The long-standing challenges to the practical implementation of rechargeable zinc-air batteries (ZABs) are the electrochemical irreversibility of the Zn anode and degradation of the air cathodes in alkaline electrolyte, which eventually results in poor cycle life and low cell voltage.
Credit: Image by ZHANG Xinbo
The long-standing challenges to the practical implementation of rechargeable zinc-air batteries (ZABs) are the electrochemical irreversibility of the Zn anode and degradation of the air cathodes in alkaline electrolyte, which eventually results in poor cycle life and low cell voltage.
To improve the reversibility of ZABs, exhaustive efforts have been made to exploit highly survivable catalysts for the air cathode while weakening the corrosion of the Zn anode through electrode design or electrolyte additives. These strategies can alleviate but not completely overcome the core challenges associated with the strongly alkaline electrolyte.
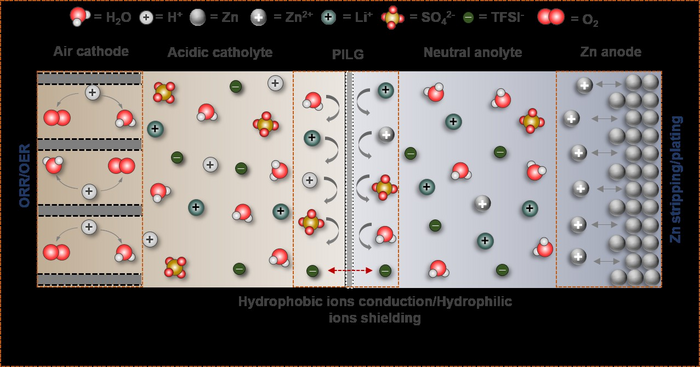
Taking a different approach, a research team led by ZHANG Xinbo from the Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry (CIAC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently developed a high-voltage, stable hybrid ZAB by using a neutral Zn anode, an acidic cathode, and a dual-hydrophobic-induced, proton-shuttle-shielding membrane to separate the two electrodes.
Their findings were published in Joule.
The researchers found that highly reversible Zn plating/stripping can be achieved in neutral electrolytes, while acidic electrolytes are essential for making the air cathode immune to CO2 poisoning issues. Therefore, they proposed a hybrid ZAB by decoupling the functional environments of the acidic air cathode and neutral Zn anode.
However, the essential prerequisite for long-time operation of a hybrid ZAB is that the two electrodes work independently in their respective environments, thus completely and permanently preventing proton crossover from catholyte to anolyte. Based on this prerequisite, the researchers proposed a proton-shuttle-shielding, hydrophobic-ion-conducting membrane to make this hybrid system possible.
Notably, this hybrid cell permits the optimized redox chemistry of both the Zn anode and the air cathode. This enables stable Zn stripping/plating in the neutral electrolyte and the high voltage of the oxygen redox reaction in the acidic electrolyte. As a result, the hybrid ZAB exhibits a high working voltage of 1.5 V and long cycle life of 2000 h.
ZHANG and his team proposed two types of hybrid cell prototypes that would employ the proton-shuttle-shielding, hydrophobic-ion-conducting strategy. Both the hybrid Zn-Mn battery and hybrid Zn-Br battery are expected to exhibit potentially high voltage and a long cycle life, thus showing the feasibility of using such hybrid cells to create high-energy-density aqueous batteries.
According to ZHANG, “The rise of a hybrid ZAB might also stimulate the development of many burgeoning areas, such as acidic ORR/OER in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells and electrolyzers.”
DOI
10.1016/j.joule.2022.05.019
Article Title
A high-voltage and stable zinc-air battery enabled by dual-hydrophobic-induced proton shuttle shielding
Article Publication Date
20-Jun-2022




