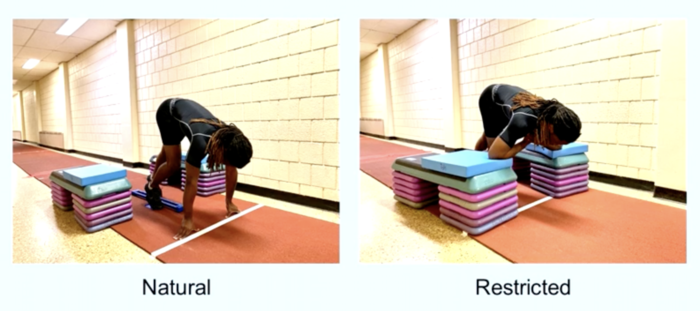
DALLAS (SMU) – New research into human speed from a team at SMU (Southern Methodist University,) and West Chester University suggests that athletes who performed short sprints with their arms closed across their chests were nearly as fast as when they sprinted with their normal arm swing.
Credit: Lance Brooks
DALLAS (SMU) – New research into human speed from a team at SMU (Southern Methodist University,) and West Chester University suggests that athletes who performed short sprints with their arms closed across their chests were nearly as fast as when they sprinted with their normal arm swing.
The findings, published in the journal Gait & Posture, offer additional fundamental insights regarding limb synchronization during sprint performance.
“Our findings suggest the classic view that arm swing directly drives leg motion to affect performance is not well-supported,” said Peter Weyand, a renowned expert in human speed who leads SMU’s Locomotor Performance Lab.
The coauthors of the research are lead author Lance C. Brooks, a doctoral student studying with Weyand in the Department of Applied Physiology & Wellness; Weyand, who is Glenn Simmons Endowed Professor of Applied Physiology and Biomechanics in the Department of Applied Physiology & Wellness in SMU’s Annette Caldwell Simmons School of Education & Human Development; and Kenneth P. Clark, an associate professor in the Department of Kinesiology at West Chester University. Brooks previously studied under Clark at West Chester University as he completed his master’s degree in exercise science and biomechanics.
The study examined the velocity of participants first sprinting 30 meters with regular arm motion, then again with restricted arm motion. When study participants sprinted with restricted arm motion, their 30-meter sprint time slowed down by only 0.08 seconds on average, a 1.6 percent difference from when the participants sprinted while moving their arms.
“We were surprised by the small magnitude of difference between the two experimental conditions. It is generally believed that the arms substantially influence the movement of the legs, and therefore running speed, which clearly is not the case,” Brooks said.
“When the athletes sprinted with restricted arm swing, the torso rotated back and forth appreciably more than normal to counterbalance the swinging legs,” Brooks added. “We believe that this extra torso rotation effectively compensated for arm swing to help maintain the body’s forward-facing orientation and the overall mechanics needed for speed.”
The study’s results strongly suggest that human runners use arm motion to prevent the body from rotating away from its forward-facing orientation.
“The compensatory torso twisting movements we observed during arm motion restriction indicate that runners swing their arms as the simplest and most natural strategy to prevent undesirable bodily rotations,” Clark said.
Do the team’s findings mean we will see less arm-swinging among sprinters in competitive sprinting? Probably not, as the difference in timed results is often razor-thin in timed competitions. The researchers point to the results of the 2020 Olympics Men’s 100-meter final, where the difference between the Gold and Bronze medal was only 0.09 seconds.
But the study’s findings are still an important step toward better understanding the influence of arm rotation on sprint performance.
“Virtually all runners choose to swing their arms to maintain a forward-facing position,” Weyand said. “The classic studies on the ‘why’ of arm motion during human locomotion are 40 or more years old and focused primarily on walking and jogging. So, performance effects were largely unknown,” he said.
###
About SMU
SMU is the nationally ranked global research university in the dynamic city of Dallas. SMU’s alumni, faculty, and nearly 12,000 students in eight degree-granting schools demonstrate an entrepreneurial spirit as they lead change in their professions, communities, and the world.
About Simmons School of Education & Human Development
The Annette Caldwell Simmons School of Education and Human Development at SMU (Southern Methodist University) reflects the University’s vision of serving the most important educational needs of our city, region and nation, graduating students for successful careers in a variety of fields and providing educational opportunities beyond traditional degree programs. Recognized as a unique and transformative leader in education research, practice and policy, the School is committed to rigorous, research-driven programs that promote evidence-based, effective practices in education and human development.
Related News
SMU joins forces with Children’s Health to harness the power of sports to improve kids’ well-being (October 28, 2021)
Journal
Gait & Posture
DOI
10.1016/j.gaitpost.2022.03.001
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Does restricting arm motion compromise short sprint running performance?
Article Publication Date
4-Mar-2022




