After the last meeting of the International Society of Microbiota (ISM), a well-documented report and statement were published. Numerous investigations showed a bidirectional interplay between gut microbiota and many organs within the human body such as the intestines, the lungs, the brain, and the skin. Large body of evidence demonstrated, more than a decade ago, that the gut microbial alteration is a key factor in the pathogenesis of many local and systemic disorders. In this regard, a deep understanding of the mechanisms involved in the gut microbial symbiosis/dysbiosis is crucial for the clinical and health field.
Credit: International Society of Microbiota
After the last meeting of the International Society of Microbiota (ISM), a well-documented report and statement were published. Numerous investigations showed a bidirectional interplay between gut microbiota and many organs within the human body such as the intestines, the lungs, the brain, and the skin. Large body of evidence demonstrated, more than a decade ago, that the gut microbial alteration is a key factor in the pathogenesis of many local and systemic disorders. In this regard, a deep understanding of the mechanisms involved in the gut microbial symbiosis/dysbiosis is crucial for the clinical and health field.
The scientific Board of ISM published the most recent studies on the involvement of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of many diseases. They also elaborated the different strategies used to manipulate the gut microbiota in the prevention and treatment of disorders. The conclusion of this report confirms again that the future of medicine and health is strongly related to our microbiota.
21 high-level authors and members of the International Society of Microbiota, coming from 8 countries and more than 10 reputable institutions published a new strategic report titled “Microbiota medicine: towards clinical revolution”. Published in the Journal of Translational Medicine, this stunning review that covers all topics you need to know concerning microbiota.
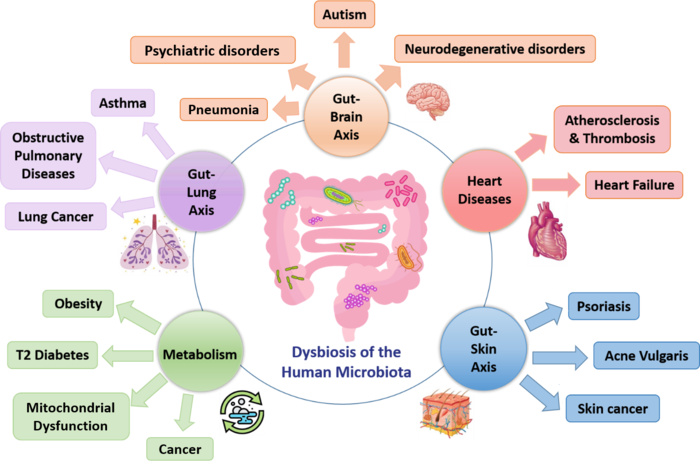
From human microbiome and microbiota dysbiosis in human diseases, to the therapeutic strategies in the gut microbiota manipulation, this article clarifies the key role and implication of microbiota in human health. Gut microbiota is in constant change with human evolution, as well as with the host gastrointestinal microenvironment, which makes it easily altered by many endogen and external factors. Among the latter, the built environment microbiome which can have a great impact on the human health.
It has been widely demonstrated that gut microbiota is tightly related to host organs through a multidirectional crosstalk involved in maintaining a global homeostasis. Among these flora-organ interactions: gut-lung, gut-brain, gut-skin axes, and many others. Any microbial dysbiosis could lead to an increased risk of pathogenesis of many diseases. For instance, some dysbioses are responsible for the inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, metabolic and cardiovascular-renal disorders, as well as neurological disorders.
In the therapeutic context, targeting specific microbial components or metabolites could provide a tool in the treatment of many diseases. Beyond having the pre- or probiotics, which are the traditional and first line choice of microbial therapies, other strategies are being clinically studied such as the FMT, metabolites, phages and miRNAs.
Prof. Marvin Edeas, the coresponding author and founder of ISM, from Institut Cochin, INSERM, Unviersité de Paris, stated “This is a great report which confirm that the future of medicine is strongly related to the quality of our microbiota. Targeting microbiota dysbiosis will be a huge challenge. Another task face us today is to target mitochondria and microbiota together. The Artificial Intelligence will push microbiota medicine to an exceptional level where we will detect rapidly microbiota dysbiosis, modulate the microbiome and treat hundred of diseases.”
You can read the full article in the BMC – Journal of Translational Medicine.
About the International Society of Microbiota (ISM):
ISM was born in 2013 after the transformation of the Task Force Mitochondria-Microbiota to a larger group gathering all actors and experts working in the field of microbiota. The idea is to bring a new level of thinking and understanding of microbiota science out of the classical existing point of view. The science of gut and microbiota is a dynamic field, with a huge evolution and affected by multi factors. ISM will bring this new dynamic point of view to accelerate the credible translation of this science into real benefit for the consumer. ISM also encourages the communication and interaction among researchers, physicians, nutritionists, industrials, food technology and strategic marketing managers through a global microbiota network, especially during its annual world meeting. In 2022, ISM is organizing its 9th world congress on Targeting Microbiota, on October 19-21, in Paris.
Journal
Journal of Translational Medicine
DOI
10.1186/s12967-022-03296-9
Method of Research
Systematic review
Article Title
Microbiota medicine: towards clinical revolution
Article Publication Date
7-Mar-2022
COI Statement
There is no conflict of interest.




