TROY, N.Y. — As our devices become smaller, faster, more energy efficient, and capable of holding larger amounts of data, spintronics may continue that trajectory. Whereas electronics is based on the flow of electrons, spintronics is based on the spin of electrons.
Credit: Jian Shi
TROY, N.Y. — As our devices become smaller, faster, more energy efficient, and capable of holding larger amounts of data, spintronics may continue that trajectory. Whereas electronics is based on the flow of electrons, spintronics is based on the spin of electrons.
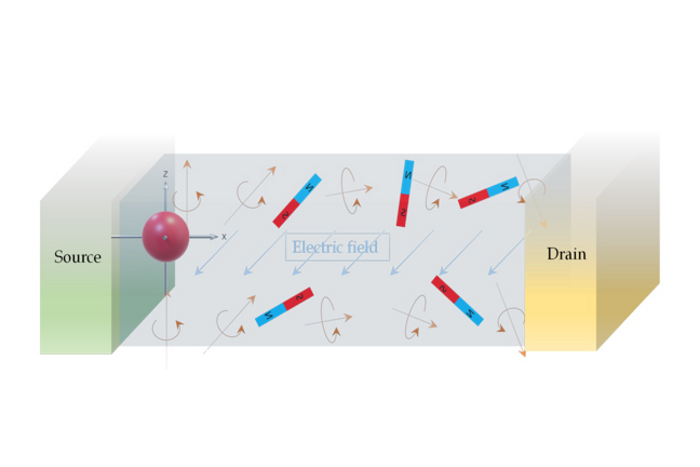
An electron has a spin degree of freedom, meaning that it not only holds a charge but also acts like a little magnet. In spintronics, a key task is to use an electric field to control electron spin and rotate the north pole of the magnet in any given direction.
The spintronic field effect transistor harnesses the so-called Rashba or Dresselhaus spin-orbit coupling effect, which suggests that one can control electron spin by electric field. Although the method holds promise for efficient and high-speed computing, certain challenges must be overcome before the technology reaches its true, miniature but powerful, and eco-friendly, potential.
For decades, scientists have been attempting to use electric fields to control spin at room temperature but achieving effective control has been elusive. In research recently published in Nature Photonics, a research team led by Jian Shi and Ravishankar Sundararaman of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and Yuan Ping of the University of California at Santa Cruz took a step forward in solving the dilemma.
“You want the Rashba or Dresselhaus magnetic field to be large to make the electron spin precess quickly,” said Dr. Shi, associate professor of materials science and engineering. “If it’s weak, the electron spin precesses slowly and it would take too much time to turn the spin transistor on or off. However, often a larger internal magnetic field, if not arranged well, leads to poor control of electron spin.”
The team demonstrated that a ferroelectric van der Waals layered perovskite crystal carrying unique crystal symmetry and strong spin-orbit coupling was a promising model material to understand the Rashba-Dresselhaus spin physics at room temperature. Its nonvolatile and reconfigurable spin-related room temperature optoelectronic properties may inspire the development of important design principles in enabling a room-temperature spin field effect transistor.
Simulations revealed that this material was particularly exciting, according to Dr. Sundararaman, associate professor of materials science and engineering. “The internal magnetic field is simultaneously large and perfectly distributed in a single direction, which allows the spins to rotate predictably and in perfect concert,” he said. “This is a key requirement to use spins for reliably transmitting information.”
“It’s a step forward toward the practical realization of a spintronic transistor,” Dr. Shi said.
The first authors of this article include graduate student Lifu Zhang and postdoctoral associate Jie Jiang from Dr. Shi’s group, as well as graduate student Christian Multunas from Dr. Sundararaman’s group.
This work was supported by the United States Army Research Office (Physical Properties of Materials program by Dr. Pani Varanasi), the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, and the National Science Foundation.
About Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Founded in 1824, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute is America’s first technological research university. Rensselaer encompasses five schools, over 30 research centers, more than 140 academic programs including 25 new programs, and a dynamic community made up of over 6,800 students and 104,000 living alumni. Rensselaer faculty and alumni include upwards of 155 National Academy members, six members of the National Inventors Hall of Fame, six National Medal of Technology winners, five National Medal of Science winners, and a Nobel Prize winner in Physics. With nearly 200 years of experience advancing scientific and technological knowledge, Rensselaer remains focused on addressing global challenges with a spirit of ingenuity and collaboration. To learn more, please visit www.rpi.edu.
Contact:
Katie Malatino
Sr. Communications Specialist
518-276-2146
[email protected]
Deanna Cohen
Director of Media Relations
518-233-4828
For general inquiries: [email protected]
Visit the Rensselaer research and discovery blog: https://everydaymatters.rpi.edu/
Follow us on Twitter: @RPINews
Journal
Nature Photonics
DOI
10.1038/s41566-022-01016-9
Article Title
Room-temperature electrically switchable spin–valley coupling in a van der Waals ferroelectric halide perovskite with persistent spin helix
Article Publication Date
2-Jun-2022




