Reflecting on fond memories goes a step beyond making you feel warm and fuzzy: nostalgia can reduce pain perception. Nostalgia decreases activity in pain-related brain areas and decreases subjective ratings of thermal pain, according to research recently published in JNeurosci.
Credit: Zhang et al., JNeurosci 2021
Reflecting on fond memories goes a step beyond making you feel warm and fuzzy: nostalgia can reduce pain perception. Nostalgia decreases activity in pain-related brain areas and decreases subjective ratings of thermal pain, according to research recently published in JNeurosci.
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences measured the brain activity of adults with fMRI while the participants rated the nostalgia levels of images and rated the pain of thermal stimuli. The nostalgic images featured scenes and items from an average childhood, like a popular candy, cartoon TV show, and schoolyard game. Images in the control condition depicted corresponding scenes and items from modern life. Viewing nostalgic images reduced pain ratings compared to viewing control images, with the strongest effect on low intensity pain.
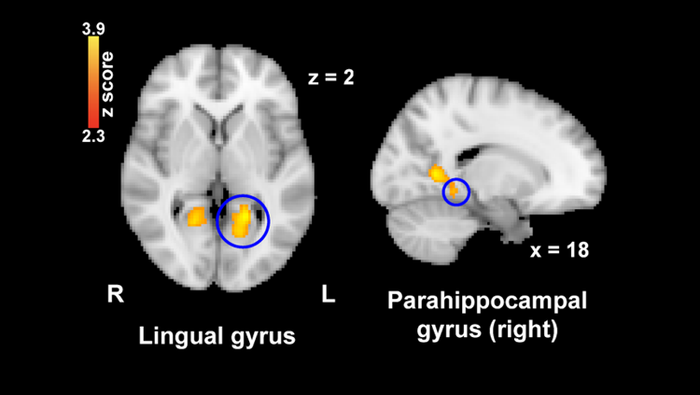
Viewing nostalgic images also reduced activity in the left lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus, two brain regions implicated in pain perception. Activity in the thalamus, a brain region involved in relaying information between the body and the cortex, was linked to both nostalgia and pain ratings; the thalamus may integrate nostalgia information and transmit it to pain pathways. Nostalgia may be a drug-free way to alleviate low levels of pain, like headaches or mild clinical pain.
###
Paper title: Thalamocortical Mechanisms for Nostalgia-induced Analgesia
Please contact [email protected] for the full-text PDF and to join SfN’s journals media list.
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci, the Society for Neuroscience’s first journal, was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors’ changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world’s largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 37,000 members in more than 90 countries and over 130 chapters worldwide.
Journal
JNeurosci
DOI
10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2123-21.2022
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Thalamocortical mechanisms for nostalgiainduced analgesia
Article Publication Date
28-Feb-2022




