WASHINGTON, May 31, 2022 – Examining a city’s magnetic footprint can be used to monitor the health of those cities, including a possible early warning system for trouble with pollution and as a tool for optimizing energy conservation.
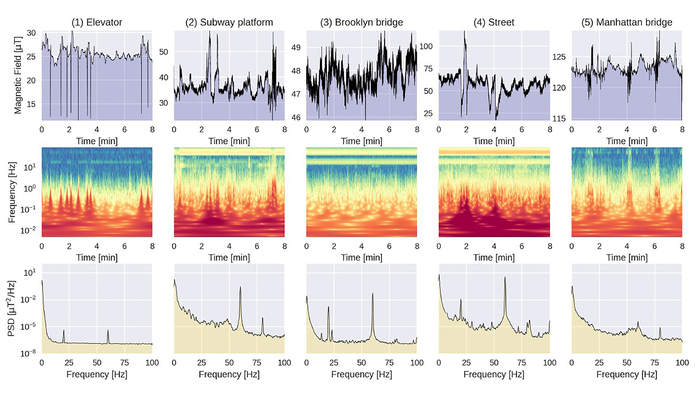
Credit: Vincent Dumont, Trevor Bowen, Roger Roglans, Gregory Dobler, Mohit S. Sharma, Andreas Karpf, Stuart D. Bale, Arne Wickenbrock, Elena Zhivun, Thomas Whitmore Kornack, Jonathan S. Wurtele, and Dmitry Budker
WASHINGTON, May 31, 2022 – Examining a city’s magnetic footprint can be used to monitor the health of those cities, including a possible early warning system for trouble with pollution and as a tool for optimizing energy conservation.
In Journal of Applied Physics, from AIP Publishing, researchers from the United States and Germany present a comparative analysis of urban magnetic fields between two U.S. cities: Berkeley, California, and the Brooklyn borough of New York City. They explore what kinds of information can be extracted using data from magnetic field sensors to understand the working of cities and provide insights that may be crucial for preventative studies.
Cities are well known for their extremely noisy characteristics and a fertile ground for learning about urban science. Magnetic field activity from various sources in the city can provide insight into what is going on during a 24-hour period.
“A city is viewed as a physical system akin to a distant astronomical object that can be studied using a variety of multispectral techniques,” said Vincent Dumont, from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. “In short, our project was inspired by our desire to apply what we learned practicing fundamental physics research to the study of cities.”
To do this, researchers collected magnetic field data continuously during a four-week period, using synchronized measurements with a network of sensitive magnetometers. Data was processed and analyzed using modern data analysis techniques.
In their current work comparing two very different cities, Brooklyn and Berkeley, they discovered Berkeley reaches a near-zero magnetic field activity during the night, while Brooklyn’s magnetic activity continues day and night.
“Again, not too surprisingly, we discovered that ‘New York never sleeps,’ or more seriously, there are indeed a number of magnetic signatures specific to each city,” he said.
The researchers hope their network magnetometry and smart data analysis combination can become a valuable tool for multidisciplinary urban science.
“This work builds on our earlier experiments conducted around the city of Berkeley, in the San Francisco Bay Area,” Dumont said. “We identified the dominant sources of magnetic signals – which, not too surprisingly, turned out to be the trains of the Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) system, and learned to glean weaker signals from this dominant background.”
“We hope this line of research will be picked up and further developed both by the members of our team as well as others, hopefully within cities around the world,” he said.
In recent years, this approach to study cities via their noise via data from magnetic field sensors emerged and was pursued by the Center for Urban Science and Progress in New York.
Techniques using data from magnetic field sensors are particularly useful for fundamental physics research, such as the Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory experiment for the detection of gravitational waves or the Global Network of Optical Magnetometers for Exotic Physical Searches collaboration for dark matter searches.
###
The article “Do cities have a unique magnetic pulse?” is authored by Vincent Dumont, Trevor Bowen, Roger Roglans, Gregory Dobler, Mohit S. Sharma, Andreas Karpf, Stuart D. Bale, Arne Wickenbrock, Elena Zhivun, Thomas Whitmore Kornack, Jonathan S. Wurtele, and Dmitry Budker. The article will appear in The Journal of Applied Physics on May 31, 2022 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0088264). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0088264.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
The Journal of Applied Physics is an influential international journal publishing significant new experimental and theoretical results in all areas of applied physics. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/jap.
###
Journal
Journal of Applied Physics
DOI
10.1063/5.0088264
Article Title
Do cities have a unique magnetic pulse?
Article Publication Date
31-May-2022




