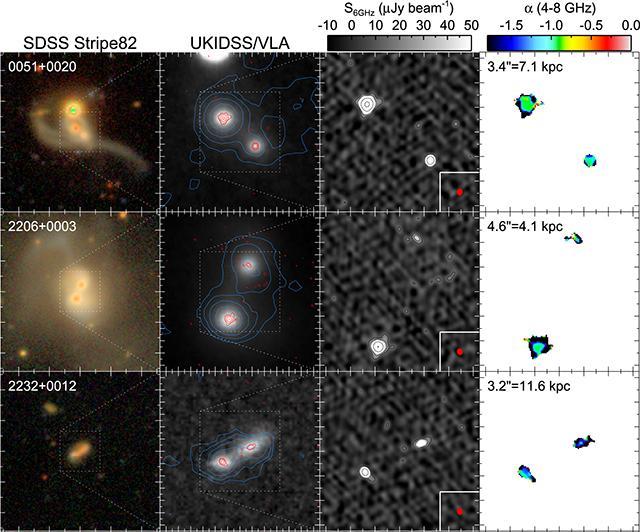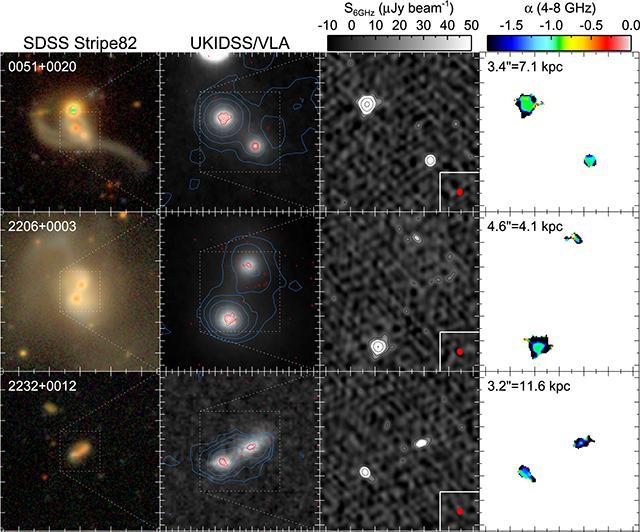
Credit: Hai Fu, University of Iowa
In roughly four billion years, the Milky Way will be no more.
Indeed, our home galaxy is on course to collide and unite with the Andromeda Galaxy, at present some two million light years away.
Of course, we don't notice that the two galaxies are drawing closer together.
"To the human perspective, our galaxy doesn't appear to be changing," says University of Iowa astrophysicist Hai Fu, "but in the history of the universe, it is changing all the time."
Galaxies have been merging for most of the universe's 13-billion-year history, and scientists have been observing these mergers for some time. What they don't fully understand is how mergers occur.
Fu, an assistant professor in physics and astronomy, aims to clarify the phenomenon by observing supermassive black holes (with a mass of about one billion suns), which are at the center of most galaxies. Astrophysicists believe large galaxies grow by devouring smaller ones. In such cases, the black holes of both are expected to orbit each other and eventually merge. Fu and his team won a three-year, $405,011 grant from the National Science Foundation to find and characterize these celestial events.
"What we're trying to see is the late stages of merging galaxies, when two galaxies are so close together they unleash tidal forces of energy, kind of like the pulsing tidal forces caused when the sun and moon line up with the Earth but much, much more intense," he says.
Fu will scan a large chunk of the night sky–imagine the moon multiplied 1,200 across the sky and you'll have a sense of the size–to find evidence of black holes' accretion, or mass-gathering.
"Pairs of galaxies with accreting black holes are rare and difficult to find," Fu says, "and that's why we need such a large area to survey."
Black holes aren't always accreting. But those that are resemble someone on an eating binge. Accreting black holes hungrily absorb material around them. Slowly, as they munch on more and more cosmic food, they pull their host galaxies closer together.
"They're no longer on a diet," Fu says.
All that eating unleashes a torrent of energy, intense bursts of light called quasars that are so bright they nearly obscure the galaxies themselves. Those quasars should be easy to observe, even at great distances, but most of the light they produce is actually extinguished by the dust brewed up in the merging activity.
Thankfully, supermassive black holes also emit radio waves, and those emissions "come to the rescue because they don't get extinguished by the dust," Fu says.
Fu and his team will examine radio-emission maps captured by the Very Large Array, one of the world's premier astronomical radio observatories, located in New Mexico and operated by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, an NSF facility. The group will confirm its findings through optical observations at the W.M. Keck Observatory, located on Mauna Kea, a dormant volcano in Hawaii.
The NSF grant also will fund the student-led building of an "augmented reality sandbox" to demonstrate gravity's influence in the universe, such as on the orbits of planets, the accretion disk around a black hole or neutron star, and the complex orbits of stars in elliptically shaped galaxies.
Nine undergraduates have so far been involved in the project; they divided into teams to write the software programming, build the sandbox (with actual sand), and create an app for Android tablets.
The sandbox will be used in astronomy classes, physics demonstrations for K-12 students in the greater Iowa City area, and exhibitions at the UI Museum of Natural History and the UI Mobile Museum.
The sandbox is expected to be complete by the end of the spring 2017 semester.
"It is quite impressive," Fu says. "The students may not necessarily like taking exams, but they work really well in teams."
###
Media Contact
Richard Lewis
[email protected]
319-384-0012
@uiowa
http://www.uiowa.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag