Dr. John H. Beigel, associate director for clinical research in NIAID’s Division of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, is available to discuss the study.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact the NIAID News & Science Writing Branch, (301) 402-1663, [email protected].
NIAID conducts and supports research—at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide—to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
Journal
Cell Reports Medicine
DOI
10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100679




