SAN DIEGO, March 23, 2022 — Diamonds aren’t just glittery, sparkly gems for jewelry. The smallest ones, only a few nanometers wide, are also crucial for drug delivery, sensors and quantum computer processors. Producing diamond nanoparticles that are consistently sized is important to the success of these technologies. Now, scientists report a method to grow ultra-uniform nanodiamonds without the need for explosives. The technique also could be used to add beneficial single-atom defects in otherwise perfect crystals.
Credit: Tengteng Lyu
SAN DIEGO, March 23, 2022 — Diamonds aren’t just glittery, sparkly gems for jewelry. The smallest ones, only a few nanometers wide, are also crucial for drug delivery, sensors and quantum computer processors. Producing diamond nanoparticles that are consistently sized is important to the success of these technologies. Now, scientists report a method to grow ultra-uniform nanodiamonds without the need for explosives. The technique also could be used to add beneficial single-atom defects in otherwise perfect crystals.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2022 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person March 20-24, with on-demand access available March 21-April 8. The meeting features more than 12,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“It’s fascinating that although a diamond is chemically rather simple — it is one element, carbon — making this material at the nanometer scale is extremely difficult,” says Hao Yan, Ph.D., the project’s principal investigator.
Carbon becomes a diamond when atoms of this element are arranged into a rigid 3D cubic pattern under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. Researchers previously have created nanodiamonds in the lab by detonating an explosive, such as trinitrotoluene (known as TNT), in a sealed stainless-steel container. The blast converts the carbon in the explosive material into tiny diamond particles. However, this crude method is hard to control, explains Yan. The crystals that form are uneven in size, requiring additional steps to sort them for different technologies.
To devise a more precise way to make nanodiamonds, Yan’s group at the University of North Texas looked into the chemistry that nature uses. “We realized that places where diamonds are formed in the Earth’s mantle contain a lot of iron and iron-carbon compounds, including carbides and carbonates,” Yan says. And when iron carbide reacts with iron oxide between the crust and the upper mantle, diamonds grow.
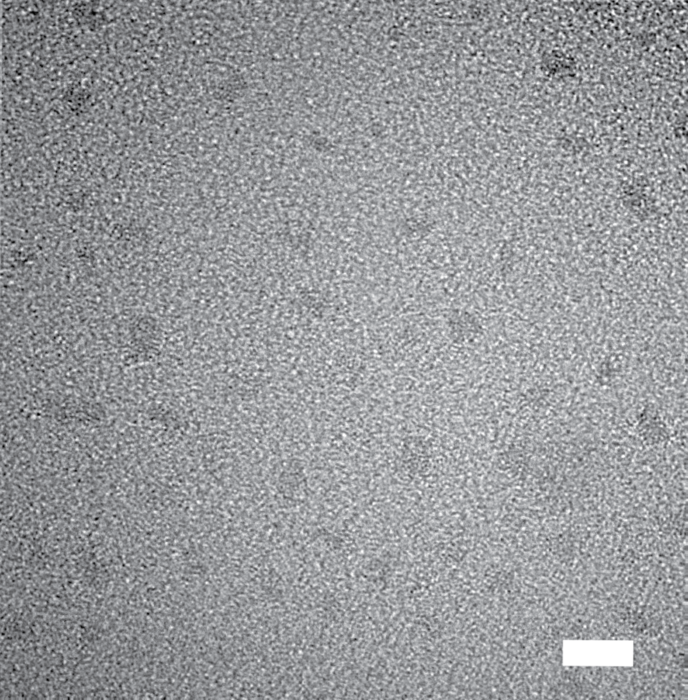
Armed with this knowledge, Tengteng Lyu, a graduate student in Yan’s lab who is presenting their work at the meeting, designed a chemical process to imitate the lithospheric environment found below Earth’s surface. First, Lyu created evenly sized nanoparticles of iron carbide as the carbon source for the diamonds. The tiny particles were dotted throughout an iron oxide matrix, as though the iron carbide were chocolate chips within cookie dough.
Then, Lyu placed the carbon-precursor “dough” in a high-pressure and high-temperature environment, similar to the conditions at locations where natural diamonds form. The compounds reacted, and very uniform nanodiamonds resulted. The new method makes crystals as small as 2 nm wide with differences between them of less than a nanometer. Yan says that this is one order of magnitude better than anyone can do without additional post-synthetic treatment or purification steps.
Creating uniform, perfect nanodiamonds is great, says Yan, but these materials can be even more useful when they have defects, such as empty spots in the diamond’s structure and the replacement of neighboring carbon atoms with nitrogen, silicon, nickel or another element. Because the non-carbon atoms color the material slightly, they are called “color centers.” Nanoparticles with only one color center are highly desirable because they can securely store information in quantum computers and telecommunication devices.
Traditionally, a high-energy beam of atoms, such as nitrogen or silicon, is used to bombard the diamond and embed these elements in the crystal’s structure. However, this method cannot control how many color centers are added to one diamond, requiring post-processing steps to get crystals with a single-atom defect. In addition, according to Lyu’s extensive computational modeling work, when the diameters of diamonds shrink to 2-3 nm — the size range that Yan’s team can now make consistently — this atom beam approach becomes energetically unfavorable. But with their new method, Yan thinks they could design a way to replace one carbon of the thousands present in their carbon-precursor “dough.” He estimates that they could now make enough single-color center nanodiamonds for a couple thousand quantum computers with one synthesis experiment, though the tiny crystals would need to be arranged properly before computations could be made.
“We now have an ideal platform to devise a way for making a single-color center nanodiamond, which is a breakthrough for a number of diamond-related technologies. But also, in a broader sense, it would be a fascinating demonstration of how you can control a single atom in a much larger structure,” says Yan.
The researchers acknowledge support from the University of North Texas and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
A recorded media briefing on this topic will be posted Wednesday, March 23, by 10 a.m. Eastern time at www.acs.org/acsspring2022briefings.
ACS Spring 2022 will be a vaccination-required and mask-recommended event for all attendees, exhibitors, vendors, and ACS staff who plan to participate in-person in San Diego, CA. For detailed information about the requirement and all ACS safety measures, please visit the ACS website.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive press releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Title
Controlled synthesis of sub-five-nanometer diamond particles
Abstract
Diamond nanoparticles in the sub-five-nanometer size regime are crucial for several emerging technologies including subcellular imaging, quantum information processing, and drug delivery. State-of-the-art methods to produce nanodiamonds include mechanical grinding of bulk crystals, decomposition of hydrocarbon molecules, and detonation of explosives. However, no existing technique is capable of precise size control in the sub-five-nanometer regime.
Here we describe a method for controlled synthesis of nanodiamond with 2-5 nm diameter. The key innovation lies in the utilization of metal carbide nanoparticles as carbon sources. The reaction between these metal carbides with metal oxides under high-pressure-high-temperature conditions yields diamond nanoparticles with <5 nm diameter, uniform size, and high crystallinity. The size of the nanodiamond is precisely tuned by the nanostructured carbon precursor. Chemical doping of the precursor allows controlled incorporation of functional defects, enabling these nanodiamonds for key applications as bio-compatible high-resolution fluorescent markers, storage bits for quantum information processing, photon and electron sources as well as vehicles for targeted drug delivery.



